android 代码布局 基于Android代码实现常用布局
人气:0想了解基于Android代码实现常用布局的相关内容吗,在本文为您仔细讲解android 代码布局的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:android代码布局,android常用布局,android纯代码布局,下面大家一起来学习吧。
关于 android 常用布局,利用 XML 文件实现已经有很多的实例了。但如何利用代码实现呢?当然利用代码实现没有太大的必要,也是不提倡的,但我觉得利用代码实现这些布局,可以更好的了解 SDK API ,所以在此也整理一些,和大家分享一下。
首先看一下,布局所对应的类的 API 继承图:

android常用布局的代码实现所有的布局都会对应相关的类,这些类都是继承自 android.view.ViewGroup 类的。而 LinearLayout,RelativeLayout 都是在 android.widget 包里的。另外,TableLayout 是继承自 LinearLayout.
下面直接贴代码了。
// 利用代码设置 线性布局
private void setLinearLayout(){
LinearLayout llayout = new LinearLayout(this);
llayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL); // 设置线性布局的排列方式
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setText("代码实现的线性布局");
textView.setTextColor(Color.RED);
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER); // 设置文本内容的对齐方式
LinearLayout.LayoutParams ll_lpara = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(MP,WC);
// ll_lpara.gravity = Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL; // 设置控件在布局中的对齐方式
llayout.addView(textView,ll_lpara);
Button btn = new Button(this);
btn.setText("按钮");
llayout.addView(btn,ll_lpara); // 按指定属性添加控件
setContentView(llayout);
}
实现效果图:

=========================================================================
// 利用代码设置 相对布局
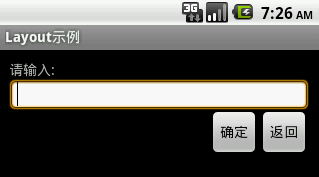
private void setRelativeLayout(){
RelativeLayout rlayout = new RelativeLayout(this);
rlayout.setPadding(10, 10, 10, 10); // 单位: pixels
int textViewID = 100;
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setId(textViewID);
textView.setText("请输入:");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara1 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(MP, WC);
rlayout.addView(textView, rl_lpara1);
int editTextID = 200;
EditText editText = new EditText(this);
editText.setId(editTextID);
editText.setBackgroundResource(android.R.drawable.editbox_background); // 设置背景 , 同android:backgroumd
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(MP, WC);
rl_lpara2.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW,textViewID); // 设置相对属性,需先指定相对控件的ID
rlayout.addView(editText, rl_lpara2);
int backBtnID = 300;
Button backBtn = new Button(this);
backBtn.setId(backBtnID);
backBtn.setText("返回");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara3 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(WC, WC);
rl_lpara3.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, editTextID);
rl_lpara3.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT); // 设置与父控件的相对属性
rlayout.addView(backBtn, rl_lpara3);
Button okBtn = new Button(this);
okBtn.setText("确定");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rl_lpara4 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(WC, WC);
rl_lpara4.addRule(RelativeLayout.LEFT_OF, backBtnID);
rl_lpara4.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_TOP,backBtnID);
rlayout.addView(okBtn, rl_lpara4);
setContentView(rlayout);
}
实现效果图:
=========================================================================
// 利用代码设置 表格布局
private void setTableLayout(){
TableLayout tlayout = new TableLayout(this);
tlayout.setColumnStretchable(2, true); // 拉长索引从0开始的第2列
TableLayout.LayoutParams tl_lpara = new TableLayout.LayoutParams(MP,WC);
// 1. TableRow 不需要设置 layout_width, layout_height
// 2. TableRow 中的控件不能设置 layout_span 属性
TableRow tr1 = new TableRow(this);
TextView textView0 = new TextView(this);
textView0.setText("第0列");
tr1.addView(textView0);
TextView textView1 = new TextView(this);
textView1.setText("第1列");
tr1.addView(textView1);
TextView textView2 = new TextView(this);
textView2.setText("第2列");
textView2.setBackgroundColor(Color.CYAN);
tr1.addView(textView2);
tlayout.addView(tr1, tl_lpara);
TableRow tr2 = new TableRow(this);
Button btn0 = new Button(this);
btn0.setText("按钮0");
tr2.addView(btn0);
Button btn1 = new Button(this);
btn1.setText("按钮1");
tr2.addView(btn1);
Button btn2 = new Button(this);
btn2.setText("按钮2");
tr2.addView(btn2);
Button btn3 = new Button(this);
btn3.setText("按钮3");
tr2.addView(btn3);
tlayout.addView(tr2, tl_lpara);
setContentView(tlayout);
}
实现效果图:

加载全部内容