libra共识算法分析
Yarkin 人气:1
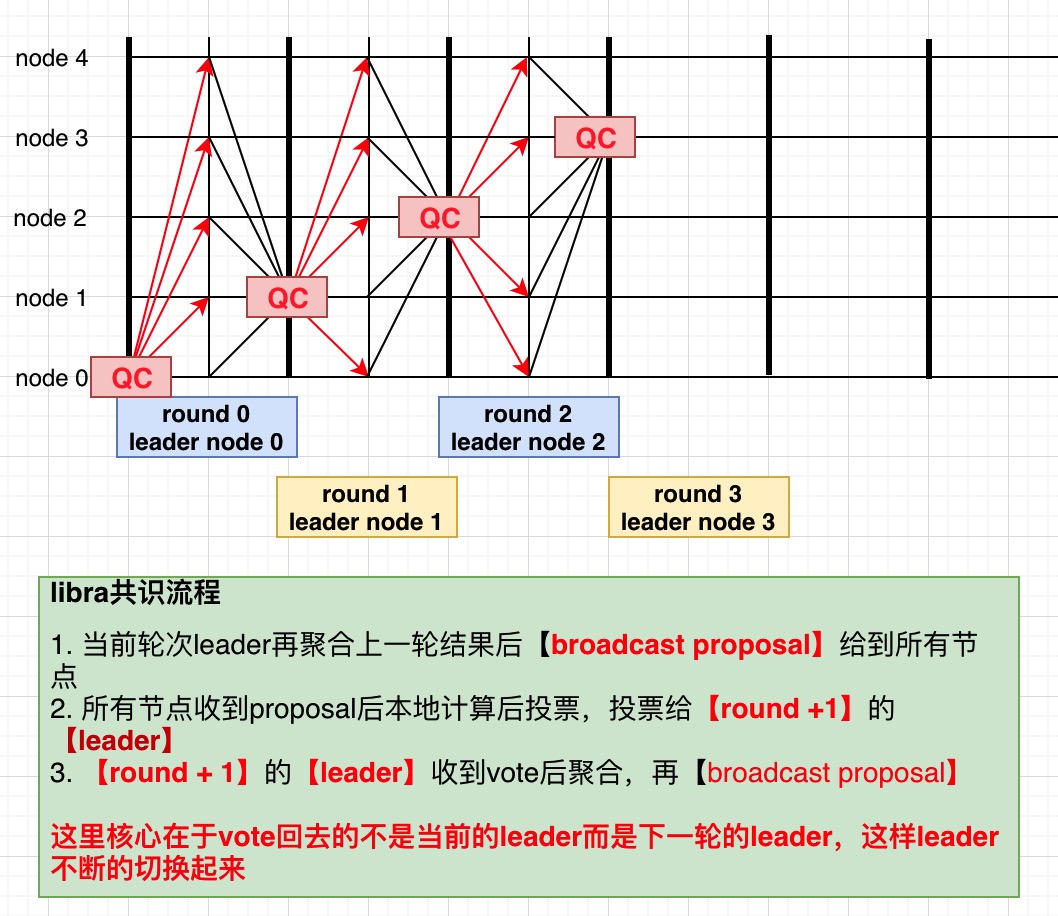
- 核心算法说明
- 基于chained实现,整体上是当前轮推动下一轮共识继续下去, 如此来持续运转下去, 数据有效性证明基于(QC)实现
- leader广播proposal消息{round, qc, propsal}
- replica收到proposal后本地计算后发送投票信息到下一个leader
- 下一个leader负责聚合(qc_aggrate)后再通过proposal消息广播出来进入下一轮
- 活性证明, 数据有效性基于(TC)实现
- 每个节点一旦进入一轮新的共识就会开始计时, 一旦超时就广播timeout_vote消息
- 其他节点收到后本地放到pending_vote队列中, 然后开始本地等待其他节点的timeout_vote投票来名聚合, 一旦签名聚合成功, 则进入下一轮, 并计算相应轮次的leader, 给该leader发起投票,如此将重新起搏整条链的共识
- 关于轮次
- 每个节点的轮次是严格递增的,只有收到有效数据才会增加轮次,增加轮次的规则就是看(QC和TC)两者的高度谁高,谁高那就使用谁的轮次,因为TC/QC都是有法律效应的
- 基于chained实现,整体上是当前轮推动下一轮共识继续下去, 如此来持续运转下去, 数据有效性证明基于(QC)实现
活性证明【降维到传统pbft广播实现】
libra活性证明基于tc(timeoutcetificate)来实现,在每轮启动时(收到proposal处理时)本地设置一个定时器,该定时器触发后直接广播timeoutvote_msg到所有节点,每个节点自己本地聚合生成相应的timeoutcetificate,一旦聚合完成就会round+1,然后投递vote信息到round + 1的leader,这样round + 1的leader又可以驱动起来。为了对齐时间,间隔时间会随着本地timeout次数的增加而变长,每次以1.5的n个指数被递增。直到收到新的leader发出来的proposal为止。
1.触发:
本地设置timeout时间process_local_timeout在timeout时广播timeout_vote
// 处理本地超时事件
pub async fn process_local_timeout(&mut self, round: Round) {
// 根据当前轮次信息和base_ms设置超时, 一旦超时则抛出timeout事件, 然后又触发到proces_local_timeout
// 注意:这里不会引起轮次增加
pacemaker.process_local_timeout(round)
// 根据情况广播timeout_vote
let timeout_vote_msg = VoteMsg::new(timeout_vote, self.gen_sync_info());
// 广播,每个节点都广播出来
self.network.broadcast_vote(timeout_vote_msg).await
}
2.投票处理
收到timeoutvotemsg,收到的节点自己聚合
// 处理投票业务
pub async fn process_vote(&mut self, vote_msg: VoteMsg) {
if !vote_msg.vote().is_timeout() {
// ...非超时投票处理
} else {
// 添加投票信息
self.add_vote(vote_msg.vote();
}
}
// 统计投票信息
async fn add_vote(&mut self, vote: &Vote) -> anyhow::Result<()> {
// Add the vote and check whether it completes a new QC or a TC
let res = self.pending_votes.insert_vote(vote, &self.validators);
match res {
VoteReceptionResult::NewQuorumCertificate(qc) => {
// ..
// 聚合qc签名
self.new_qc_aggregated(qc, vote.author()).await
}
// 觉tc签名
VoteReceptionResult::NewTimeoutCertificate(tc) => self.new_tc_aggregated(tc).await,
}
}
// tc聚合处理
async fn new_tc_aggregated(&mut self, tc: Arc<TimeoutCertificate>) -> anyhow::Result<()> {
// 证书处理
self.process_certificates(
self.block_store.highest_quorum_cert().as_ref(),
Some(tc.as_ref()),
)
}
3.certificate处理
接收certificate后进行处理
async fn process_certificates(
&mut self,
qc: &QuorumCert,
tc: Option<&TimeoutCertificate>,
) -> anyhow::Result<()> {
// pacemaker处理证明, 触发轮次切换
if let Some(new_round_event) = self.pacemaker.process_certificates(
Some(qc.certified_block().round()),
tc_round,
highest_committed_proposal_round,
) {
// 切换轮次, 如果是leader则广播proposal, 如果不是leader则等着
self.process_new_round_event(new_round_event).await;
}
}
// 处理certificate的时候明确new-round,pacemaker更新本地round
pub fn process_certificates(
&mut self,
hqc_round: Option<Round>,
htc_round: Option<Round>,
highest_committed_round: Option<Round>,
) -> Option<NewRoundEvent> {
// 明确计算出新的轮次后才会更新轮次
let new_round = std::cmp::max(qc_round, tc_round) + 1;
if new_round > self.current_round {
// Start a new round.
self.current_round = new_round;
// 新轮次重置超时
let timeout = self.setup_timeout();
let new_round_reason = if qc_round >= tc_round {
NewRoundReason::QCReady
} else {
NewRoundReason::Timeout
};
let new_round_event = NewRoundEvent {
round: self.current_round,
reason: new_round_reason,
timeout,
};
debug!("Starting new round: {}", new_round_event);
return Some(new_round_event);
}
}
4.切换轮次
async fn process_new_round_event(&mut self, new_round_event: NewRoundEvent) {
// 基于roating leader选择算法选择leader
// backup什么事情都不做
if self
.proposer_election
.is_valid_proposer(self.proposal_generator.author(), new_round_event.round)
.is_none()
{
return;
} else {
// leader广播new proposals
let proposal_msg = match self.generate_proposal(new_round_event).await {
// ...
};
network.broadcast_proposal(proposal_msg).await;
}
}
5.参与新的共识
加载全部内容