注解开发SpringMVC 使用注解开发SpringMVC详细配置教程
Baret H ~ 人气:01、使用注解开发SpringMVC
1、新建一个普通的maven项目,添加web支持
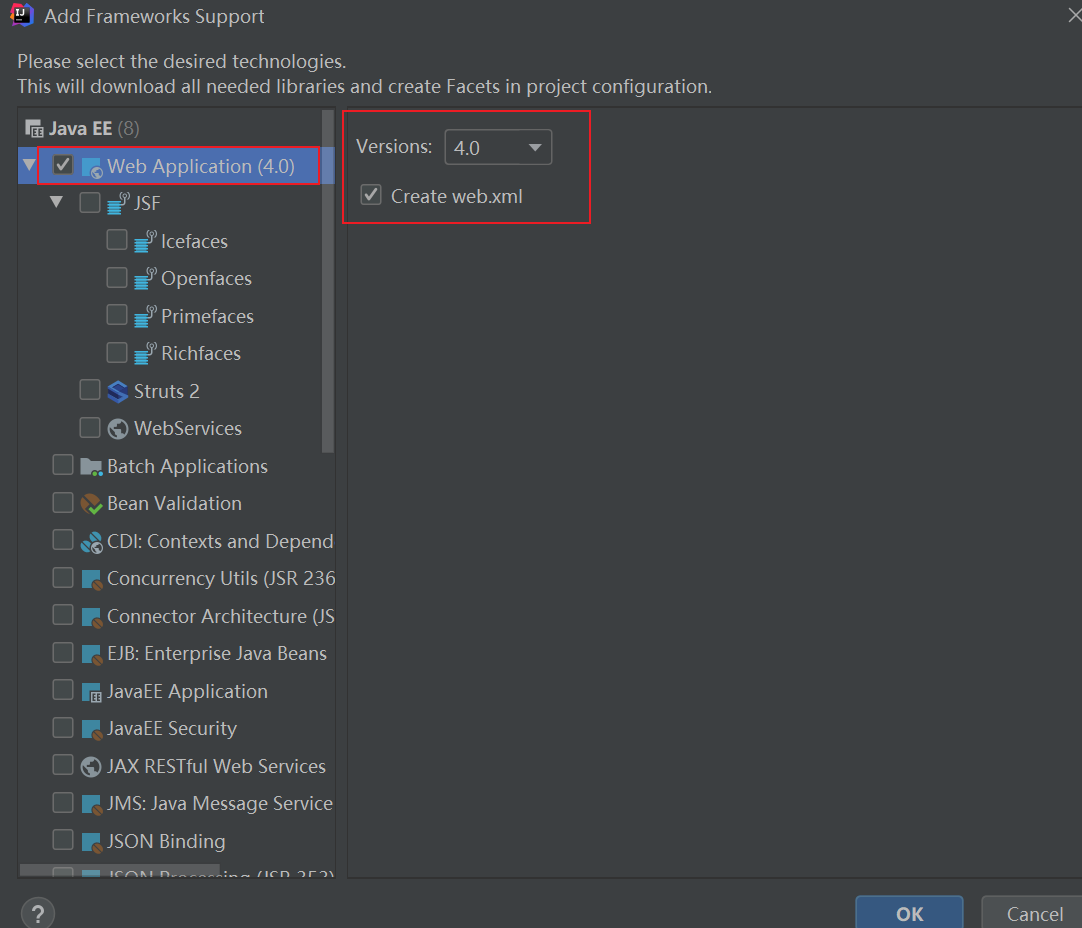
2、在pom.xml中导入相关依赖
SpringMVC相关
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
Servlet
<dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> </dependency>
jsp
<dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.2 </version> </dependency>
为了防止资源导出失败,我们加入以下代码
<!--在build中配置resources,防止我们资源导出失败的问题--> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>true</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>true</filtering> </resource> </resources> </build>
3、配置web.xml
注意web.xml的版本要为最新版
注册DispatcherServlet
- 需要绑定一个SpringMVC配置文件,下一步我们将创建
- 设置启动级别为1
- 设置映射路径为
/
<!--1.注册DispatcherServlet--> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!--关联一个springmvc的配置文件:【servlet-name】-servlet.xml--> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!--启动级别-1--> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!--/ 匹配所有的请求;(不包括.jsp)--> <!--/* 匹配所有的请求;(包括.jsp)--> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
4、编写SpringMVC配置文件
上述
DispatcherServlet绑定该配置文件,主要配置以下几个部分:
1. 自动扫描包
让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理
<context:component-scan base-package="controller"/>
2. 过滤静态资源
它会像一个检查员,对进入DispatcherServlet的URL进行筛查,如果发现是静态资源的请求,就将该请求转由Web应用服务器默认的Servlet处理,如果不是静态资源的请求,才由DispatcherServlet继续处理。
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>

3. 支持mvc注解驱动
在Spring中一般用
@RequestMapping注解来完成映射关系
为了使其生效, 必须向上下文中注册两个实例:
- DefaultAnnotationHandLerMapping(处理器映射器)
- AnnotationMethodHandLerAdapter(处理器适配器)
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入
4. 视图解析器
<!--视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!--后缀--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean>
完整代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!--自动扫描包,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理--> <context:component-scan base-package="controller"/> <!--过滤静态资源,让SpringMVC不处理静态资源 .css .js .mp3 .mp4 .html--> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!-- 支持mvc注解驱动 在spring中一般用@RequestMapping注解完成映射关系 要想使@RequestMapping注解生效 必须向上下文中注册DefaultAnnotationHandLerMapping(处理器映射器) 和一个AnnotationMethodHandLerAdapter(处理器适配器)实例 这两个实例分别在类级别和方法级别处理 annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!--视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!--后缀--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans>
SpringMVC必须配置的三大件
- 处理器映射器
- 处理器适配器
- 视图解析器
当我们用注解实现时,只需要手动配置视图解析器,另外两个只需要开启注解驱动即可,省去了大量xml片段
5、创建controller
在src/main/java目录下新建controller包,在其中新建HelloController.java
package controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
//封装数据
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVCAnnotation");
return "hello";//会被视图解析器处理
}
}
- @Controller是为了让SpringIOC容器初始化时自动扫描到该类
- @RequestMapping是为了映射请求路径,直接再其中设置路径名即可,这里为\hello
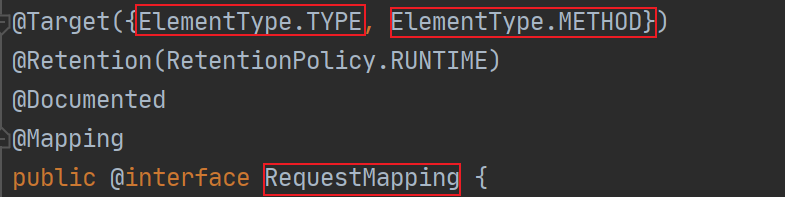
可以在类上使用,也可以直接在方法上使用,同时使用时,在类上使用相当于父路径
- 方法声明中的Model参数是用于向视图中封装数据
- 方法返回的结果是视图的名称,这里为hello,加上配置文件中的前后缀变成WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp
6、创建视图层
编写要请求的jsp页面,这里显示上述存入视图的参数
在web/WEB-INF/下新建jsp包,在其中新建hello.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${msg}
</body>
</html>
7、在项目结构中添加lib目录
该步骤是为了防止最终出现404错误,这是IDEA自己的问题
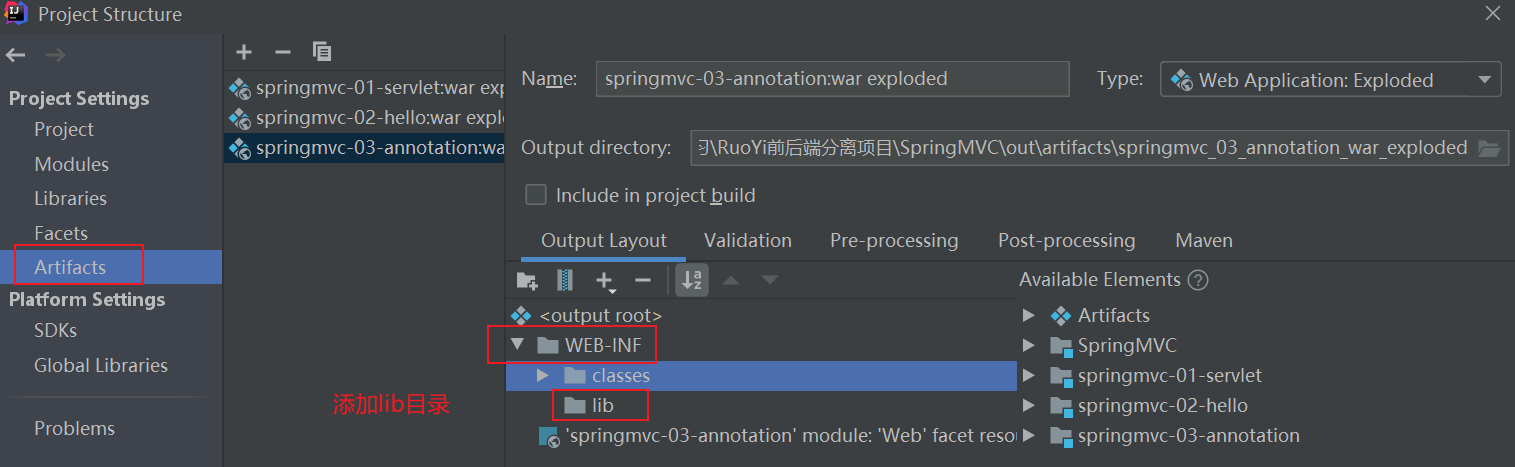
选中所有的包,导入
8、配置Tomcat运行测试
运行测试,访问http://localhost:8080/hello,成功访问
2、控制器Controller
- 控制器复杂提供访问应用程序的形为,通常通过接口定义或者注解定义两种方式实现
- 控制器负责解析用户请求并将其转换为一个模型
- 在SpringMVC中一个控制器类可以包含多个方法
- 在SpringMVC中,对于Controller的配置方式有很多种
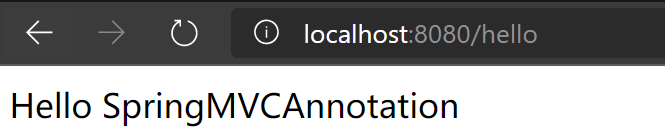
1. 实现Controller接口
Controller是一个接口,在org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc包下,接口中只有一个方法;
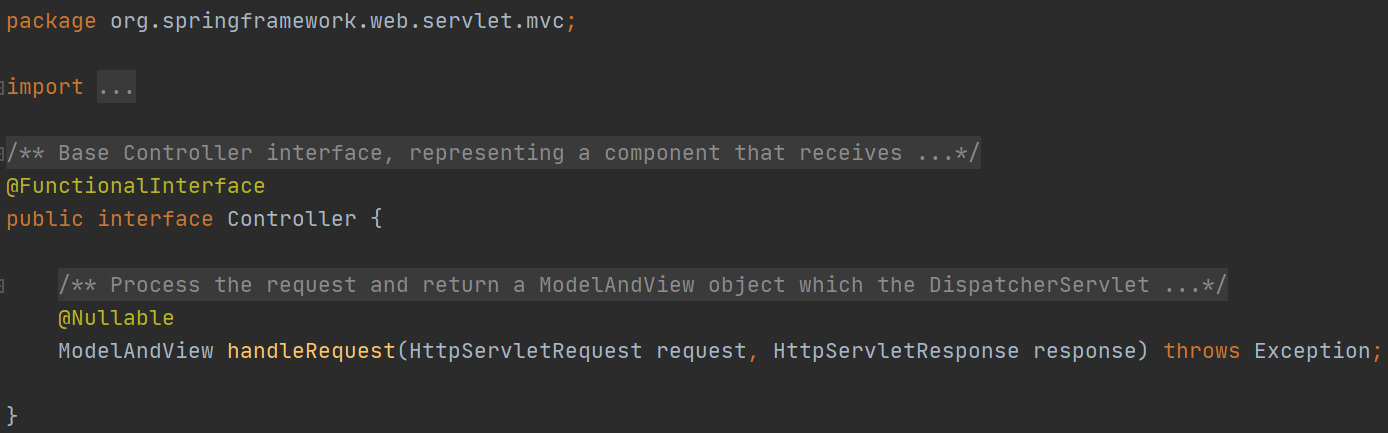
接下来的操作代码基于上一篇博客第一个SpringMVC程序
我们删除springmvc-servlet配置文件中处理映射器和处理适配器的配置,只留下一个视图解析器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!--后缀--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> <!--Handler--> <bean id="/hello" class="controller.HelloController"/> </beans>
然后配置Tomcat运行测试,同样访问http://localhost:8080/hello
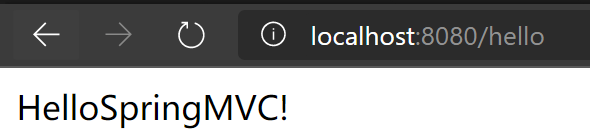
发现也可以成功运行,我们先前之所以写上处理映射器和处理适配器的配置,是为了了解其执行原理,显示调用,真实开发中,不需要配置,SpringMVC已经帮我们配置好了的
缺点:
一个控制器中只有一个方法,如果要多个方法则需要定义多个Controller,比较麻烦;2. 使用注解@Controller
@Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器,这是我们最长使用的方式
Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
<context:component-scan base-package="controller"/>
例如上述类:
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
//封装数据
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVCAnnotation");
return "hello";//会被视图解析器处理
}
}
被这个注解的类中的所有方法,如果返间值是String,并且有具体页面可以跳转,那么就会被视图解析器解折
例如我们在其中增加一个方法,同样返回hello视图
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
//封装数据
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVCAnnotation");
return "hello";//会被视图解析器处理
}
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg","This is the second request");
return "hello";
}
}
再次配置Tomcat运行测试,首先访问http://localhost:8080/hello
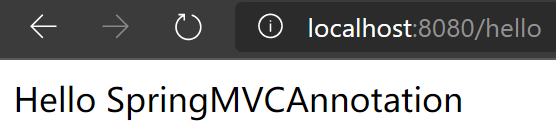
再访问http://localhost:8080/hello2
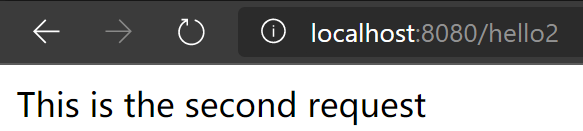
可以发现,我们的两个请求都可以指向一个视图,但是页面结果的结果是不一样的,从这里可以看出视图是被复用的,而控制器与视图之间是弱偶合关系。
3、@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping注解用于映射url到控制器或一个特定的处理程序方法,可用于类或方法上
用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径
我们修改上述方法,在类上增加该注解
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/h")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
//封装数据
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVCAnnotation");
return "hello";//会被视图解析器处理
}
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg","This is the second request");
return "hello";
}
}
然后配置Tomcat运行测试,我们再输入http://localhost:8080/hello,
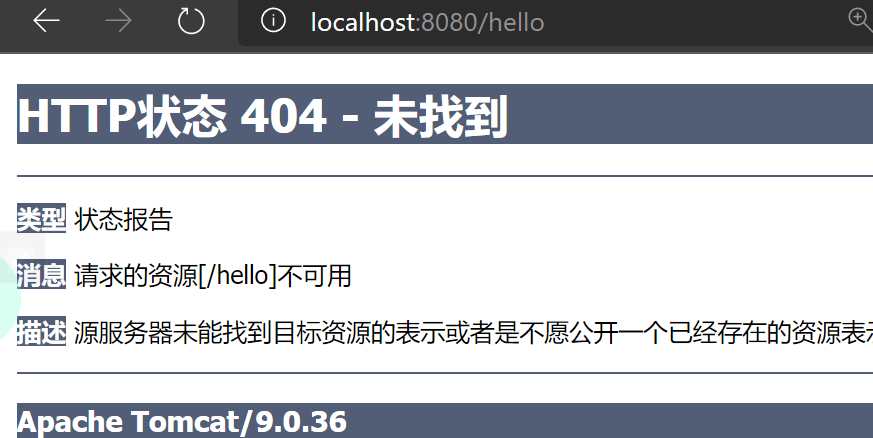
直接404找不到报错了,这是因为我们在类上添加该注解,相当于一个父路径
再次访问http://localhost:8080/h/hello,成功!
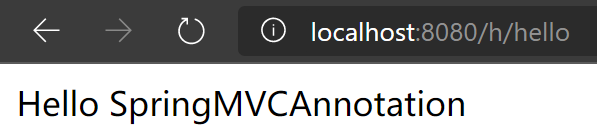
总结
加载全部内容