【原创】Linux select/poll机制原理分析
LoyenWang 人气:1
# 前言
- `Read the fucking source code!` --By 鲁迅
- `A picture is worth a thousand words.` --By 高尔基
# 1. 概述
Linux系统在访问设备的时候,存在以下几种IO模型:
1. `Blocking IO Model,阻塞IO模型`;
2. `Nonblocking I/O Model,非阻塞IO模型`;
3. `I/O Multiplexing Model,IO多路复用模型`;
4. `Signal Driven I/O Model,信号驱动IO模型`;
5. `Asynchronous I/O Model,异步IO模型`;
今天我们来分析下IO多路复用机制,在Linux中是通过`select/poll/epoll`机制来实现的。
先看一下阻塞IO模型与非阻塞IO模型的特点:
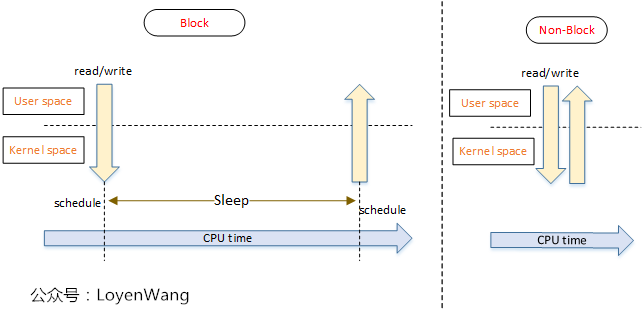
- 阻塞IO模型:在IO访问的时候,如果条件没有满足,会将当前任务切换出去,等到条件满足时再切换回来。
- 缺点:阻塞IO操作,会让处于同一个线程的执行逻辑都在阻塞期间无法执行,这往往意味着需要创建单独的线程来交互。
- 非阻塞IO模型:在IO访问的时候,如果条件没有满足,直接返回,不会block该任务的后续操作。
- 缺点:非阻塞IO需要用户一直轮询操作,轮询可能会来带CPU的占用问题。
对单个设备IO操作时,问题并不严重,如果有多个设备呢?比如,在服务器中,监听多个Client的收发处理,这时候IO多路复用就显得尤为重要了,来张图:
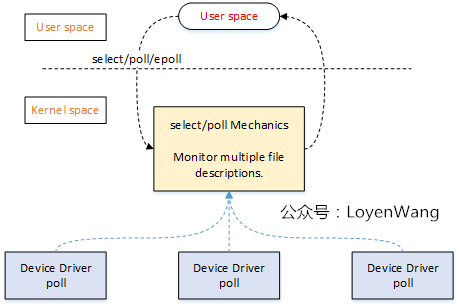
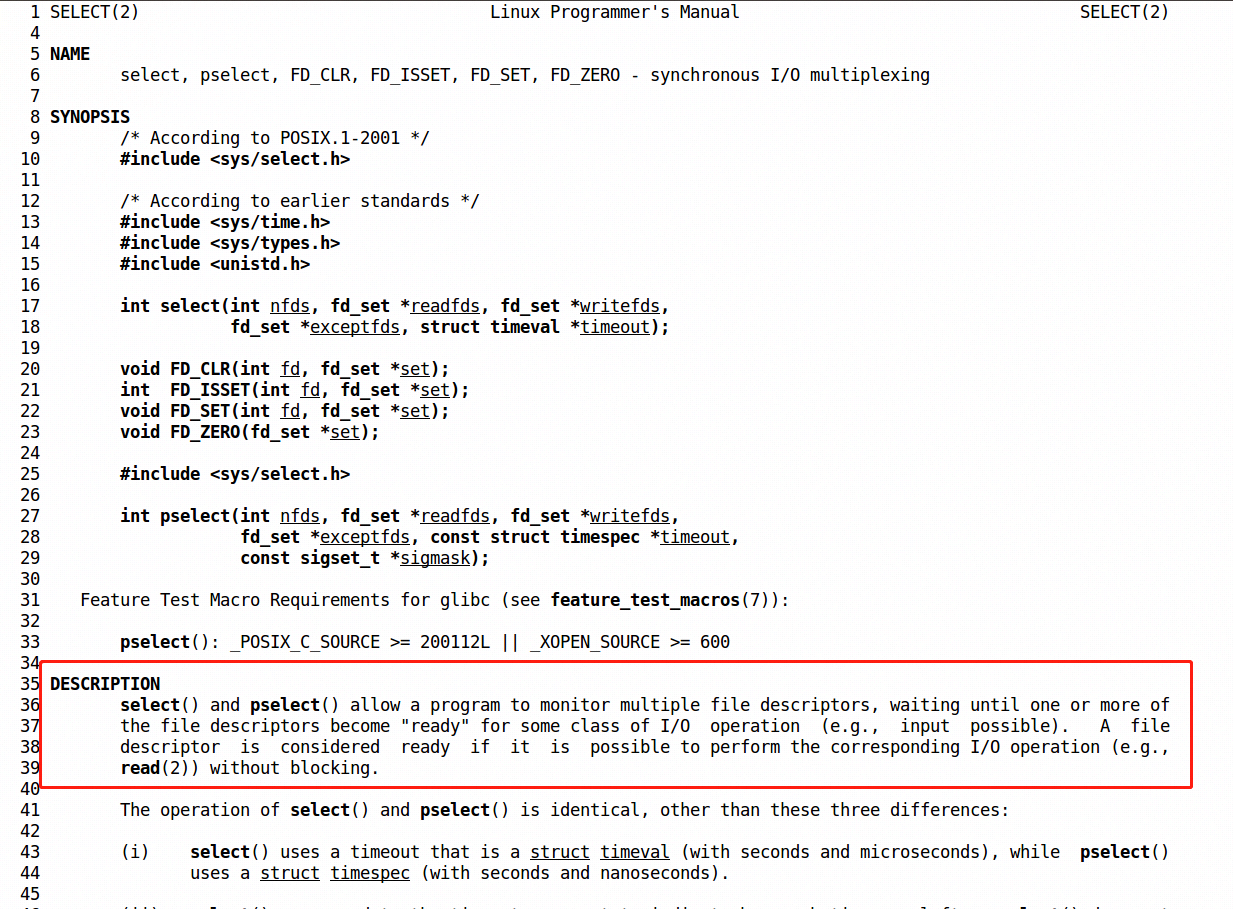
如果这个图,让你有点迷惑,那就像个男人一样,`man`一下`select/poll`函数吧:
- `select`:
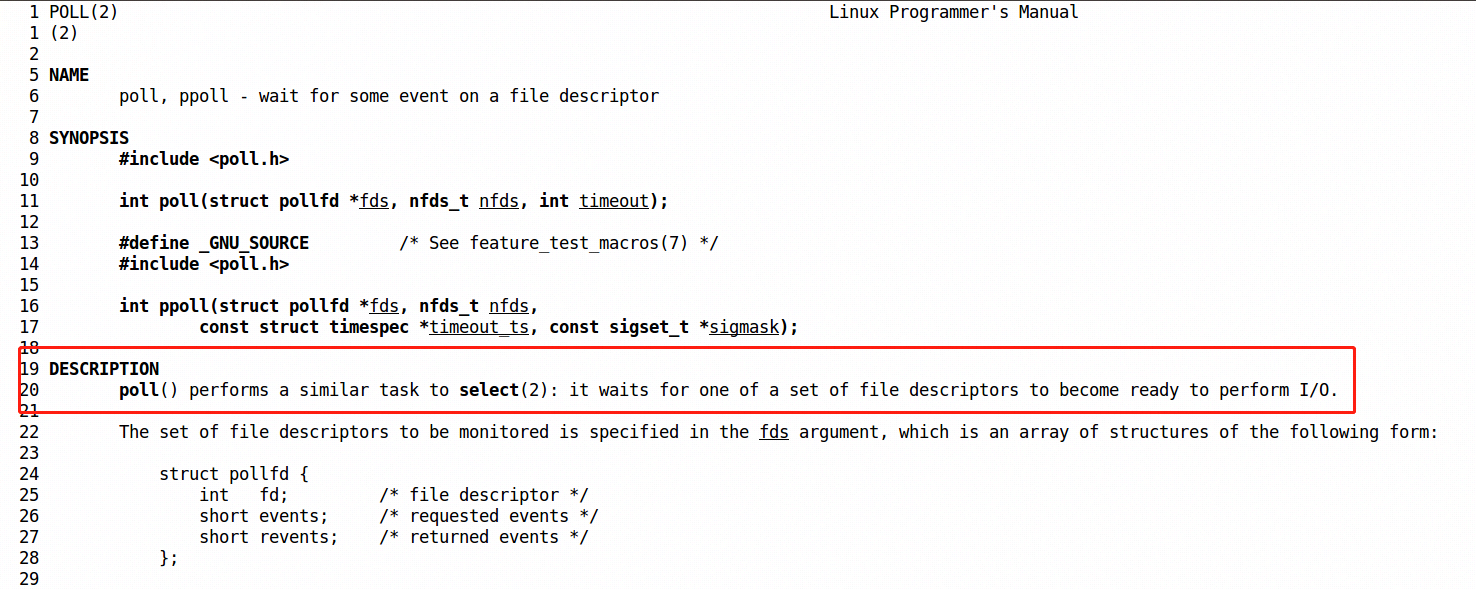
- `poll`
简单来说,`select/poll`能监听多个设备的文件描述符,只要有任何一个设备满足条件,`select/poll`就会返回,否则将进行睡眠等待。
看起来,`select/poll`像是一个管家了,统一负责来监听处理了。
已经迫不及待来看看原理了,由于底层的机制大体差不多,我将选择`select`来做进一步分析。
# 2. 原理
## 2.1 select系统调用
从`select`的系统调用开始:
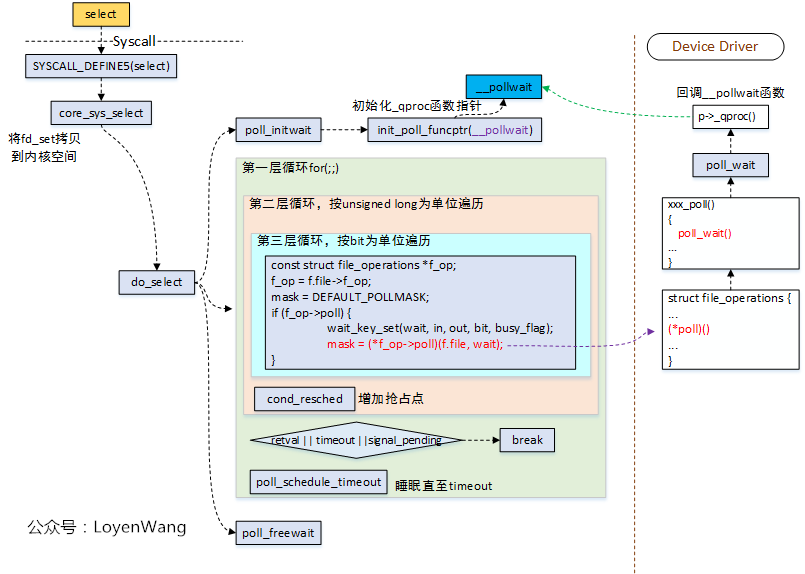
- `select`系统调用,最终的核心逻辑是在`do_select`函数中处理的,参考`fs/select.c`文件;
- `do_select`函数中,有几个关键的操作:
1. 初始化`poll_wqueues`结构,包括几个关键函数指针的初始化,用于驱动中进行回调处理;
2. 循环遍历监测的文件描述符,并且调用`f_op->poll()`函数,如果有监测条件满足,则会跳出循环;
3. 在监测的文件描述符都不满足条件时,`poll_schedule_timeout`让当前进程进行睡眠,超时唤醒,或者被所属的等待队列唤醒;
- `do_select`函数的循环退出条件有三个:
1. 检测的文件描述符满足条件;
2. 超时;
3. 有信号要处理;
- 在设备驱动程序中实现的`poll()`函数,会在`do_select()`中被调用,而驱动中的`poll()`函数,需要调用`poll_wait()`函数,`poll_wait`函数本身很简单,就是去回调函数`p->_qproc()`,这个回调函数正是`poll_initwait()`函数中初始化的`__pollwait()`;
所以,来看看`__pollwait()`函数喽。
## 2.2 `__pollwait`

- 驱动中的`poll_wait`函数回调`__pollwait`,这个函数完成的工作是向`struct poll_wqueue`结构中添加一条`poll_table_entry`;
- `poll_table_entry`中包含了等待队列的相关数据结构;
- 对等待队列的相关数据结构进行初始化,包括设置等待队列唤醒时的回调函数指针,设置成`pollwake`;
- 将任务添加到驱动程序中的等待队列中,最终驱动可以通过`wake_up_interruptile`等接口来唤醒处理;
这一顿操作,其实就是驱动向`select`维护的`struct poll_wqueue`中注册,并将调用`select`的任务添加到驱动的等待队列中,以便在合适的时机进行唤醒。所以,本质上来说,这是基于等待队列的机制来实现的。
是不是还有点抽象,来看看数据结构的组织关系吧。
## 2.3 数据结构关系
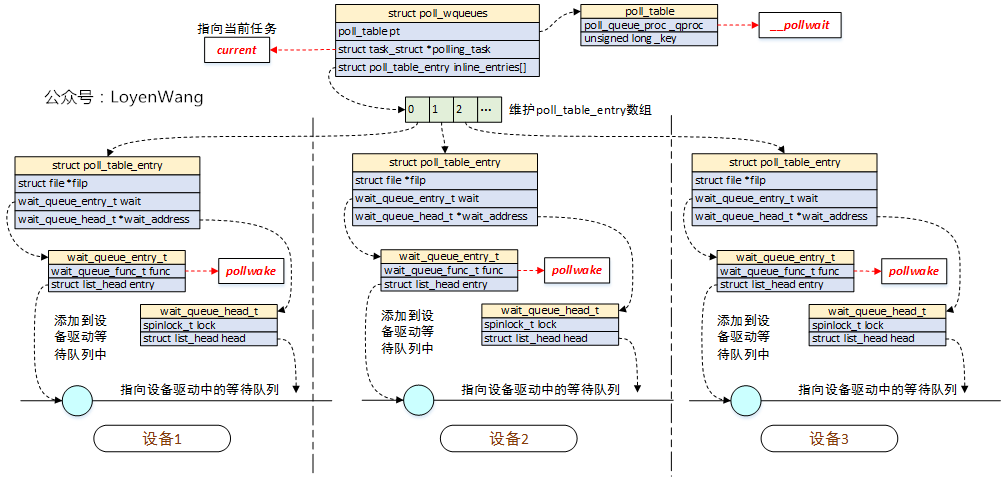
- 调用`select`系统调用的进程/线程,会维护一个`struct poll_wqueues`结构,其中两个关键字段:
1. `pll_table`:该结构体中的函数指针`_qproc`指向`__pollwait`函数;
2. `struct poll_table_entry[]`:存放不同设备的`poll_table_entry`,这些条目的增加是在驱动调用`poll_wait->__pollwait()`时进行初始化并完成添加的;
## 2.4 驱动编写启示
如果驱动中要支持`select`的接口调用,那么需要做哪些事情呢?
如果理解了上文中的内容,你会毫不犹豫的大声说出以下几条:
1. 定义一个等待队列头`wait_queue_head_t`,用于收留等待队列任务;
2. `struct file_operations`结构体中的`poll`函数需要实现,比如`xxx_poll()`;
3. `xxx_poll()`函数中,当然不要忘了`poll_wait`函数的调用了,此外,该函数的返回值`mask`需要注意是在条件满足时对应的值,比如`EPOLLIN/EPOLL/EPOLLERR`等,这个返回值是在`do_select()`函数中会去判断处理的;
4. 条件满足的时候,`wake_up_interruptible`唤醒任务,当然也可以使用`wake_up`,区别是:`wake_up_interruptible`只能唤醒处于`TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE`状态的任务,而`wake_up`能唤醒处于`TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE`和`TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE`状态的任务;
## 2.5 `select/poll`的差异
- `select`与`poll`本质上基本类似,其中`select`是由`BSD UNIX`引入,`poll`由`SystemV`引入;
- `select`与`poll`需要轮询文件描述符集合,并在用户态和内核态之间进行拷贝,在文件描述符很多的情况下开销会比较大,`select`默认支持的文件描述符数量是1024;
- Linux提供了`epoll`机制,改进了`select`与`poll`在效率与资源上的缺点,未深入了解;
# 3. 示例代码
## 3.1 内核驱动
示例代码中的逻辑:
1. 驱动维护一个count值,当count值大于0时,表明条件满足,poll返回正常的mask值;
2. poll函数每执行一次,count值就减去一次;
3. count的值可以由用户通过`ioctl`来进行设置;
```c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define POLL_DEV_NAME "poll"
#define POLL_MAGIC 'P'
#define POLL_SET_COUNT (_IOW(POLL_MAGIC, 0, unsigned int))
struct poll_dev {
struct cdev cdev;
struct class *class;
struct device *device;
wait_queue_head_t wq_head;
struct mutex poll_mutex;
unsigned int count;
dev_t devno;
};
struct poll_dev *g_poll_dev = NULL;
static int poll_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = g_poll_dev;
return 0;
}
static int poll_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static unsigned int poll_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *wait)
{
unsigned int mask = 0;
struct poll_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
mutex_lock(&dev->poll_mutex);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->wq_head, wait);
if (dev->count > 0) {
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
/* decrease each time */
dev->count--;
}
mutex_unlock(&dev->poll_mutex);
return mask;
}
static long poll_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
struct poll_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int cnt;
switch (cmd) {
case POLL_SET_COUNT:
mutex_lock(&dev->poll_mutex);
if (copy_from_user(&cnt, (void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd))) {
pr_err("copy_from_user fail:%d\n", __LINE__);
return -EFAULT;
}
if (dev->count == 0) {
wake_up_interruptible(&dev->wq_head);
}
/* update count */
dev->count += cnt;
mutex_unlock(&dev->poll_mutex);
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations poll_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = poll_open,
.release = poll_close,
.poll = poll_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = poll_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = poll_ioctl,
};
static int __init poll_init(void)
{
int ret;
if (g_poll_dev == NULL) {
g_poll_dev = (struct poll_dev *)kzalloc(sizeof(struct poll_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (g_poll_dev == NULL) {
pr_err("struct poll_dev allocate fail\n");
return -1;
}
}
/* allocate device number */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&g_poll_dev->devno, 0, 1, POLL_DEV_NAME);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("alloc_chrdev_region fail:%d\n", ret);
goto alloc_chrdev_err;
}
/* set char-device */
cdev_init(&g_poll_dev->cdev, &poll_fops);
g_poll_dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
ret = cdev_add(&g_poll_dev->cdev, g_poll_dev->devno, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("cdev_add fail:%d\n", ret);
goto cdev_add_err;
}
/* create device */
g_poll_dev->class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, POLL_DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(g_poll_dev->class)) {
pr_err("class_create fail\n");
goto class_create_err;
}
g_poll_dev->device = device_create(g_poll_dev->class, NULL,
g_poll_dev->devno, NULL, POLL_DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(g_poll_dev->device)) {
pr_err("device_create fail\n");
goto device_create_err;
}
mutex_init(&g_poll_dev->poll_mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&g_poll_dev->wq_head);
return 0;
device_create_err:
class_destroy(g_poll_dev->class);
class_create_err:
cdev_del(&g_poll_dev->cdev);
cdev_add_err:
unregister_chrdev_region(g_poll_dev->devno, 1);
alloc_chrdev_err:
kfree(g_poll_dev);
g_poll_dev = NULL;
return -1;
}
static void __exit poll_exit(void)
{
cdev_del(&g_poll_dev->cdev);
device_destroy(g_poll_dev->class, g_poll_dev->devno);
unregister_chrdev_region(g_poll_dev->devno, 1);
class_destroy(g_poll_dev->class);
kfree(g_poll_dev);
g_poll_dev = NULL;
}
module_init(poll_init);
module_exit(poll_exit);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("select/poll test");
MODULE_AUTHOR("LoyenWang");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
```
## 3.2 测试代码
测试代码逻辑:
1. 创建一个设值线程,用于每隔2秒来设置一次count值;
2. 主线程调用`select`函数监听,当设值线程设置了count值后,select便会返回;
```c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static void *set_count_thread(void *arg)
{
int fd = *(int *)arg;
unsigned int count_value = 1;
int loop_cnt = 20;
int ret;
while (loop_cnt--) {
ret = ioctl(fd, NOTIFY_SET_COUNT, &count_value);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("ioctl set count value fail:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
int fd;
int ret;
pthread_t setcnt_tid;
int loop_cnt = 20;
/* for select use */
fd_set rfds;
struct timeval tv;
fd = open("https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dev/poll", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dev/poll open failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
/* wait up to five seconds */
tv.tv_sec = 5;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
ret = pthread_create(&setcnt_tid, NULL,
set_count_thread, &fd);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("set_count_thread create fail: %d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
while (loop_cnt--) {
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(fd, &rfds);
ret = select(fd + 1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
//ret = select(fd + 1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret == -1) {
perror("select()");
break;
}
else if (ret)
printf("Data is available now.\n");
else {
printf("No data within five seconds.\n");
}
}
ret = pthread_join(setcnt_tid, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("set_count_thread join fail.\n");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
```

加载全部内容