IDEA Postfix Completion IDEA巧用Postfix Completion让码速起飞(小技巧)
白菜Java自习室 人气:01. 情景展示
自从做 Java 开发之后,IDEA 编辑器是不可少的。 在 IDEA 编辑器中,有很多高效的代码补全功能,尤其是 Postfix Completion 功能,可以让编写代码更加的流畅。
Postfix completion 本质上也是代码补全,它比 Live Templates 在使用上更加流畅一些,我们可以看一下下面的这张图。
2. 设置界面
可以通过如下的方法打开 Postfix 的设置界面,并开启 Postfix。

3. 常用的 Postfix 模板
3.1. boolean 变量模板
!: Negates boolean expression
//before
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
m(b!);
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
m(!b);
}
}
if: Checks boolean expression to be 'true'
//before
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
b.if
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
if (b) {
}
}
}
else: Checks boolean expression to be 'false'.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
b.else
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
if (!b) {
}
}
}
3.2. array 变量模板
for: Iterates over enumerable collection.
//before
public class Foo {
void m() {
int[] values = {1, 2, 3};
values.for
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m() {
int[] values = {1, 2, 3};
for (int value : values) {
}
}
}
fori: Iterates with index over collection.
//before
public class Foo {
void m() {
int foo = 100;
foo.fori
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m() {
int foo = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < foo; i++) {
}
}
}
3.3. 基本类型模板
opt: Creates Optional object.
//before
public void m(int intValue, double doubleValue, long longValue, Object objValue) {
intValue.opt
doubleValue.opt
longValue.opt
objValue.opt
}
//after
public void m(int intValue, double doubleValue, long longValue, Object objValue) {
OptionalInt.of(intValue)
OptionalDouble.of(doubleValue)
OptionalLong.of(longValue)
Optional.ofNullable(objValue)
}
sout: Creates System.out.println call.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
b.sout
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(boolean b) {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
3.4. Object 模板
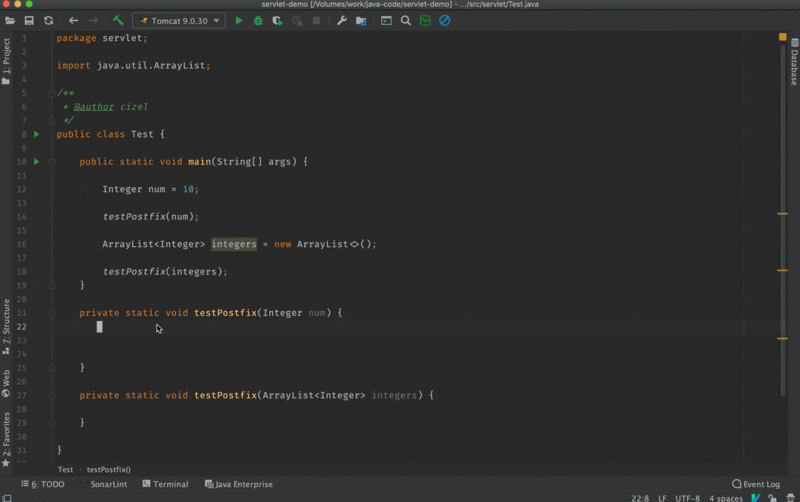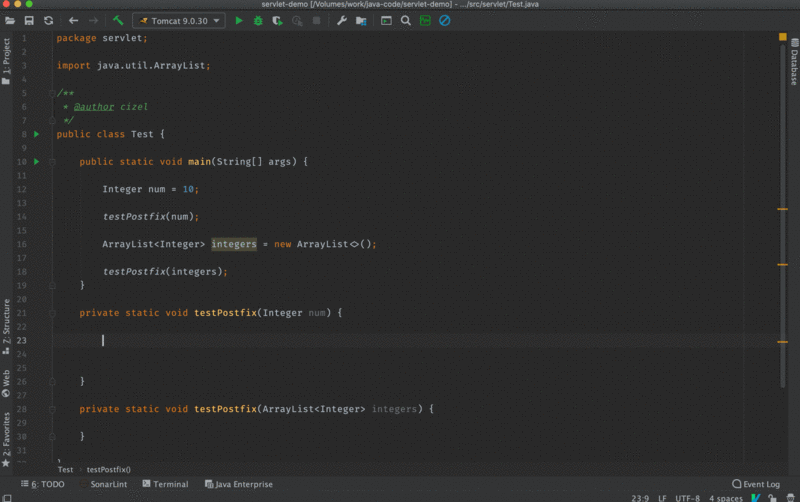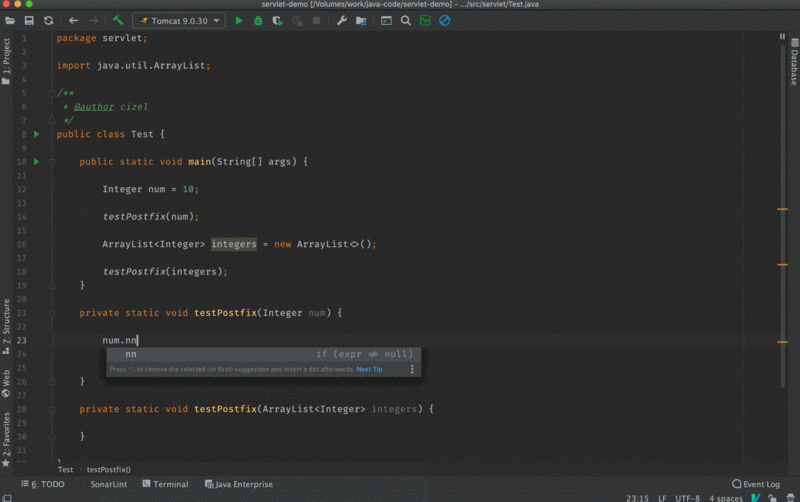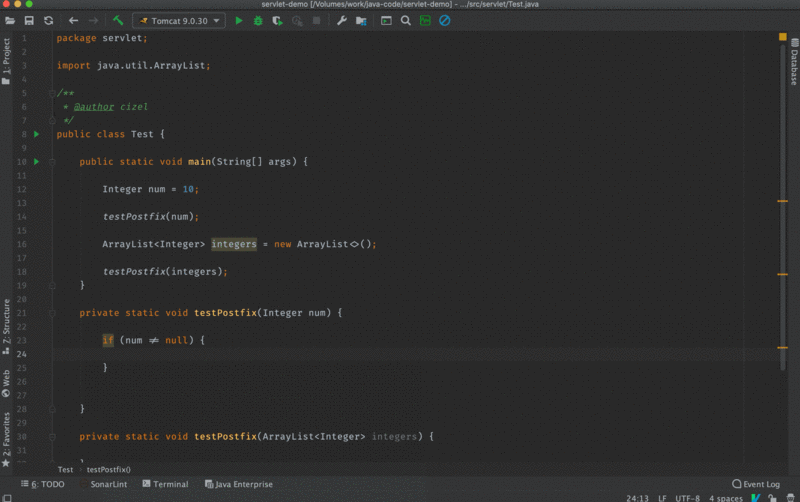
nn: Checks expression to be not-null.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
o.nn
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
if (o != null){
}
}
}
null: Checks expression to be null.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
o.null
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
if (o != null){
}
}
}
notnull: Checks expression to be not-null.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
o.notnull
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
if (o != null){
}
}
}
val: Introduces variable for expression.
//before
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
o instanceof String.var
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
void m(Object o) {
boolean foo = o instanceof String;
}
}
3.5. 其他模板
new: Inserts new call for the class.
//before Foo.new //after new Foo()
return: Returns value from containing method.
//before
public class Foo {
String m() {
"result".return
}
}
//after
public class Foo {
String m() {
return "result";
}
}
加载全部内容