spring boot security Spring Boot中整合Spring Security并自定义验证代码实例
嗡汤圆 人气:0最终效果
1、实现页面访问权限限制
2、用户角色区分,并按照角色区分页面权限
3、实现在数据库中存储用户信息以及角色信息
4、自定义验证代码
效果如下:
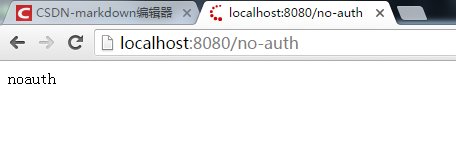
1、免验证页面
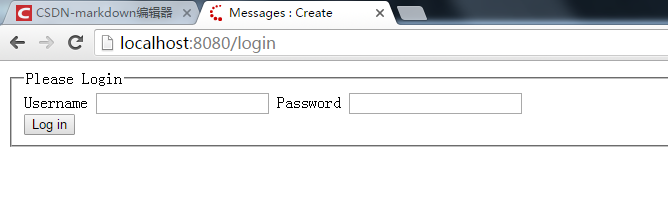
2、登陆页面
在用户未登录时,访问任意有权限要求的页面都会自动跳转到登陆页面。
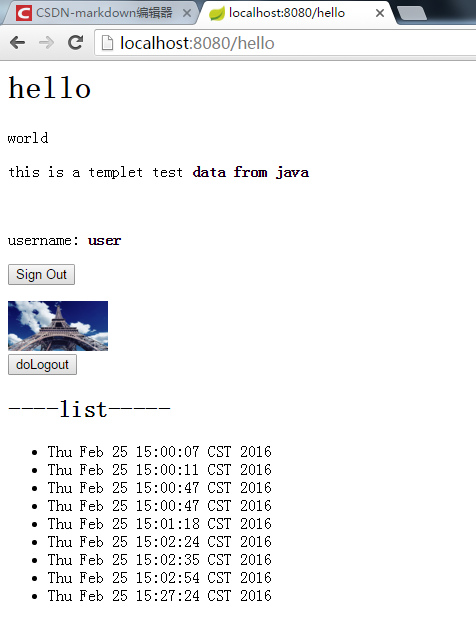
3、需登陆才能查看的页面
用户登陆后,可以正常访问页面资源,同时可以正确显示用户登录名:
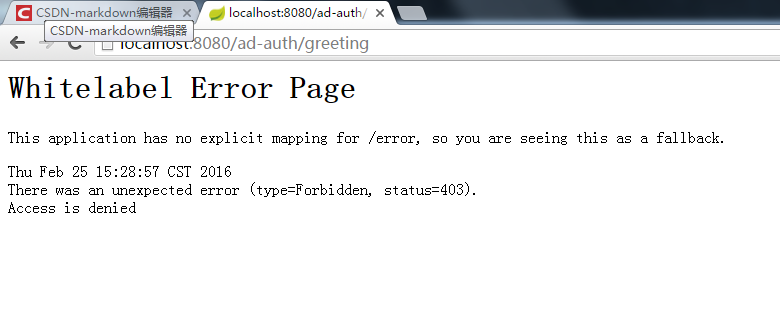
4、用户有角色区分,可以指定部分页面只允许有相应用户角色的人使用
4.1、只有ADMIN觉得用户才能查看的页面(权限不足)
4.2、只有ADMIN觉得用户才能查看的页面(权限满足)
以下具体说明实现步骤。
代码实现
MAVEN引入依赖
在pom.xml中引入spring security依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置Spring Security
在Spring中,配置和使用Spring Security,在不需要修改太多流程细节的情况下仅需声明好拦截规则,同时自定义验证过程中的主要实现接口(用户信息UserDetails,用户信息获取服务UserDetailsService,验证工具AuthenticationProvider)即可。其余的流程将由Spring自动接管,非常方便。
启动配置
在项目包下添加WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的具体实现类,实现Spring Security的启动配置
代码如下:
@Configurable
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)//允许进入页面方法前检验
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationProvider provider;//自定义验证
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;//自定义用户服务
@Autowired
public void configAuthentication(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception{
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(StaticParams.PATHREGX.NOAUTH,
StaticParams.PATHREGX.CSS,StaticParams.PATHREGX.JS,StaticParams.PATHREGX.IMG).permitAll()//无需访问权限
.antMatchers(StaticParams.PATHREGX.AUTHADMIN).hasAuthority(StaticParams.USERROLE.ROLE_ADMIN)//admin角色访问权限
.antMatchers(StaticParams.PATHREGX.AUTHUSER).hasAuthority(StaticParams.USERROLE.ROLE_USER)//user角色访问权限
.anyRequest()//all others request authentication
.authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.and()
.logout().permitAll();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//将验证过程交给自定义验证工具
auth.authenticationProvider(provider);
}
URL拦截配置
URL拦截配置可以在上一小节的WebSecurityConfig 中配置,但是此方法适用于大方向上的配置,具体的特殊路径也可以在@Controller的注解中具体配置。
如下:
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('"+StaticParams.USERROLE.ROLE_ADMIN+"')")//这里可以指定特定角色的用户访问权限
@RequestMapping(value = "adminrequire", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String adminrequire(){
return "HELLO from web but you should be admin";
}
用户、角色表
在本文例子中用户和角色可以有一对多的关系因此可以将用户和角色分成两张表。有些例子将用户和权限写在同一张表上也是可以的。
/*用户表*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class SystemUser {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String password;
public SystemUser(){}
public SystemUser(SystemUser user){
this.userName = user.getUserName();
this.password = user.getPassword();
this.id = user.getId();
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
/*角色表*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "user_role")
public class UserRole {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String role;
private Long userId;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getRole() {
return role;
}
public void setRole(String role) {
this.role = role;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
}
自定义验证
在Spring Boot的Spring Security的教程中默认的用户名、密码、权限是在代码中指定的
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER");
}
这显然是不符合应用需求的,所以我们需要提供自定义的AuthenticationProvider,并在上边代码中替换即可。在此之前,我们应该重写获取用户User和权限的方法。通过查询相关资料和API,方法提供如下:
自定义UserDetails
UserDetails代表了Spring Security的用户认证实体,带有用户名、密码、权限列表、过期特性等性质,可以自己声明类实现UserDetails接口,如果不想自己声明,也可以用SpringSecurity的默认实现org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User 本文例子中采用自定义类:
public class MyUserDetails extends SystemUser implements UserDetails{
private List<UserRole> roles;
public MyUserDetails(SystemUser user, List<UserRole> roles){
super(user);
this.roles = roles;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
if(roles == null || roles.size() <1){
return AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("");
}
StringBuilder commaBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for(UserRole role : roles){
commaBuilder.append(role.getRole()).append(",");
}
String authorities = commaBuilder.substring(0,commaBuilder.length()-1);
return AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(authorities);
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return super.getPassword();
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return super.getUserName();
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
自定义UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService提供了获取UserDetails的方式,只要实现UserDetailsService接口即可,最终生成用户和权限共同组成的UserDetails,在这里就可以实现从自定义的数据源中获取用户信息了:
@Service("MyUserDetailsImpl")
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Resource(name = "SystemUserServiceImpl")
private SystemUserService systemUserService;
@Resource(name = "UserRoleServiceImpl")
private UserRoleService userRoleService;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
SystemUser user;
try {
user = systemUserService.findByName(userName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("user select fail");
}
if(user == null){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("no user found");
} else {
try {
List<UserRole> roles = userRoleService.getRoleByUser(user);
return new MyUserDetails(user, roles);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("user role select fail");
}
}
}
}
自定义AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider 提供用户UserDetails的具体验证方式,在这里可以自定义用户密码的加密、验证方式等等。因为博文主要讲的是如何引入Spring Security和如何自定义验证代码,所以这里为了简便,我直接采用明文比较方式:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private MyUserDetailsService userService;
/**
* 自定义验证方式
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
MyUserDetails user = (MyUserDetails) userService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if(user == null){
throw new BadCredentialsException("Username not found.");
}
//加密过程在这里体现
if (!password.equals(user.getPassword())) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Wrong password.");
}
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = user.getAuthorities();
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user, password, authorities);
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> arg0) {
return true;
}
}
加载全部内容