Java反射,泛型在Json中的运用
Super~me 人气:0
最近项目中遇到了Json数据自动获取的功能,不然令人想起java的反射,已经很长时间没复习java了正好一块连java的这一块内容一起过一遍。java中的反射无疑就相当于java开发者的春天,在众多的框架中也能看到它的身影,可以在运行时检查类,接口、变量和方法等信息,可以实例化调用方法以及设置变量值等。本文主要以代码的形式直接将反射,泛型的运用展现出来。
###java中的反射###
首先新建一个基础类Author。
```
package bean;
/**
*
* @author Super~me
* Description: 基础类
*
*/
public class Author {
private static String TAG="Big";
private String name;
private int age;
public Author(){}
public Author(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Author [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
private String pMethod(String t){
String result=t+" Private Method";
return result;
}
}
```
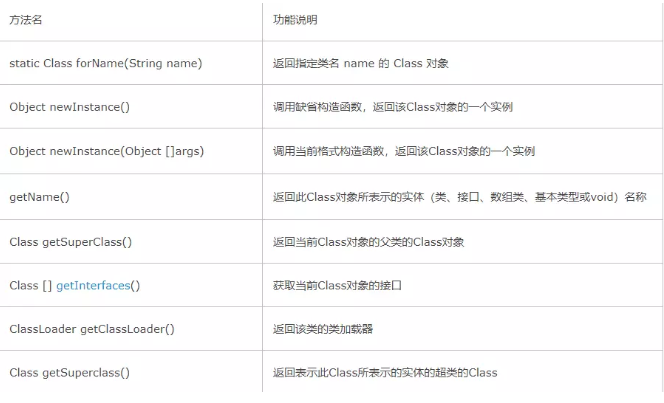
然后新建一个反射类,运用反射方法对上面的类进行访问.包括对私有方法的访问,对私有属性的访问等。其中常用的一些方法以及解释:
```
//对象的创建
public static void reflectNewInstance(){
try {
Class<?> authorclass=Class.forName(path_reflectfrom);
Object object =authorclass.newInstance();
Author author=(Author) object;
author.setName("周大亨");
author.setAge(89);
System.out.println("author: "+author.toString());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//对私有的方法进行反射
public static void reflectPrivateConstructor(){
try {
Class<?> authorclass =Class.forName(path_reflectfrom);
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor =authorclass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object object=declaredConstructor.newInstance("lida",88);
Author author=(Author) object;
System.out.println( "Author: "+author.toString());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//反射私有的属性
public static void reflectPrivateField(){
try {
Class<?> authorclass =Class.forName(path_reflectfrom);
Object authorobject=authorclass.newInstance();
Field field=authorclass.getDeclaredField("TAG");
field.setAccessible(true);
String tag=(String)field.get(authorobject);
System.out.println( "private field Tag:"+tag);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//反射获取私有的方法
private static void reflectMethod(){
try {
Class<?> authorclass=Class.forName(path_reflectfrom);
Object authorobject=authorclass.newInstance();
Method authormethod=authorclass.getDeclaredMethod("pMethod", String.class);
authormethod.setAccessible(true);
String string=(String)authormethod.invoke(authorobject, TAG);
System.out.println( "private Method: "+string);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
```
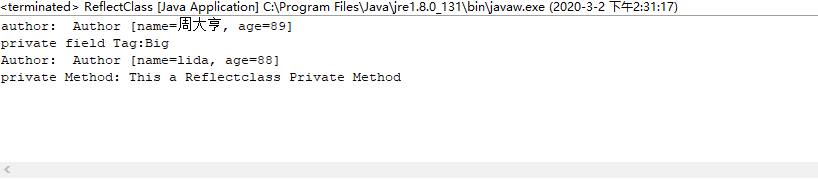
通过控制台打印以上信息:查看运用结果
```
ReflectClass.reflectNewInstance();
ReflectClass.reflectPrivateField();
ReflectClass.reflectPrivateConstructor();
ReflectClass.reflectMethod();
```
运行结果:
###泛型的运用###
对于泛型其实很好理解,通俗点讲就是我们将类型也当成了参数进行传值,这样做代码的安全性很大的被提升了,也为较大的优化带来可能。泛型可以使编译器知道一个对象的限定类型是什么,这样编译器就可以在一个高的程度上验证这个类型消除了强制类型转换 使得代码可读性好,减少了很多出错的机会。但是也要记住泛型的规范,比如静态的变量和方法不能引用泛型变量,我们也不能利用instanceof等方法对泛型的类型进行判断,当然这样做也毫无意义,重要的一点是泛型类不能继承Exception或者Throwable。泛型的继承中,不论子类是否为泛型类,所继承和实现的父类接口都有被指定。
常用的泛型类型变量:
E:元素(Element)
K:关键字(Key)
N:数字(Number)
T:类型(Type)
V:值(Value)
另外泛型界定的概念主要是指对泛型类型进行一个限定。比如:`public static T add(T str1, T str2) { return "";}`
###利用泛型和反射实现对json数据的保存###
```
//利用反射获取json数据到java类
private static void getJson(){
try {
String json = "{\"name\":\"Miss王\",\"age\":79}";
JSONObject source=JSONObject.parseObject(json);
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("bean.Author");
Object obj = aClass.newInstance();
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(source.getString(field.getName()));
if (field.getGenericType().toString().equals(String.class.toString())) {
field.set(obj, source.getString(field.getName()));
} else if (field.getGenericType().toString().equals(int.class.toString())) {
field.set(obj, source.getInteger(field.getName()));
}
}
Author author = (Author) obj;
System.out.print(author);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
```
我们想把以上的实现封装起来,这时就用了泛型。
```
//泛型+反射实现json数据读取到java类
public static T getJsonClass(String json, Class beanclass) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(json);
Object obj = beanclass.newInstance();
//拿到所以元素
Field[] declaredFields = beanclass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.getGenericType().toString().equals(String.class.toString())) {
String value=jsonObject.getString(field.getName());
if(value!=null){
field.set(obj,value);
System.out.println(value);
}
} else if (field.getGenericType().toString().equals(int.class.toString())) {
if(jsonObject.getInteger(field.getName())!=null)
field.set(obj,jsonObject.getInteger(field.getName()));
}
}
return (T) obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
```
调用实现:
```
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String json = "{\"name\":\"李先生\",\"age\":82}";
//ReflectJson.getJson();
//解析json然后换成实体类
Author author=getJsonClass(json, Author.class);
System.out.print( author.toString());
}
```
运行结果:


加载全部内容