ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector源码分析
moyuduo 人气:0ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector源码分析
ArrayList
ArrayList是一个底层使用数组来存储对象,但不是线程安全的集合类
ArrayList的类结构关系
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
}

ArrayList实现了List接口,List接口中定义了一些对列表通过下标进行添加删除等方法
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,这个接口是一个标记接口,接口中并没有任何的方法,ArrayList底层是用数组来存储对象,当然是能够通过下标随机访问的,实现了RandomAccess接口的类在查询时的速度会很快但是添加删除元素慢,而LinkedList是通过链表的方式实现的,它没有实现RandomAccess接口,在查询时慢但是增加删除的速度快
所以在使用集合遍历大量数据时,可以先用instanceof来判断集合是不是实现了RandomAccess
public void test1() {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
if(list instanceof RandomAccess) {//RandomAccess实现类,使用下标访问
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
//todo
}
}else {//不是RandomAccess实现类,使用iterator遍历
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
//todo
}
}
}
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,所以可以合法调用clone方法,如果没有实现Cloneable接口,那么会抛出CloneNotSupporteddException,详见
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,可以将对象序列化,用于传输或持久化,详见
属性
//序列化Id
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
//默认初始化大小
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//空数组对象,用于有参构造且初始化大小为0时
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//空数组对象,用于无参构造时,这两个属性主要用来区分创建ArrayList时有没有指定容量
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//保存对象的容器,使用transient修饰即在序列化时,不进行序列化,这是因为ArrayList添加了序列化方法private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)只把保存的数据序列化了,而不是把整个数组序列化,提高效率
transient Object[] elementData;
//保存的对象个数
private int size;
//最大容量2的31次方减9
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
构造器
ArrayList提供了三个构造器,一个是指定初始化大小的构造器,一个人无参默认初始化大小构造器,一个是使用集合初始化的构造器
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
//数组的大小为指定大小
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
//大小为0用一个共享的空数组赋值
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
public ArrayList() {
//用共享的空数组赋值,不使用EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA主要是区分是使用的哪个构造器
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// 集合为空,使用空数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
添加元素
在数组尾添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
//计算容量
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {//通过无参构造器创建
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// 如果最小需要的容量>数组大小
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
//进行扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新容量=老容量+老容量>>1;老容量>>1即老容量无符号右移1位,即除以2,所以最后新容量是老容量的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)//新容量比最小容量小那么把最小容量赋值给新容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)//如果minCapacity很大,计算得出newCapacity超出最大容量
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 复制未扩容之前的数据
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
//如果最小容量还超出ArrayList规定的最大值那么数组大小为Integer.MAX_VALUE否则为ArrayList规定的最大值
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
在指定位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
//检查添加元素的下标
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//检查容量,进行扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// public static native void arraycopy(src, srcPos,dest, destPos,length);
//src:源数组;srcPos:源数组起始下标;dest:目标数组;destPos:目标数组起始下标;length:拷贝长度
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
//元素的下标必须为0-size
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
移除元素
按照下标移除元素
public E remove(int index) {
//检查下标
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
//按照下标获取元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//计算需要移动的数据个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//清理数组elementData[size]位置的元素
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
//下标必须在0到size-1之间
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
按值移除元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {//如果移除的元素为null,依次遍历保存的元素,移除第一个为null的元素
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//移除
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
//使用equals判断是否相等
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
//计算移除后需要移动的元素个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//清理数组elementData[size]位置的元素
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
modCount
ArrayList在进行add、set、remove时,都进行了modCount+1操作,这个属性与fast fail有关,当对象创建Iterator对象时会把modCount赋值给expectedModCount,当使用Iterator进行遍历时,如果发现对象的modCount与expectedModCount不相等,会直接抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
...
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
...
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)//直接抛出异常
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
出现情况:当Iterator遍历时,如果对象的modCount和expectedModCount不等就会抛出异常,主要有这些情况
- 使用iterator遍历时,进行了add、remove等破坏结构的操作
- 多线程环境下,一个线程在遍历时,另一个线程进行了add、remove等破坏结构的操作
通过源码学习,我发现set方法并没有增加modCount,为什么呢?难道一个线程在使用iterator遍历,另外一个线程改变了一个位置的元素,Iterator不用抛出异常?有知道的请赐教!
LinkedList
LinkedList类结构
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
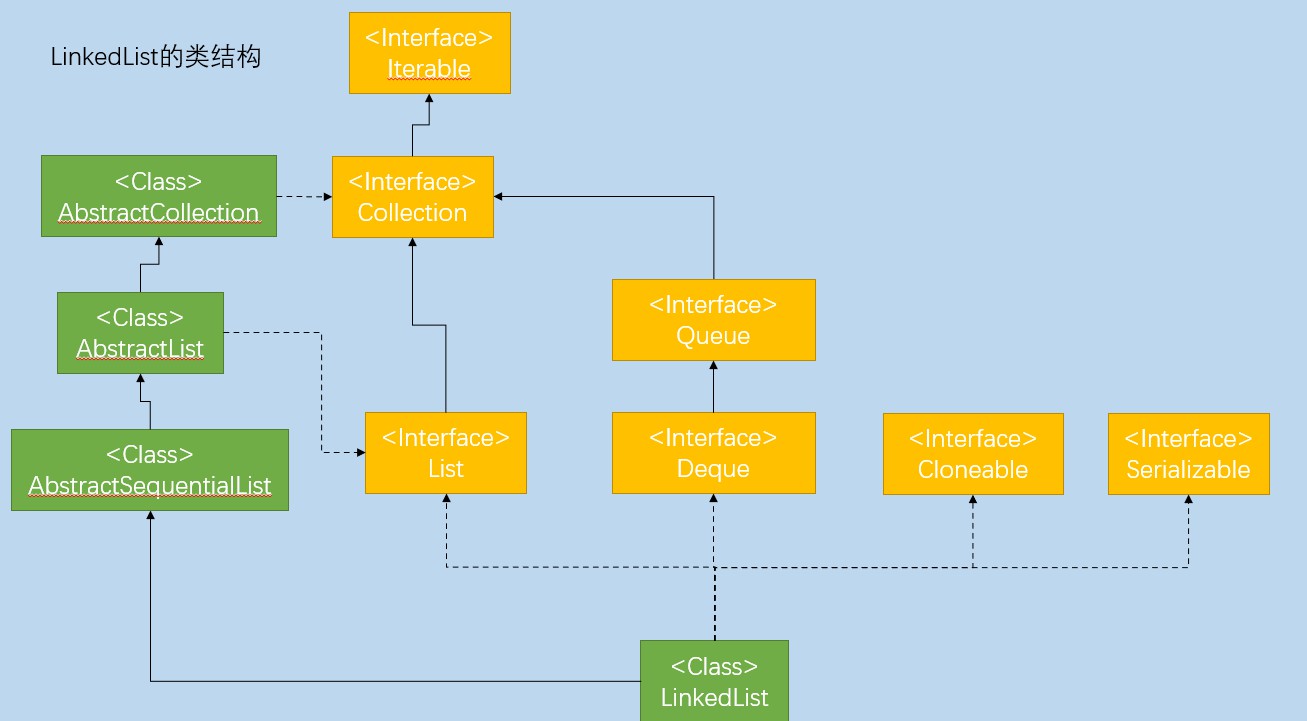
LinkedList继承AbstractSequentialList可以实现通过Iterator的随机访问
LinkedList实现List接口可以进行添加删除等操作
LinkedList实现了DeQue,允许在队列的两端进行入队和出队,所以可以把LinkedList当做队列或栈使用
LinkedList实现了Cloneable,可以通过clone快速克隆对象
LinkedList实现了Serializable接口,可以将LinkedList序列化,进行流操作
构造器
public LinkedList() {
}
//使用集合初始化链表
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
属性
//链表的大小,transient表明在序列化的时候不进行序列化,但是LinkedList自定义的序列化方法中进行了序列化
transient int size = 0;
//链表的头节点
transient Node<E> first;
//链表的尾节点
transient Node<E> last;
节点
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
//前驱
Node<E> next;
//后继
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
可以看到LinkedList是一个双向链表
方法
Deque是一个双端链表,即链表可有当做栈和队列使用
getFirst方法,相当于Queue中的element方法,如果队空,就抛出异常
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
getLast方法
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
removeFirst方法,相当于Queue的remove方法,删除队头元素,如果队空,抛出异常
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
//如果原头节点的后继为空,那么把尾指针也更新为空
last = null;
else
//原头节点的后继为不空,那么需要把它的前驱更新为空
next.prev = null;
//更新链表大小
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
removeLast方法,如果队空,抛出异常
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
//如果原尾指针的前驱为空,那么头指针指向也为空
first = null;
else
//原尾指针的前驱不为空,那么它的后继应该改为空
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
addFirst方法,相当于Statck中的push方法
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
//创建一个前驱为空,后驱为first的新节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
//如果原头指针为空,那么把尾指针也赋值为新加节点
last = newNode;
else
//原头指正不空,把它的前驱更新为新节点
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
addLast方法,相当于Queue中的add方法
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
//如果原为指针指向就为空,那么头指针也指向新节点
first = newNode;
else
//原为指针指向就不为空,那么它的后继更新为新加节点
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
add方法是重写AbstractList中的方法,即往List中添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
remove方法移除链表中指定元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
//如果要移除的对象为null,那么取链表中找第一个null元素并移除
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {//使用equals比较两个对象是否相同
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
addAll方法向链表中添加指定集合的元素
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
//如果集合大小为0
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
//什么一个前驱节点和一个后继节点
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
//如果添加的位置恰好是size即在链表最后添加,那么后继为null,前驱为链表尾指针
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)//如果没有前驱节点
//把链表头指针指向新节点
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
//前驱节点赋值为当前新节点
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {//如果没有后继节点
//把尾指针指向'前驱节点'
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
clear方法清空链表,但是modCount并不会清空
public void clear() {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
//help GC?
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
get方法获取指定下标元素,非法下标抛出异常
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//通过一个二分遍历拿元素
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
set方法设置指定下标元素值,非法下标抛出异常,set方法modCount不++?why?
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
//获取元素
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
//替换
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
add方法,指定下标添加元素,非法下标抛出异常
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)//链表尾添加元素
linkLast(element);
else
//链表中间位置添加元素
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)//添加元素位置前驱为null,即添加位置本来就是头指针位置
first = newNode;
else
//更新前驱的next为当前添加节点
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
remove方法,移除指定下标元素,非法下标抛出异常
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {//如果移除节点的前驱为null,即移除节点为头指针指向位置
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
//help GC?
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {//如果移除节点的后继节点为null,即移除节点是尾指针指向位置
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
//help GC?
x.next = null;
}
//help GC?
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
peek方法,获取链表头节点,可为Queue/Stack方法,Queue方法即获取队手元素,Stack方法即获取栈顶元素
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
element方法,获取链表头节点,与peek方法不同的是,如果队列为空,抛出异常
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
//链表空抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
poll方法移除链表头节点,链表空返回null
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
remove方法移除链表头节点,链表空抛出异常
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
//链表空抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
offer方法,在链表尾添加元素
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
offerFirst方法,在链表头添加节点,对应栈的入栈操作
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
offerLast方法,在链表尾添加元素,本质上和offer方法没有区别
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
peekFirst方法,查看链表头节点,相当于Queue和Stack的peek方法,链表空返回null
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
peekLast方法,查看链表尾节点,链表空返回null
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
pollFirst方法,查看并删除链表头节点,链表空返回null
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
pollLast查看并删除链表尾节点,链表空返回null
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
push方法头节点位置添加,Stack的push方法
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
pop方法删除头节点位置元素,Stack的pop方法
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)//链表空抛异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
removeFirstOccurrence方法从头结点开始查找指定元素并移除
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {//要移除的元素为null
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {//从头查找,移除第一个为null元素
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {//依次遍历
if (o.equals(x.item)) {//使用equals判断相等
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
removeLastOccurrence方法从尾节点开始查找并移除指定元素
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {//如果移除元素为null
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {//从后往前遍历
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {//使用equals判断相等
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
listIterator方法返回链表迭代器
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
//由于LinkedList是双向链表,所以可以双向遍历
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
//expectedModCount保存拿到迭代器时,LinkedList的modCount值,与快速失败有关
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)//如果链表的modCount和拿到迭代器时modCount不同,说明在迭代过程中,链表进行了破坏结构的修改,那么应该直接抛出异常
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
Vector
类结构

可以看到,Vector的类结构和ArrayList的一模一样
Vector继承AbstractList实现了List接口
Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,可以随机访问
Vector实现了Cloneable接口,可以使用克隆对象
Vector实现了Serializable接口,可以序列化
属性
//保存对象的数组
protected Object[] elementData;
//保存元素个数
protected int elementCount;
//增长因子
protected int capacityIncrement;
//定义的最大容量,为2的31次方-9
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
构造器
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {//指定初始容量和增长因子
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
//直接把数组创建为初始化值大小
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
//把增长因子设置为0
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
//默认初始化大小为10
this(10);
}
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
方法
线程安全的方法
copyInto方法把元素拷贝到指定数组
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
trimToSize方法把保存元素的数组修改到保存元素个数大小
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {//如果元素个数比容量小
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
ensureCapacity方法用于添加元素时,确保数组大小
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)//如果需要的最小容量大于数组大小
//扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//如果指定了增长因子而且增长因子>0那么新容量就等于原容量+增长因子,否则就是原容量的二倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
setSize方法设置向量的大小
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {//如果新容量比原容量大,多的元素全为null
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
//新容量比原容量小
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
removeElementAt移除指定位置元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
//要移动的元素个数
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
insertElementAt指定位置插入元素
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
//确保容量
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
addElement在尾部添加元素
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
//确保容量
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
removeElement移除指定元素
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAllElements移除所有元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// Let gc do its work
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
elementCount = 0;
}
get获取指定位置元素
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
set替换指定位置元素
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
add方法添加元素,与addElement方法的区别仅仅是返回值不同
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
remove移除尾元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
add指定位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
remove移除指定位置元素
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//计算要移动的元素个数
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
listIterator获取向量的迭代器,可以进行向前向后遍历
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
final class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public E previous() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.set(lastRet, e);
}
}
public void add(E e) {
int i = cursor;
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.add(i, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
}
}
可以看到Vector和ArrayList的源码基本相同,只是Vector是线程安全的,还有就是Vector和ArrayList在扩容上有一点点不同,Vector如果指定了增长因子,那么新容量是原容量+增长因子,而ArrayList是直接扩大两倍原容量
加载全部内容