Swing五种常见的布局方式 java中Swing五种常见的布局方式
彬菌 人气:0想了解java中Swing五种常见的布局方式的相关内容吗,彬菌在本文为您仔细讲解Swing五种常见的布局方式的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:java,Swing,布局方式,下面大家一起来学习吧。
1、 边界布局(BorderLayout)
2、流式布局(FlowLayout)
3、网格布局(GridLayout)
4、盒子布局(BoxLaYout)
5、空布局(null)
还有其他两种布局,分别是GridBagLayout(网格包布局)、CardLayout(卡片布局)
注意:JFrame和JDialog默认布局为BorderLayout,JPanel和Applet默认布局为FlowLayout
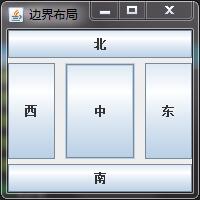
边界布局示例代码:
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class BorderLayoutExample extends JFrame{
JButton btn1=new JButton("东");
JButton btn2=new JButton("南");
JButton btn3=new JButton("西");
JButton btn4=new JButton("北");
JButton btn5=new JButton("中");
BorderLayoutExample(){
init();
this.setTitle("边界布局");
this.setResizable(true);
this.setSize(200, 200);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
}
void init(){
this.setLayout(new BorderLayout(10,5)); //默认为0,0;水平间距10,垂直间距5
this.add(btn1,BorderLayout.EAST);
this.add(btn2,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.add(btn3,BorderLayout.WEST);
this.add(btn4,BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.add(btn5,BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new BorderLayoutExample();
}
}
运行结果:
流式布局示例代码:
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class FlowLayoutExample extends JFrame{
JButton btn1=new JButton("one");
JButton btn2=new JButton("two");
JButton btn3=new JButton("three");
JButton btn4=new JButton("four");
JButton btn5=new JButton("five");
FlowLayoutExample(){
init();
this.setTitle("流式布局");
this.setResizable(true);
this.setSize(200, 200);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
}
void init(){
this.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,10,5)); //默认为居中;水平间距10,垂直间距5
this.add(btn1);
this.add(btn2);
this.add(btn3);
this.add(btn4);
this.add(btn5);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new FlowLayoutExample();
}
}
运行结果:

网格布局示例代码:
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class GridLayoutExample extends JFrame{
JButton btn1=new JButton("one");
JButton btn2=new JButton("two");
JButton btn3=new JButton("three");
JButton btn4=new JButton("four");
JButton btn5=new JButton("five");
GridLayoutExample(){
init();
this.setTitle("表格布局");
this.setResizable(true);
this.setSize(300, 200);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
}
void init(){
this.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,3,10,5)); //默认为1行,n列;2行3列,水平间距10,垂直间距5
this.add(btn1);
this.add(btn2);
this.add(btn3);
this.add(btn4);
this.add(btn5);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new GridLayoutExample();
}
}
运行结果:

盒子布局示例代码:
import javax.swing.Box;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class BoxLaYoutExample extends JFrame{
JButton btn1=new JButton("one");
JButton btn2=new JButton("two");
JButton btn3=new JButton("three");
JButton btn4=new JButton("four");
JButton btn5=new JButton("five");
BoxLaYoutExample(){
init();
this.setTitle("表格布局");
this.setResizable(true);
this.setSize(300, 200);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
}
void init(){
this.setLayout(new BoxLayout(this.getContentPane(),BoxLayout.X_AXIS));
//可以使用Box容器代替
//Box box = new Box(BoxLayout.Y_AXIS);box.add(btn...);box.add(creat..);
this.add(btn1);
this.add(btn2);
this.getContentPane().add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(10)); //采用x布局时,添加固定宽度组件隔开
//this.getContentPane().add(Box.createVerticalStrut(5)); //采用y布局时,添加固定高度组件隔开
this.add(btn3);
this.add(btn4);
this.add(btn5);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new BoxLaYoutExample();
}
}
运行结果:

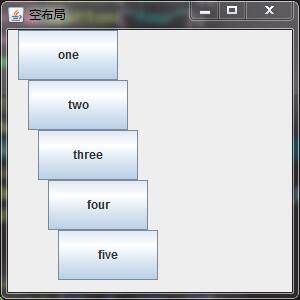
空布局示例代码:
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class NullLayoutExample extends JFrame{
JButton btn1=new JButton("one");
JButton btn2=new JButton("two");
JButton btn3=new JButton("three");
JButton btn4=new JButton("four");
JButton btn5=new JButton("five");
NullLayoutExample(){
init();
this.setTitle("空布局");
this.setResizable(true);
this.setSize(300, 300);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
}
void init(){
this.setLayout(null);
btn1.setBounds(10, 0, 100, 50); //x坐标10,y坐标0,组件宽100,高50
btn2.setBounds(20, 50, 100, 50);
btn3.setBounds(30, 100, 100, 50);
btn4.setBounds(40, 150, 100, 50);
btn5.setBounds(50, 200, 100, 50);
this.add(btn1);
this.add(btn2);
this.add(btn3);
this.add(btn4);
this.add(btn5);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new NullLayoutExample();
}
}
运行结果:
加载全部内容