接口自动化框架pyface详细介绍
东方er 人气:1
# 版权说明
本框架系本人结合一些实践经验和开源框架设计思想,**在家**基于兴趣爱好独立完成的代码开发。
源码只保存在私人电脑,办公电脑上无。github开源与公司无关,先把关系撇清,不涉及侵权。
嘘。
# 框架定位
首先最重要的就是学习交流,无商业用途。其次本框架有一定实用价值,可作为工作辅助工具,解决现有技术无法处理的问题。最后可以优化改造投入生产实用(若有更好的idea请务必告诉我,求知若渴)。
# 设计思想
 # 技术栈
说明文字为本框架中用途。
python:脚本语言。
requests:http请求库。
allure:测试报告
numpy:数据格式兼容。
pandas:mysql返回数据处理。
PyMySQL:连接mysql。
SQLAlchemy:mysql连接引擎,支持ORM。
texttable:日志打印sql查询结果表格。
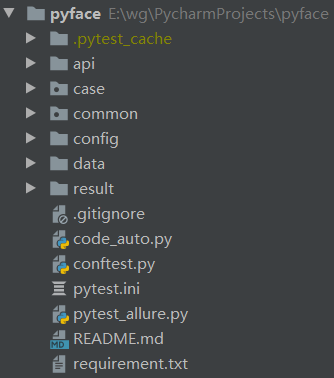
# 目录结构
# 技术栈
说明文字为本框架中用途。
python:脚本语言。
requests:http请求库。
allure:测试报告
numpy:数据格式兼容。
pandas:mysql返回数据处理。
PyMySQL:连接mysql。
SQLAlchemy:mysql连接引擎,支持ORM。
texttable:日志打印sql查询结果表格。
# 目录结构
 # 用例组织方式
模板代码使用code_auto.py自动生成。
```python
self.api_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'api'), 'bu') # 1
self.case_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint') # 2
self.uri = '/api/post' # 3
self.description = 'Demo auto code' # 4
# 5
self.body = """{}
"""
```
1 输入api子目录名称。接口是按业务部门来区分的,子目录名称建议按业务部门(bu==Business Unit)来设置。
2 输入测试用例子目录名称。现在流行敏捷开发,建议按迭代sprint或独立功能模块命名。
3 接口uri。需要注意的是,开头要有1个斜杠`/`。
4 接口描述。如名称、作用。
5 请求体。
执行后在api和case目录生成测试初始化代码。
域名、Headers/Cookie涉及到环境变量,在data/env设置。
```python
class _GldExp:
x = 1
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
test_url = 'https://x'
class _Gld:
x = 2
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
"username",
"password")
test_url = 'https://x'
def uuid_list(n):
"""Uuid list
@param n: Number
@return: A uuid list
"""
return [str(uuid.uuid4()).replace('-', '') for i in range(n)]
# Set environment name
vars_ = _GldExp
```
2个内部类`_GldExp`和`_Gld`,定义参数化环境变量。
在env文件中可以定义一些业务相关函数。公共函数需要放到common/func,建议不要轻易把框架无关的函数放到公共函数里面。
`import env`后,使用`vars_`引用来调用具体的环境变量,如`vars_.test_url`。
# 测试代码编写方式
api/bu目录下,每个接口==1个py文件。
```python
class ApiPost(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
api继承了基类Api。根据不同环境初始化`vars_.test_url`,`load()`方法用于加载参数,`send()`方法用于发送请求(视不同method修改对应的请求方法&参数,如`get`,可以在`common/request.py`中找到相关定义)。
**测试代码完全面向对象。**
```python
def test_default():
x = ApiPost()
x.load().send()
```
这样能很方便的在接口之间传递参数,以及做参数化的工作。
比如,在接口.py中,需要参数化body的name:
```
def load(self):
self.body = {
"name": self.name
}
```
PyCharm会提示此属性未定义,忽略它。
在测试代码中写参数化就很简单:
```python
x.name = 'dongfanger'
x.load().send()
```
# JMeter参数化方式
本框架参数化借鉴了JMeter的参数化方式。也就是,在接口发请求后,对参数赋值;在接口收到相应后,提取参数。**这也是测试代码要完全面向对象的原因。**
面向对象能较好的组织测试代码,使代码逻辑清晰,阅读易于理解。
比如,先定义2个接口,苹果树和商店:
```python
class AppleTree(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/apple/tree"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
```python
class ShopSale(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/shop/sale"
def load(self):
self.body = {
"apple": self.apple
}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
测试代码编写,苹果树先生产苹果,再运输到商店,商店卖苹果:
```python
def test_apple_to_shop():
apple_tree = AppleTree()
apple_tree.load().send() # 生产苹果
good_apple = apple_tree.content['good_apple'] # content在Api基类中定义
shop_sale = ShopSale()
shop_sale.apple = good_apple # 传递参数
shop_sale.load().send()
print(shop_sale.content)
```
content在Api基类中定义:
```python
def set_content(self):
"""After request, assert status and set content
"""
status_ok(self.res)
res_json = self.res.json()
assert 1000 == res_json.get('status')
try:
self.content = res_json['content']
except KeyError:
logger.info(f"{'*' * 26}\n"
f"Response no content\n"
f"{'*' * 26}\n")
```
先断言返回状态ok,再取响应json里面key为content的value。不同公司json规范不一样,需要做调整。
# 批量执行用例生成测试报告
pytest_allure.py批量执行测试用例。
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'case')
```
默认执行case目录下`test_`开头或结尾的文件(pytest规则)。测试方法需要以`test_`开头。
可以指定目录,如:
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint0001')
```
本框架借助`pytest_sessionfinish `hook函数实现了生成测试报告并自动打开浏览器。
```python
def pytest_sessionfinish(session):
allure_report_dir_test = session.config.getoption('allure_report_dir')
if allure_report_dir_test:
html_dir = os.path.join(allure_report_dir_test, 'html')
os.system(f'mkdir {html_dir}')
os.system(f"allure generate {allure_report_dir_test} -o {html_dir}")
os.system(f"allure open {html_dir}")
```
# mysql支持
mysql主要用于:一提供参数化赋值;二数据库比对断言。
commonshttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dao.py实现了相关功能。在data/env.py中根据环境定义好连接后,通过`vars_`使用。
```python
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
```
```python
sql_result = vars_.dao_x.select('select id, name from new_table;')
```
dao实现采用了pandas+sqlalchemy,对返回结果取值就可以按dataframe来,如`sql_result['name'][0]`。
借助texttable会打印表格日志,观察数据。
```
[2020-03-22 18:14:13]Running sql
select id, name from new_table;
[2020-03-22 18:14:14]Sql result:
+----+------+
| id | name |
+====+======+
| 1 | w |
+----+------+
| 2 | g |
+----+------+
```
值得说明的是,为了数据校验方便,默认会把无小数的float转换为int,如`5.0`->`5`。
```python
@staticmethod
def _convert(x):
"""Convert logic code
@param x: Single cell data
@return: Converted single cell data
"""
# float to int
if isinstance(x, float) and x % 1 == 0:
return int(x)
return x
```
# 结语
开源使我快乐。
分享才能收获更多。
我在github等你。
https://github.comhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dongfanger/pyface
# 用例组织方式
模板代码使用code_auto.py自动生成。
```python
self.api_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'api'), 'bu') # 1
self.case_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint') # 2
self.uri = '/api/post' # 3
self.description = 'Demo auto code' # 4
# 5
self.body = """{}
"""
```
1 输入api子目录名称。接口是按业务部门来区分的,子目录名称建议按业务部门(bu==Business Unit)来设置。
2 输入测试用例子目录名称。现在流行敏捷开发,建议按迭代sprint或独立功能模块命名。
3 接口uri。需要注意的是,开头要有1个斜杠`/`。
4 接口描述。如名称、作用。
5 请求体。
执行后在api和case目录生成测试初始化代码。
域名、Headers/Cookie涉及到环境变量,在data/env设置。
```python
class _GldExp:
x = 1
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
test_url = 'https://x'
class _Gld:
x = 2
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
"username",
"password")
test_url = 'https://x'
def uuid_list(n):
"""Uuid list
@param n: Number
@return: A uuid list
"""
return [str(uuid.uuid4()).replace('-', '') for i in range(n)]
# Set environment name
vars_ = _GldExp
```
2个内部类`_GldExp`和`_Gld`,定义参数化环境变量。
在env文件中可以定义一些业务相关函数。公共函数需要放到common/func,建议不要轻易把框架无关的函数放到公共函数里面。
`import env`后,使用`vars_`引用来调用具体的环境变量,如`vars_.test_url`。
# 测试代码编写方式
api/bu目录下,每个接口==1个py文件。
```python
class ApiPost(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
api继承了基类Api。根据不同环境初始化`vars_.test_url`,`load()`方法用于加载参数,`send()`方法用于发送请求(视不同method修改对应的请求方法&参数,如`get`,可以在`common/request.py`中找到相关定义)。
**测试代码完全面向对象。**
```python
def test_default():
x = ApiPost()
x.load().send()
```
这样能很方便的在接口之间传递参数,以及做参数化的工作。
比如,在接口.py中,需要参数化body的name:
```
def load(self):
self.body = {
"name": self.name
}
```
PyCharm会提示此属性未定义,忽略它。
在测试代码中写参数化就很简单:
```python
x.name = 'dongfanger'
x.load().send()
```
# JMeter参数化方式
本框架参数化借鉴了JMeter的参数化方式。也就是,在接口发请求后,对参数赋值;在接口收到相应后,提取参数。**这也是测试代码要完全面向对象的原因。**
面向对象能较好的组织测试代码,使代码逻辑清晰,阅读易于理解。
比如,先定义2个接口,苹果树和商店:
```python
class AppleTree(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/apple/tree"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
```python
class ShopSale(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/shop/sale"
def load(self):
self.body = {
"apple": self.apple
}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
测试代码编写,苹果树先生产苹果,再运输到商店,商店卖苹果:
```python
def test_apple_to_shop():
apple_tree = AppleTree()
apple_tree.load().send() # 生产苹果
good_apple = apple_tree.content['good_apple'] # content在Api基类中定义
shop_sale = ShopSale()
shop_sale.apple = good_apple # 传递参数
shop_sale.load().send()
print(shop_sale.content)
```
content在Api基类中定义:
```python
def set_content(self):
"""After request, assert status and set content
"""
status_ok(self.res)
res_json = self.res.json()
assert 1000 == res_json.get('status')
try:
self.content = res_json['content']
except KeyError:
logger.info(f"{'*' * 26}\n"
f"Response no content\n"
f"{'*' * 26}\n")
```
先断言返回状态ok,再取响应json里面key为content的value。不同公司json规范不一样,需要做调整。
# 批量执行用例生成测试报告
pytest_allure.py批量执行测试用例。
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'case')
```
默认执行case目录下`test_`开头或结尾的文件(pytest规则)。测试方法需要以`test_`开头。
可以指定目录,如:
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint0001')
```
本框架借助`pytest_sessionfinish `hook函数实现了生成测试报告并自动打开浏览器。
```python
def pytest_sessionfinish(session):
allure_report_dir_test = session.config.getoption('allure_report_dir')
if allure_report_dir_test:
html_dir = os.path.join(allure_report_dir_test, 'html')
os.system(f'mkdir {html_dir}')
os.system(f"allure generate {allure_report_dir_test} -o {html_dir}")
os.system(f"allure open {html_dir}")
```
# mysql支持
mysql主要用于:一提供参数化赋值;二数据库比对断言。
commonshttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dao.py实现了相关功能。在data/env.py中根据环境定义好连接后,通过`vars_`使用。
```python
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
```
```python
sql_result = vars_.dao_x.select('select id, name from new_table;')
```
dao实现采用了pandas+sqlalchemy,对返回结果取值就可以按dataframe来,如`sql_result['name'][0]`。
借助texttable会打印表格日志,观察数据。
```
[2020-03-22 18:14:13]Running sql
select id, name from new_table;
[2020-03-22 18:14:14]Sql result:
+----+------+
| id | name |
+====+======+
| 1 | w |
+----+------+
| 2 | g |
+----+------+
```
值得说明的是,为了数据校验方便,默认会把无小数的float转换为int,如`5.0`->`5`。
```python
@staticmethod
def _convert(x):
"""Convert logic code
@param x: Single cell data
@return: Converted single cell data
"""
# float to int
if isinstance(x, float) and x % 1 == 0:
return int(x)
return x
```
# 结语
开源使我快乐。
分享才能收获更多。
我在github等你。
https://github.comhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dongfanger/pyface
 # 技术栈
说明文字为本框架中用途。
python:脚本语言。
requests:http请求库。
allure:测试报告
numpy:数据格式兼容。
pandas:mysql返回数据处理。
PyMySQL:连接mysql。
SQLAlchemy:mysql连接引擎,支持ORM。
texttable:日志打印sql查询结果表格。
# 目录结构
# 技术栈
说明文字为本框架中用途。
python:脚本语言。
requests:http请求库。
allure:测试报告
numpy:数据格式兼容。
pandas:mysql返回数据处理。
PyMySQL:连接mysql。
SQLAlchemy:mysql连接引擎,支持ORM。
texttable:日志打印sql查询结果表格。
# 目录结构
 # 用例组织方式
模板代码使用code_auto.py自动生成。
```python
self.api_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'api'), 'bu') # 1
self.case_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint') # 2
self.uri = '/api/post' # 3
self.description = 'Demo auto code' # 4
# 5
self.body = """{}
"""
```
1 输入api子目录名称。接口是按业务部门来区分的,子目录名称建议按业务部门(bu==Business Unit)来设置。
2 输入测试用例子目录名称。现在流行敏捷开发,建议按迭代sprint或独立功能模块命名。
3 接口uri。需要注意的是,开头要有1个斜杠`/`。
4 接口描述。如名称、作用。
5 请求体。
执行后在api和case目录生成测试初始化代码。
域名、Headers/Cookie涉及到环境变量,在data/env设置。
```python
class _GldExp:
x = 1
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
test_url = 'https://x'
class _Gld:
x = 2
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
"username",
"password")
test_url = 'https://x'
def uuid_list(n):
"""Uuid list
@param n: Number
@return: A uuid list
"""
return [str(uuid.uuid4()).replace('-', '') for i in range(n)]
# Set environment name
vars_ = _GldExp
```
2个内部类`_GldExp`和`_Gld`,定义参数化环境变量。
在env文件中可以定义一些业务相关函数。公共函数需要放到common/func,建议不要轻易把框架无关的函数放到公共函数里面。
`import env`后,使用`vars_`引用来调用具体的环境变量,如`vars_.test_url`。
# 测试代码编写方式
api/bu目录下,每个接口==1个py文件。
```python
class ApiPost(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
api继承了基类Api。根据不同环境初始化`vars_.test_url`,`load()`方法用于加载参数,`send()`方法用于发送请求(视不同method修改对应的请求方法&参数,如`get`,可以在`common/request.py`中找到相关定义)。
**测试代码完全面向对象。**
```python
def test_default():
x = ApiPost()
x.load().send()
```
这样能很方便的在接口之间传递参数,以及做参数化的工作。
比如,在接口.py中,需要参数化body的name:
```
def load(self):
self.body = {
"name": self.name
}
```
PyCharm会提示此属性未定义,忽略它。
在测试代码中写参数化就很简单:
```python
x.name = 'dongfanger'
x.load().send()
```
# JMeter参数化方式
本框架参数化借鉴了JMeter的参数化方式。也就是,在接口发请求后,对参数赋值;在接口收到相应后,提取参数。**这也是测试代码要完全面向对象的原因。**
面向对象能较好的组织测试代码,使代码逻辑清晰,阅读易于理解。
比如,先定义2个接口,苹果树和商店:
```python
class AppleTree(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/apple/tree"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
```python
class ShopSale(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/shop/sale"
def load(self):
self.body = {
"apple": self.apple
}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
测试代码编写,苹果树先生产苹果,再运输到商店,商店卖苹果:
```python
def test_apple_to_shop():
apple_tree = AppleTree()
apple_tree.load().send() # 生产苹果
good_apple = apple_tree.content['good_apple'] # content在Api基类中定义
shop_sale = ShopSale()
shop_sale.apple = good_apple # 传递参数
shop_sale.load().send()
print(shop_sale.content)
```
content在Api基类中定义:
```python
def set_content(self):
"""After request, assert status and set content
"""
status_ok(self.res)
res_json = self.res.json()
assert 1000 == res_json.get('status')
try:
self.content = res_json['content']
except KeyError:
logger.info(f"{'*' * 26}\n"
f"Response no content\n"
f"{'*' * 26}\n")
```
先断言返回状态ok,再取响应json里面key为content的value。不同公司json规范不一样,需要做调整。
# 批量执行用例生成测试报告
pytest_allure.py批量执行测试用例。
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'case')
```
默认执行case目录下`test_`开头或结尾的文件(pytest规则)。测试方法需要以`test_`开头。
可以指定目录,如:
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint0001')
```
本框架借助`pytest_sessionfinish `hook函数实现了生成测试报告并自动打开浏览器。
```python
def pytest_sessionfinish(session):
allure_report_dir_test = session.config.getoption('allure_report_dir')
if allure_report_dir_test:
html_dir = os.path.join(allure_report_dir_test, 'html')
os.system(f'mkdir {html_dir}')
os.system(f"allure generate {allure_report_dir_test} -o {html_dir}")
os.system(f"allure open {html_dir}")
```
# mysql支持
mysql主要用于:一提供参数化赋值;二数据库比对断言。
commonshttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dao.py实现了相关功能。在data/env.py中根据环境定义好连接后,通过`vars_`使用。
```python
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
```
```python
sql_result = vars_.dao_x.select('select id, name from new_table;')
```
dao实现采用了pandas+sqlalchemy,对返回结果取值就可以按dataframe来,如`sql_result['name'][0]`。
借助texttable会打印表格日志,观察数据。
```
[2020-03-22 18:14:13]Running sql
select id, name from new_table;
[2020-03-22 18:14:14]Sql result:
+----+------+
| id | name |
+====+======+
| 1 | w |
+----+------+
| 2 | g |
+----+------+
```
值得说明的是,为了数据校验方便,默认会把无小数的float转换为int,如`5.0`->`5`。
```python
@staticmethod
def _convert(x):
"""Convert logic code
@param x: Single cell data
@return: Converted single cell data
"""
# float to int
if isinstance(x, float) and x % 1 == 0:
return int(x)
return x
```
# 结语
开源使我快乐。
分享才能收获更多。
我在github等你。
https://github.comhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dongfanger/pyface
# 用例组织方式
模板代码使用code_auto.py自动生成。
```python
self.api_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'api'), 'bu') # 1
self.case_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint') # 2
self.uri = '/api/post' # 3
self.description = 'Demo auto code' # 4
# 5
self.body = """{}
"""
```
1 输入api子目录名称。接口是按业务部门来区分的,子目录名称建议按业务部门(bu==Business Unit)来设置。
2 输入测试用例子目录名称。现在流行敏捷开发,建议按迭代sprint或独立功能模块命名。
3 接口uri。需要注意的是,开头要有1个斜杠`/`。
4 接口描述。如名称、作用。
5 请求体。
执行后在api和case目录生成测试初始化代码。
域名、Headers/Cookie涉及到环境变量,在data/env设置。
```python
class _GldExp:
x = 1
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
test_url = 'https://x'
class _Gld:
x = 2
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
"username",
"password")
test_url = 'https://x'
def uuid_list(n):
"""Uuid list
@param n: Number
@return: A uuid list
"""
return [str(uuid.uuid4()).replace('-', '') for i in range(n)]
# Set environment name
vars_ = _GldExp
```
2个内部类`_GldExp`和`_Gld`,定义参数化环境变量。
在env文件中可以定义一些业务相关函数。公共函数需要放到common/func,建议不要轻易把框架无关的函数放到公共函数里面。
`import env`后,使用`vars_`引用来调用具体的环境变量,如`vars_.test_url`。
# 测试代码编写方式
api/bu目录下,每个接口==1个py文件。
```python
class ApiPost(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
api继承了基类Api。根据不同环境初始化`vars_.test_url`,`load()`方法用于加载参数,`send()`方法用于发送请求(视不同method修改对应的请求方法&参数,如`get`,可以在`common/request.py`中找到相关定义)。
**测试代码完全面向对象。**
```python
def test_default():
x = ApiPost()
x.load().send()
```
这样能很方便的在接口之间传递参数,以及做参数化的工作。
比如,在接口.py中,需要参数化body的name:
```
def load(self):
self.body = {
"name": self.name
}
```
PyCharm会提示此属性未定义,忽略它。
在测试代码中写参数化就很简单:
```python
x.name = 'dongfanger'
x.load().send()
```
# JMeter参数化方式
本框架参数化借鉴了JMeter的参数化方式。也就是,在接口发请求后,对参数赋值;在接口收到相应后,提取参数。**这也是测试代码要完全面向对象的原因。**
面向对象能较好的组织测试代码,使代码逻辑清晰,阅读易于理解。
比如,先定义2个接口,苹果树和商店:
```python
class AppleTree(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/apple/tree"
def load(self):
self.body = {}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
```python
class ShopSale(Api):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.url = vars_.test_url + "/api/post/shop/sale"
def load(self):
self.body = {
"apple": self.apple
}
return self
def send(self):
self.res = self.req.post(url=self.url, headers=vars_.headers, json=self.body)
self.set_content()
return self.res
```
测试代码编写,苹果树先生产苹果,再运输到商店,商店卖苹果:
```python
def test_apple_to_shop():
apple_tree = AppleTree()
apple_tree.load().send() # 生产苹果
good_apple = apple_tree.content['good_apple'] # content在Api基类中定义
shop_sale = ShopSale()
shop_sale.apple = good_apple # 传递参数
shop_sale.load().send()
print(shop_sale.content)
```
content在Api基类中定义:
```python
def set_content(self):
"""After request, assert status and set content
"""
status_ok(self.res)
res_json = self.res.json()
assert 1000 == res_json.get('status')
try:
self.content = res_json['content']
except KeyError:
logger.info(f"{'*' * 26}\n"
f"Response no content\n"
f"{'*' * 26}\n")
```
先断言返回状态ok,再取响应json里面key为content的value。不同公司json规范不一样,需要做调整。
# 批量执行用例生成测试报告
pytest_allure.py批量执行测试用例。
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'case')
```
默认执行case目录下`test_`开头或结尾的文件(pytest规则)。测试方法需要以`test_`开头。
可以指定目录,如:
```python
# Input the directory to run pytest
run_dir = os.path.join(os.path.join(base_dir, 'case'), 'sprint0001')
```
本框架借助`pytest_sessionfinish `hook函数实现了生成测试报告并自动打开浏览器。
```python
def pytest_sessionfinish(session):
allure_report_dir_test = session.config.getoption('allure_report_dir')
if allure_report_dir_test:
html_dir = os.path.join(allure_report_dir_test, 'html')
os.system(f'mkdir {html_dir}')
os.system(f"allure generate {allure_report_dir_test} -o {html_dir}")
os.system(f"allure open {html_dir}")
```
# mysql支持
mysql主要用于:一提供参数化赋值;二数据库比对断言。
commonshttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dao.py实现了相关功能。在data/env.py中根据环境定义好连接后,通过`vars_`使用。
```python
dao_x = Dao('host:port',
'username',
'password')
```
```python
sql_result = vars_.dao_x.select('select id, name from new_table;')
```
dao实现采用了pandas+sqlalchemy,对返回结果取值就可以按dataframe来,如`sql_result['name'][0]`。
借助texttable会打印表格日志,观察数据。
```
[2020-03-22 18:14:13]Running sql
select id, name from new_table;
[2020-03-22 18:14:14]Sql result:
+----+------+
| id | name |
+====+======+
| 1 | w |
+----+------+
| 2 | g |
+----+------+
```
值得说明的是,为了数据校验方便,默认会把无小数的float转换为int,如`5.0`->`5`。
```python
@staticmethod
def _convert(x):
"""Convert logic code
@param x: Single cell data
@return: Converted single cell data
"""
# float to int
if isinstance(x, float) and x % 1 == 0:
return int(x)
return x
```
# 结语
开源使我快乐。
分享才能收获更多。
我在github等你。
https://github.comhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dongfanger/pyface
加载全部内容