实战_Spring_Cloud
Lancel0t 人气:1目录
- 前言
- 开发环境
- 源码地址
- 创建工程
- 服务注册中心(Eureka)
- Eureka Server
- Eureka Client
- 注册中心高可用
- 小结
- 负载均衡(Ribbon)
- RestTemplate调用
- 负载均衡调用
- 应用名称调用
- 小结
- 声明式服务调用(Feign)
- 服务端实现
- 客户端实现
- 小结
- 统一配置中心(Config)
- Config Server
- 向服务中心注册
- 服务提供端改造
- 配置动态刷新
- 配置 Webhook
- 小结
- 异步消息(Stream)
- 应用场景
- 当前项目场景
- stream-rabbit集成
- 改造Order和Product项目
- 小结
- 微服务网关(Zuul)
- 工作原理
- 添加网关
- 自定义路由
- Cookie与头信息
- 动态路由
- 自定义Filter
- 限流
- 小结
- 服务容错(Hystrix)
- 设计原则
- 如何实现
- 触发降级
- 超时设置
- 熔断机制
- 可视化组件
- 小结
- 服务追踪(Sleuth)
- OpenTracing
- 链路追踪
- Zipkin
- 小结
- 容器化部署
- 安装Docker
- 安装Docker-Compose
- Eureka部署
- MySQL部署
- RabbitMQ
- OpenZipkin
- 编排镜像
前言
开发环境
部署环境:阿里云ECS服务器
- 操作系统:CentOS 7.7 64位
- IDEA 版本:2019.3.1
- docker 版本:1.13.1
- docker-compose版本:1.25.0
- spring cloud 版本:Hoxton.SR1
- spring boot 版本:2.2.2.RELEASE
- mysql 版本:5.7
- redis 版本:5.0.7
- rabbitmq 版本:3.8.2-management
- zipkin 版本:2.19.2
端口映射信息:
eureka1:8761 | eureka2:8762
config-server:8888
shopping-product:11100
shopping-order:11110
api-gateway:8080
open-api:8081
源码地址
https://github.com/lizzie2008/spring-cloud-app.git
创建工程
- 新建一个工程:选择Spring Cloud Bootstrap,对应的Spring Boot 版本2.2.2。
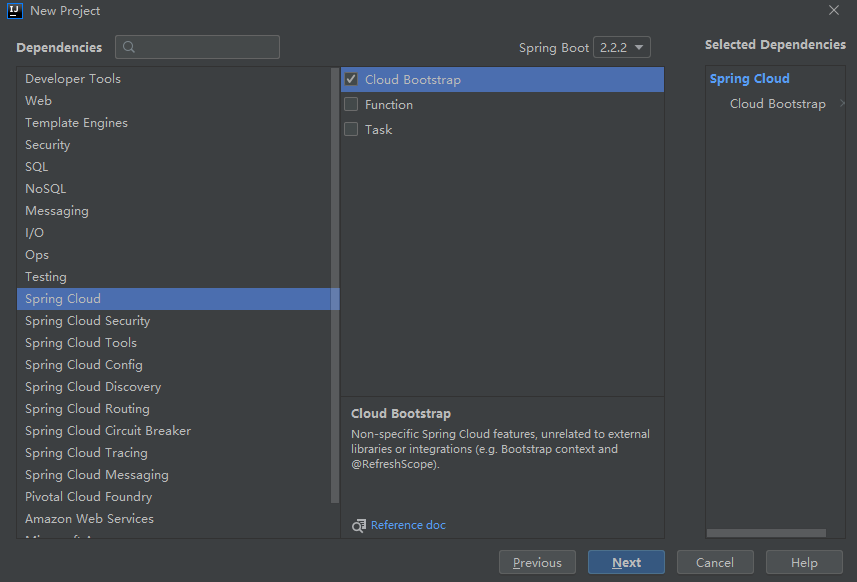
- 项目生成后,看到对应的Spring版本的依赖没有问题。
- 因为是父工程,我们将打包格式改成pom,并把src等无用的文件删除。
<groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-app</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-cloud-app</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Cloud<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/description>
<packaging>pom</packaging>服务注册中心(Eureka)
Eureka Server
- 新建Module->选择Eureka Server
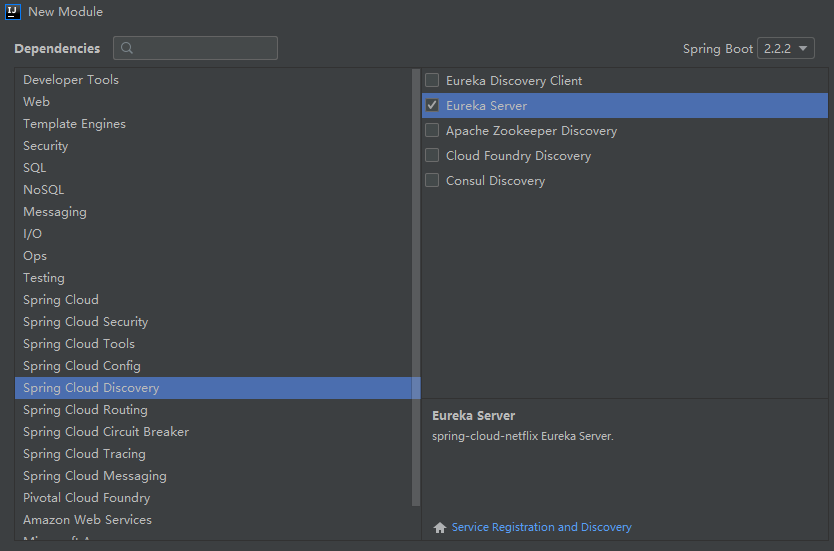
因为Module作为子项目,我们改写下对应的POM文件。
<parent> <groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-app</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId> <artifactId>eureka-server</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>eureka-server</name> <description>Registry Center<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/description> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> <https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency> <https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependencies>重新Build一下项目,能正常编译。但是此时Eureka Server是不能正常启动工作的,需要在application类增加
@EnableEurekaServer。
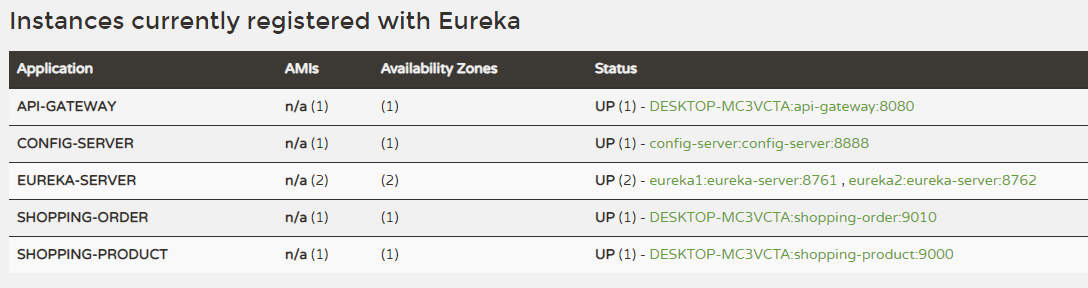
此时,我们再运行Eureka Server,发现可以正常启动服务注册服务器,服务端口8080,注册地址:http://localhost:8761/eureka/。
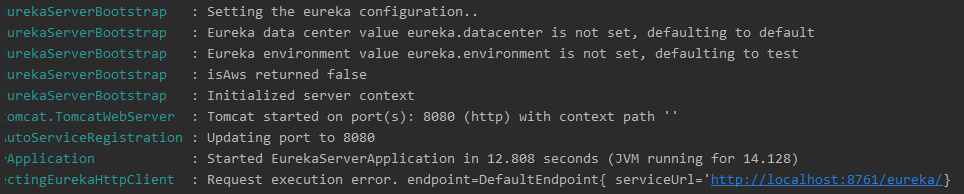
- 打开浏览器,访问8080端口,查看可视化管理界面。
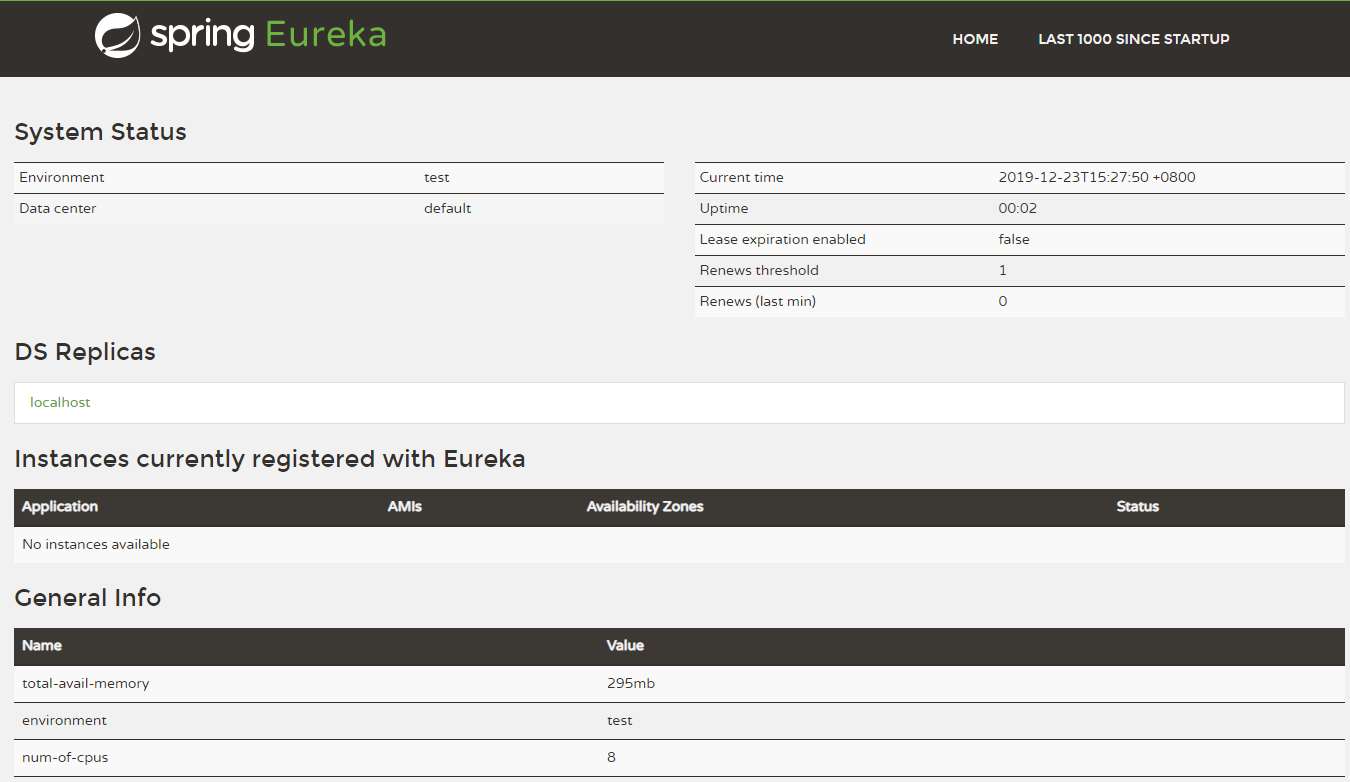
- 当然,我们没有做任何配置,并且控制台一直报错,这是因为默认情况下,本身也是需要获取注册信息和注册到注册中心,而此时找不到对应服务器。我们可以修改配置文件,做相应的配置。调整服务端口为8761,重新启动后,发现不再报错。
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: false #设置不从注册中心获取注册信息
register-with-eureka: false #设置自身不作为客户端注册到注册中心
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server #应用名称
server:
port: 8761 #应用服务端口Eureka Client
- 我们再建一个Module工程,作为服务客户端,向Eureka Server服务中心注册。
同样,我们修改POM文件,依赖于父项目,注意这里需要引入
eureka-client和spring-boot-starter-web依赖。<parent> <groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-app</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId> <artifactId>shopping-provider</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>shopping-provider</name> <description>shopping service provider<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/description> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> <https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency> <https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependencies>需要在application类增加
@EnableDiscoveryClient,同时修改配置文件。eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址 spring: application: name: shopping-provider #应用名称重启Eureka Client,启动后再次访问Eureka Server管理界面,可以发现order-provider服务已注册。
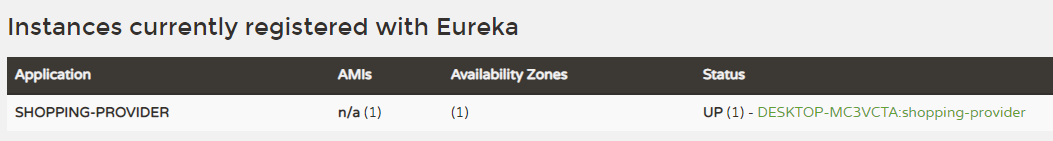
注册中心高可用
之前我们的Eureka Server是单点服务,实际生产中,经常是多台注册中心,因此我们尝试下配置2台注册中心。
启动服务器实例1:
eureka: client: # fetch-registry: false #设置不从注册中心获取注册信息 # register-with-eureka: false #设置自身不作为客户端注册到注册中心 defaultZone: http://localhost:8762/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址 spring: application: name: eureka-server1 #应用名称 server: port: 8761 #应用服务端口启动服务器实例2:
eureka: client: # fetch-registry: false #设置不从注册中心获取注册信息 # register-with-eureka: false #设置自身不作为客户端注册到注册中心 defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址 spring: application: name: eureka-server2 #应用名称 server: port: 8762 #应用服务端口重启2台注册中心,启动后分别访问2台的管理界面,可以看到2台注册中心已经相互注册。
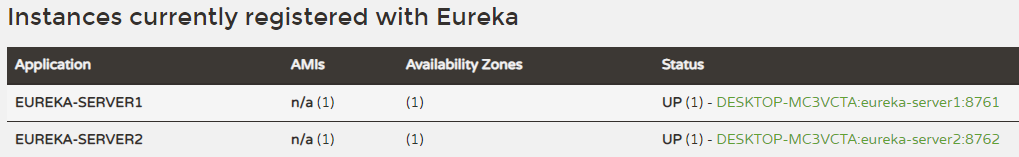
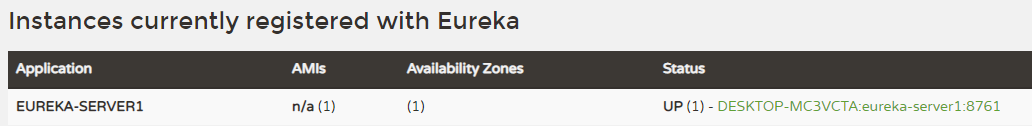
小结
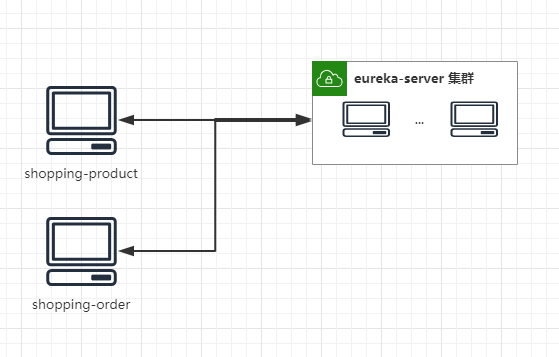
项目增加2个服务模块,并向Eureka Server注册:shopping-product(商品服务)、shopping-order(订单服务),实现相应业务逻辑,这部分详细实现不再阐述。
整体项目结构如下:
spring-cloud-app
--eureka-server(服务注册中心)
--shopping-common(购物公共模块)
--shopping-product(商品服务模块)
--shopping-order(订单服务模块)
系统架构如图,比较简单,一个集群服务中心,目前有2个服务提供并注册:
负载均衡(Ribbon)
Spring Cloud Ribbon 是一个客户端的负载均衡器,它提供对大量的HTTP和TCP客户端的访问控制。
客户端负载均衡即是当浏览器向后台发出请求的时候,客户端会向 Eureka Server 读取注册到服务器的可用服务信息列表,然后根据设定的负载均衡策略(没有设置即用默认的),抉择出向哪台服务器发送请求。
假设有以下业务场景,shopping-order模块需要调用shopping-product提供的API接口。我们看如何实现。
RestTemplate调用
第一种方法使用构造RestTemplate,调用远程API,这种方法url是写死,如果启动多台shopping-product服务的话,那又该如何?
@Test
void getProductByRestTemplate() {
//1.第一种方法
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String response = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:11100/api/products", String.class);
Assert.hasLength(response,"未获取内容");
}负载均衡调用
第二种方法:我们启动2个shopping-product服务实例,分别是11100端口和9001端口,运行测试发现,会根据loadBalancerClient负载均衡机制帮我们选择一个服务地址,进行访问调用。
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
@Test
void getProductByLoadBalance(){
//2.第二种方法,先获取负载均衡的地址再调用API
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose("shopping-product");
String url=String.format("http://%s:%s/api/products",instance.getHost(),instance.getPort());
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String response = restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
log.info("port:"+instance.getPort()+response);
}应用名称调用
但这样依旧很是麻烦,接下来看第三种方法。第三种方法屏蔽了API的具体url信息,只用ServerId,并根据负载均衡规则,自动路由到对应的地址。
因为eureka包中已经添加了对Ribbon的依赖,我们可以增加断点,调试程序,发现进入RibbonLoadBalancerClient-->choose方法,返回负载均衡策略选择的ServiceInstance。
@Component
public class RestTemplateConfiguration {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class OrderServiceTest {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void getProductByServerId() {
String response = restTemplate.getForObject("http://shopping-product/api/products", String.class);
log.info(response);
}
}当然,我们也可以指定应用服务的负载均衡策略:
shopping-order:
ribbon:
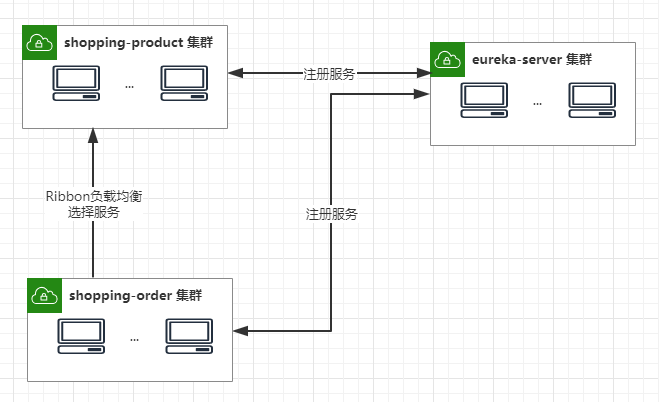
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule小结
目前系统架构如图,实现shopping-product和shopping-order集群化部署,调用方式通过客户端负载均衡,来路由消费端的请求。
声明式服务调用(Feign)
Feign是一个声明式的Web Service客户端,它的目的就是让Web Service调用更加简单。Feign提供了HTTP请求的模板,通过编写简单的接口和插入注解,就可以定义好HTTP请求的参数、格式、地址等信息。
而Feign则会完全代理HTTP请求,我们只需要像调用方法一样调用它就可以完成服务请求及相关处理。Feign整合了Ribbon和Hystrix(关于Hystrix我们后面再讲),可以让我们不再需要显式地使用这两个组件。
总起来说,Feign具有如下特性:
- 可插拔的注解支持,包括Feign注解和JAX-RS注解;
- 支持可插拔的HTTP编码器和解码器;
- 支持Hystrix和它的Fallback;
- 支持Ribbon的负载均衡;
- 支持HTTP请求和响应的压缩。
服务端实现
shopping-product服务提供端暴露API。
@GetMapping("/productInfos")
public List<ProductInfoOutput> findProductInfosByIds(@RequestParam(required = false) String productIds) throws Exception {
//如果传入商品id参数
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(productIds)) {
List<String> ids = Arrays.asList(productIds.split(","));
List<ProductInfo> productInfos = productService.findProductInfosByIds(ids);
List<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputs = ListUtils.copyProperties(productInfos, ProductInfoOutput.class);
return productInfoOutputs;
}else{
List<ProductInfo> productInfos = productService.findProductInfos();
List<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputs = ListUtils.copyProperties(productInfos, ProductInfoOutput.class);
return productInfoOutputs;
}
}客户端实现
- 引入Feign
shopping-order模块需要调用shopping-product接口,首先我们在服务调用端增加Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>启动类标注开启Feign服务
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class ShoppingOrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ShoppingOrderApplication.class,args);
}
}- 创建声明式服务
/**
* 声明式服务
*/
@FeignClient("shopping-product/api/v1")
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/productInfos")
List<ProductInfoOutput> findProductInfosByIds(@RequestParam(required = false) String productIds);
}@FeignClient(“服务名称”)映射服务调用,本质还是http请求,只不过Feign帮我们屏蔽了底层的请求路由,对开发者完全透明,使得调用远程服务感觉跟调用本地服务一致的编码体验。
本地调用测试,可以正常返回接口数据。
@GetMapping("/orders/findProductInfosByIds")
public List<ProductInfoOutput> findProductInfosByIds(){
List<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputs = productClient
.findProductInfosByIds("157875196366160022, 157875227953464068");
return productInfoOutputs;
}小结
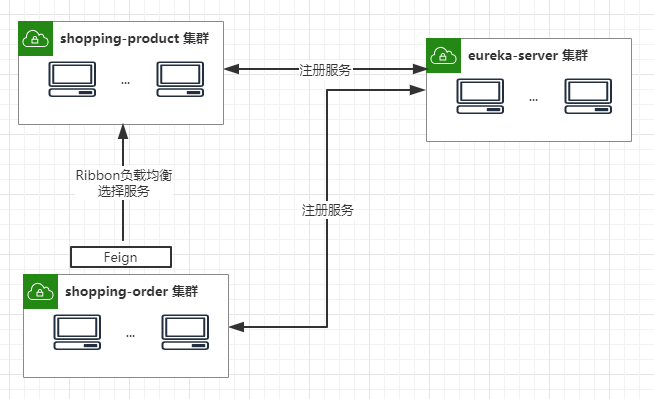
在实现负载均衡基础上,封装声明式服务调用。实现shopping-order对shopping-product的透明调用,系统架构如图如下。
统一配置中心(Config)
上个环境中,我们有2个服务提供者,首先看下各自的配置,可以发现很大一部分都是重复的。
如果微服务架构中没有使用统一配置中心时,所存在的问题:
- 配置文件分散在各个项目里,不方便维护
- 配置内容安全与权限,实际开发中,开发人员是不知道线上环境的配置的
- 更新配置后,项目需要重启
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址
spring:
application:
name: shopping-order #应用名称
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_cloud_app?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
jpa:
show-sql: true
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
server:
port: 11110对于一些简单的项目来说,我们一般都是直接把相关配置放在单独的配置文件中,以 properties 或者 yml 的格式出现,更省事儿的方式是直接放到 application.properties 或 application.yml 中。在集群部署情况下,我们尝试来实现配置的集中管理,并支持配置的动态刷新。
Config Server
- 我们新建一个Module工程,统一配置中心,保存所以的配置信息。
同样,我们作为子项目,修改相关依赖,加入对spring-cloud-config-server依赖
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>tech.lancelot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-app</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>config-server</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<!-- spring cloud config 服务端包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependencies>- application.properties进行如下配置
spring:
application:
name: config-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/lizzie2008/Central-Configuration.git #配置文件所在仓库
username: 'Github username'
password: 'Github password'
default-label: master #配置文件分支
search-paths: spring-cloud-app #配置文件所在根目录
server:
port: 8888- 在 Application 启动类上增加相关注解
@EnableConfigServer
@EnableConfigServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}- 启动服务,接下来测试一下。
Spring Cloud Config 有它的一套访问规则,我们通过这套规则在浏览器上直接访问就可以。
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties{application} 就是应用名称,对应到配置文件上来,就是配置文件的名称部分,例如我上面创建的配置文件。
{profile} 就是配置文件的版本,我们的项目有开发版本、测试环境版本、生产环境版本,对应到配置文件上来就是以 application-{profile}.yml 加以区分,例如application-dev.yml、application-sit.yml、application-prod.yml。
{label} 表示 git 分支,默认是 master 分支,如果项目是以分支做区分也是可以的,那就可以通过不同的 label 来控制访问不同的配置文件了。
我们在git项目中,新建spring-cloud-app/config-eureka-server.yml配置文件,然后访问配置中心服务器,看看能正常获取配置文件。
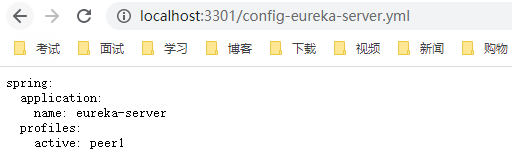
向服务中心注册
config-server本身作为一个服务,也可以作为服务提供方,向服务中心注册,其他的服务想要获取配置文件,只需要通过服务名称就会访问。
- 引入Eureka Client依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 启动类上增加
@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
@EnableConfigServer
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}- 配置文件中增加eureka注册。
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://eureka1:8761/eureka/,http://eureka2:8762/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址- 启动eureka-server,看看config-server是否注册成功。
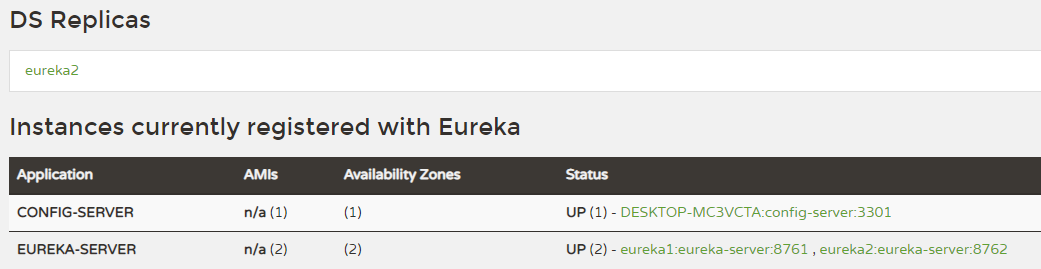
服务提供端改造
- shopping-product项目中,把原先的application.yml文件重命名为bootstrap.yml,并配置Eureka Server地址、应用名称、Config的实例名称。服务启动后,会链接Eureka Server服务器,根据Config的实例名称找到对应的Config服务器,并根据实例名称(可以增加profile属性)来匹配配置文件。
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://eureka1:8761/eureka/,http://eureka2:8762/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址
spring:
application:
name: shopping-product #应用名称
cloud:
config:
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: config-server- 之前服务端其余的配置,填写在github配置项目shopping-product.yml文件中
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_cloud_app?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
jpa:
show-sql: true
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
server:
port: 11100- 同样,shopping-order项目也如此改造,最后我们启动所有的服务,看是否都能正常启动。
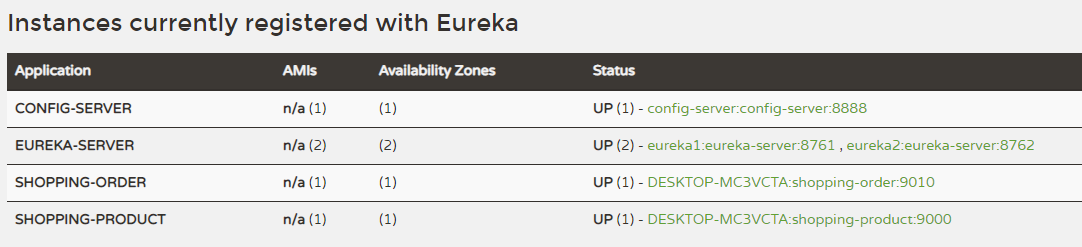
配置动态刷新
- 首先,在
shopping-product.yml增加一个配置属性来进行测试
env: dev- 新建一个测试controller来绑定这个配置属性,并提供api来返回属性的值
@RestController
@RefreshScope
@RequestMapping("api/env")
public class EnvController {
@Value("${env}")
private String env;
@RequestMapping
public String printEnv() {
return env;
}
}访问http://localhost:11100/api/env,返回当前的值dev。
Spring Cloud Config 在项目启动时加载配置内容这一机制,但是如果我们修改配置文件内容后,不会自动刷新。例如我们上面的项目,当服务已经启动的时候,去修改 github 上的配置文件内容,这时候,再次刷新页面,对不起,还是旧的配置内容,新内容不会主动刷新过来。那应该怎么去触发配置信息的动态刷新呢?
它提供了一个刷新机制,但是需要我们主动触发。那就是 @RefreshScope 注解并结合 actuator ,注意要引入 spring-boot-starter-actuator 包。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- EnvController上增加
@RefreshScope注解 - 发送 POST 请求到 http://localhost:11100/actuator/refresh 这个接口,默认没有开放endpoint的权限,所以这块我们首先配置开放权限
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"- 这时调用接口结束后,我们看到接口返回消息,表明env这个属性值已经刷新
[
"config.client.version",
"env"
]- 再次访问http://localhost:11100/api/env,返回当前的值就是修改后的值test,证明配置属性的值已经动态刷新,我们的程序也不用再次启动。
配置 Webhook
每次改了配置后,就用 postman 访问一下 refresh 接口,还是不够方便。 github 提供了一种 webhook 的方式,当有代码变更的时候,会调用我们设置的地址,来实现我们想达到的目的。
- 进入 github 仓库配置页面,选择 Webhooks ,并点击 add webhook;
填上回调的地址
也就是上面提到的 actuator/refresh 这个地址,但是必须保证这个地址是可以被 github 访问到的。这样每当github上修改了配置文件,就自动通知对应的hook地址自动刷新。
小结
整体项目结构如下:
spring-cloud-app
--config-server(统一配置中心)
--eureka-server(服务注册中心)
--shopping-common(购物公共模块)
--shopping-product(商品服务模块)
--shopping-order(订单服务模块)
更新系统架构,新建config-server节点,也向eureka-server注册,相关服务注册节点根据配置实例名称,路由到config-server节点,动态的加载配置。
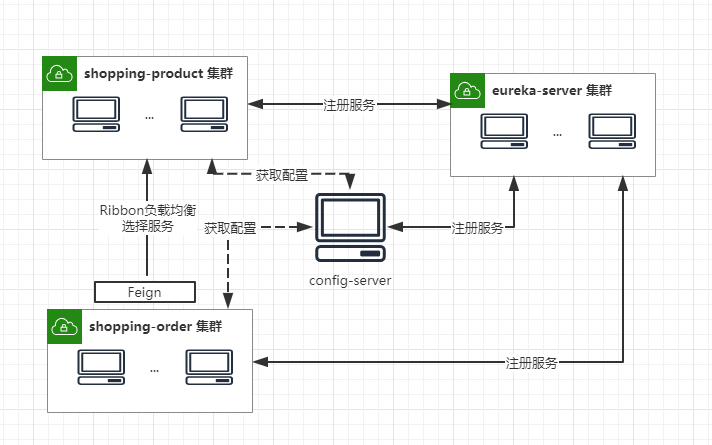
异步消息(Stream)
应用场景
1、异步处理
比如用户在电商网站下单,下单完成后会给用户推送短信或邮件,发短信和邮件的过程就可以异步完成。因为下单付款是核心业务,发邮件和短信并不属于核心功能,并且可能耗时较长,所以针对这种业务场景可以选择先放到消息队列中,有其他服务来异步处理。
2、应用解耦:
假设公司有几个不同的系统,各系统在某些业务有联动关系,比如 A 系统完成了某些操作,需要触发 B 系统及 C 系统。如果 A 系统完成操作,主动调用 B 系统的接口或 C 系统的接口,可以完成功能,但是各个系统之间就产生了耦合。用消息中间件就可以完成解耦,当 A 系统完成操作将数据放进消息队列,B 和 C 系统去订阅消息就可以了。这样各系统只要约定好消息的格式就好了。
3、流量削峰
比如秒杀活动,一下子进来好多请求,有的服务可能承受不住瞬时高并发而崩溃,所以针对这种瞬时高并发的场景,在中间加一层消息队列,把请求先入队列,然后再把队列中的请求平滑的推送给服务,或者让服务去队列拉取。
4、日志处理
kafka 最开始就是专门为了处理日志产生的。
当碰到上面的几种情况的时候,就要考虑用消息队列了。如果你碰巧使用的是 RabbitMQ 或者 kafka ,而且同样也是在使用 Spring Cloud ,那可以考虑下用 Spring Cloud Stream。Spring Cloud Stream 是消息中间件组件,它集成了 kafka 和 rabbitmq ,本文以rabbitmq 为例。
当前项目场景
分析目前shopping-order项目中,创建订单的代码如下:
/**
* 创建订单
*
*/
@Transactional
public String Create(OrderInput orderInput) throws Exception {
//扣库存
ResultVo result1=productClient.decreaseStock(orderInput.getOrderItemInputs());
if (result1.getCode() != 0)
throw new Exception("调用订单扣减库存接口出错:" + result1.getMsg());
//构建订单主表
OrderMaster orderMaster = new OrderMaster();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderInput, orderMaster);
//指定默认值
orderMaster.setOrderId(KeyUtil.genUniqueKey("OM"));
orderMaster.setOrderStatus(OrderStatus.NEW);
orderMaster.setPayStatus(PayStatus.WAIT);
//构建订单明细
List<String> productIds = orderInput.getOrderItemInputs().stream().map(OrderItemInput::getProductId).collect(Collectors.toList());
ResultVo<List<ProductInfoOutput>> result2 = productClient.findProductInfosByIds(String.join(",", productIds));
if (result2.getCode() != 0)
throw new Exception("调用订单查询接口出错:" + result2.getMsg());
List<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputs = result2.getData();
//订单金额总计
BigDecimal total = new BigDecimal(BigInteger.ZERO);
for (OrderItemInput orderItemInput : orderInput.getOrderItemInputs()) {
OrderDetail orderDetail = new OrderDetail();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderItemInput, orderDetail);
Optional<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputOptional = productInfoOutputs.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getProductId().equals(orderItemInput.getProductId())).findFirst();
if (!productInfoOutputOptional.isPresent())
throw new Exception(String.format("商品【%s】不存在", orderItemInput.getProductId()));
ProductInfoOutput productInfoOutput = productInfoOutputOptional.get();
orderDetail.setDetailId(KeyUtil.genUniqueKey("OD"));
orderDetail.setOrderId(orderMaster.getOrderId());
orderDetail.setProductName(productInfoOutput.getProductName());
orderDetail.setProductPrice(productInfoOutput.getProductPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(orderDetail.getProductQuantity())));
orderDetail.setProductIcon(productInfoOutput.getProductIcon());
total = total.add(orderDetail.getProductPrice());
orderDetailRepository.save(orderDetail);
}
orderMaster.setOrderAmount(total);
orderMasterRepository.save(orderMaster);
return orderMaster.getOrderId();
}创建订单的同时,先调用商品接口扣减库存,如果占用库存成功,再生成订单。这样的话,生成订单的操作和占用商品库存的操作其实是耦合在一起的。在实际电商高并发、高流量的情况下,我们很少这么做。所以,我们要将业务解耦,实现订单和扣减库存的异步处理。
大体思路如下:生成订单==》通知商品调用库存==》商品占用库存==》通知订单占用成功==》更新订单占用库存状态
stream-rabbit集成
shopping-order、shopping-product项目中
- 首先引入stream-rabbit依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- application.yml中作相应的配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: aliyun.host
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest- 消息接口定义
public interface StreamClient {
String INPUT = "myMessage";
@Input(StreamClient.INPUT)
SubscribableChannel input();
@Output(StreamClient.INPUT)
MessageChannel output();
}- 接收端处理逻辑
@Component
@EnableBinding(StreamClient.class)
@Slf4j
public class StreamReceiver {
@StreamListener(value = StreamClient.INPUT)
public void process(OrderInput orderInput) {
log.info("StreamReceiver: {}", orderInput);
}
}- 发送端处理逻辑
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/v1/stream")
@Slf4j
public class StreamController {
private final StreamClient streamClient;
@Autowired
public StreamController(StreamClient streamClient) {
this.streamClient = streamClient;
}
@GetMapping("/sendMessage")
public void sendMessage() {
OrderInput orderInput=new OrderInput();
orderInput.setBuyerName("小王");
orderInput.setBuyerPhone("15011111111");
orderInput.setBuyerAddress("姥姥家");
orderInput.setBuyerOpenid("11111");
streamClient.output().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(orderInput).build());
}
}启动应用程序,测试发送接口,发现spring-cloud-stream帮我们自动创建了一个队列,消息发送到这个队列,然后被接收端消费。
此时,如果我们启动多个shopping-product服务实例,会有个问题,如果发送端发送一条消息,会被2个实例同时消费,在正常的业务中,这种情况是应该避免的。所以我们需要对消息进行分组,在application.yml中增加如下配置,保证只有一个服务实例来消费。
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: aliyun.host
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
myMessage:
group: shopping-order
content-type: application/json改造Order和Product项目
shopping-order作为库存占用命令的消息发送者,首先向shopping-product发送消息stock_apply(占用库存申请),shopping-product接收此消息进行库存处理,然后将库存占用处理的结果作为消息stock_result(占用库存结果)发送,shopping-order端再收到结果消息对订单状态进行更新。
- shopping-order配置:
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
stock_apply_output: #占用库存申请
destination: stock.apply
stock_result_input: #占用库存结果
destination: stock.result
group: shopping-order- shopping-product配置:
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
stock_apply_input: #占用库存申请
destination: stock.apply
group: shopping-product
stock_result_output: #占用库存结果
destination: stock.result- shopping-order定义channel
public interface OrderStream {
String STOCK_APPLY_OUTPUT = "stock_apply_output";
@Output(OrderStream.STOCK_APPLY_OUTPUT)
MessageChannel stockApplyOutput();
String STOCK_RESULT_INPUT = "stock_result_input";
@Input(OrderStream.STOCK_RESULT_INPUT)
SubscribableChannel stockResultInput();
}- shopping-product定义channel
public interface ProductStream {
String STOCK_APPLY_INPUT = "stock_apply_input";
@Input(ProductStream.STOCK_APPLY_INPUT)
SubscribableChannel stockApplyInput();
String STOCK_RESULT_OUTPUT = "stock_result_output";
@Output(ProductStream.STOCK_RESULT_OUTPUT)
MessageChannel stockResultOutput();
}
- shopping-order发送库存申请消息
/**
* 创建订单
*/
@Transactional
public String Create(OrderInput orderInput) throws Exception {
//构建订单主表
OrderMaster orderMaster = new OrderMaster();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderInput, orderMaster);
//指定默认值
orderMaster.setOrderId(KeyUtil.genUniqueKey("OM"));
orderMaster.setOrderStatus(OrderStatus.NEW);
orderMaster.setPayStatus(PayStatus.WAIT);
//构建订单明细
List<String> productIds = orderInput.getOrderItemInputs().stream().map(OrderItemInput::getProductId).collect(Collectors.toList());
ResultVo<List<ProductInfoOutput>> result2 = productClient.findProductInfosByIds(String.join(",", productIds));
if (result2.getCode() != 0)
throw new Exception("调用订单查询接口出错:" + result2.getMsg());
List<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputs = result2.getData();
//订单金额总计
BigDecimal total = new BigDecimal(BigInteger.ZERO);
for (OrderItemInput orderItemInput : orderInput.getOrderItemInputs()) {
OrderDetail orderDetail = new OrderDetail();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderItemInput, orderDetail);
Optional<ProductInfoOutput> productInfoOutputOptional = productInfoOutputs.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getProductId().equals(orderItemInput.getProductId())).findFirst();
if (!productInfoOutputOptional.isPresent())
throw new Exception(String.format("商品【%s】不存在", orderItemInput.getProductId()));
ProductInfoOutput productInfoOutput = productInfoOutputOptional.get();
orderDetail.setDetailId(KeyUtil.genUniqueKey("OD"));
orderDetail.setOrderId(orderMaster.getOrderId());
orderDetail.setProductName(productInfoOutput.getProductName());
orderDetail.setProductPrice(productInfoOutput.getProductPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(orderDetail.getProductQuantity())));
orderDetail.setProductIcon(productInfoOutput.getProductIcon());
total = total.add(orderDetail.getProductPrice());
orderDetailRepository.save(orderDetail);
}
orderMaster.setOrderAmount(total);
orderMasterRepository.save(orderMaster);
//扣库存
StockApplyInput stockApplyInput = new StockApplyInput();
stockApplyInput.setOrderId(orderMaster.getOrderId());
stockApplyInput.setOrderItemInputs(orderInput.getOrderItemInputs());
orderStream.stockApplyOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(stockApplyInput).build());
return orderMaster.getOrderId();
}- shopping-product处理库存申请消息,并发送库存处理结果
@Service
@Slf4j
@EnableBinding(ProductStream.class)
public class ProductService {
private final ProductInfoRepository productInfoRepository;
private final ProductCategoryRepository productCategoryRepository;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ProductInfoRepository productInfoRepository,
ProductCategoryRepository productCategoryRepository) {
this.productInfoRepository = productInfoRepository;
this.productCategoryRepository = productCategoryRepository;
}
/**
* 扣减库存
*
*/
@Transactional
@StreamListener(ProductStream.STOCK_APPLY_INPUT)
@SendTo(ProductStream.STOCK_RESULT_OUTPUT)
public StockResultOutput processStockApply(StockApplyInput stockApplyInput) throws Exception {
log.info("占用库存消息被消费...");
StockResultOutput stockResultOutput = new StockResultOutput();
stockResultOutput.setOrderId(stockApplyInput.getOrderId());
try {
for (OrderItemInput orderItemInput : stockApplyInput.getOrderItemInputs()) {
Optional<ProductInfo> productInfoOptional = productInfoRepository.findById(orderItemInput.getProductId());
if (!productInfoOptional.isPresent())
throw new Exception("商品不存在.");
ProductInfo productInfo = productInfoOptional.get();
int result = productInfo.getProductStock() - orderItemInput.getProductQuantity();
if (result < 0)
throw new Exception("商品库存不满足.");
productInfo.setProductStock(result);
productInfoRepository.save(productInfo);
}
stockResultOutput.setIsSuccess(true);
stockResultOutput.setMessage("OK");
return stockResultOutput;
} catch (Exception e) {
stockResultOutput.setIsSuccess(false);
stockResultOutput.setMessage(e.getMessage());
return stockResultOutput;
}
}
}- shopping-order处理库存处理结果
@StreamListener(OrderStream.STOCK_RESULT_INPUT)
public void processStockResult(StockResultOutput stockResultOutput) {
log.info("库存消息返回" + stockResultOutput);
Optional<OrderMaster> optionalOrderMaster = orderMasterRepository.findById(stockResultOutput.getOrderId());
if (optionalOrderMaster.isPresent()) {
OrderMaster orderMaster = optionalOrderMaster.get();
if (stockResultOutput.getIsSuccess()) {
orderMaster.setOrderStatus(OrderStatus.OCCUPY_SUCCESS);
} else {
orderMaster.setOrderStatus(OrderStatus.OCCUPY_FAILURE);
}
orderMasterRepository.save(orderMaster);
}
}执行调试结果,跟踪执行结果:生成订单同时发送库存申请命令,商品模块处理库存申请成功后,返回库存占用结果告知订单模块,从而实现订单生成和商品库存占用的逻辑的解耦。
小结
在原有的架构基础上,我们对商品和订单服务进行了应用解耦,库存占用逻辑异步化,通过消息队列传递消息,并结合spring cloud stream对消息input和output绑定,使得在程序中很方便的进行消息发送和接收处理。
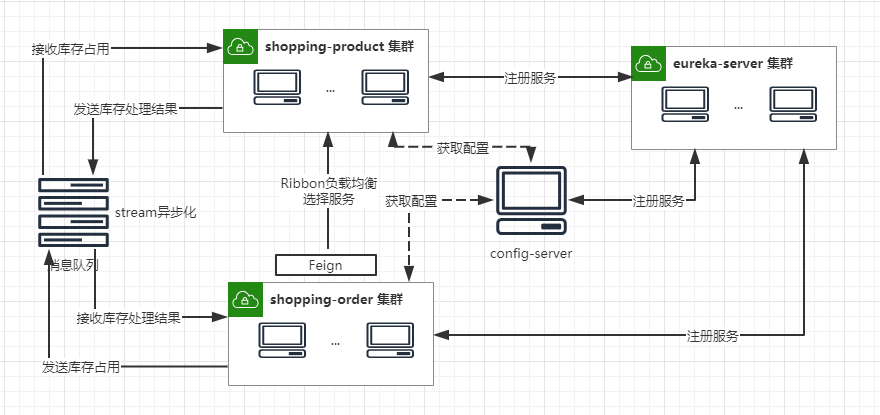
微服务网关(Zuul)
Zuul是Netflix开源的微服务网关,可以和Eureka、Ribbon、Hystrix等组件配合使用,Spring Cloud对Zuul进行了整合与增强,Zuul默认使用的HTTP客户端是Apache HTTPClient,也可以使用RestClient或okhttp3.OkHttpClient。 Zuul的主要功能是路由转发和过滤器。zuul默认和Ribbon结合实现了负载均衡的功能
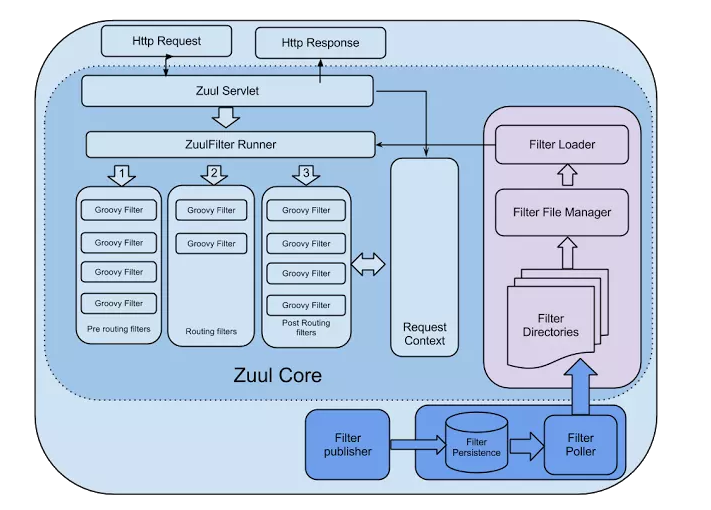
工作原理
zuul的核心是一系列的filters, 其作用类比Servlet框架的Filter,或者AOP。zuul把请求路由到用户处理逻辑的过程中,这些filter参与一些过滤处理,比如Authentication,Load Shedding等
Zuul使用一系列不同类型的过滤器,使我们能够快速灵活地将功能应用于我们的边缘服务。这些过滤器可帮助我们执行以下功能:
- 身份验证和安全性 - 确定每个资源的身份验证要求并拒绝不满足这些要求的请求
- 洞察和监控 - 在边缘跟踪有意义的数据和统计数据,以便为我们提供准确的生产视图
- 动态路由 - 根据需要动态地将请求路由到不同的后端群集
- 压力测试 - 逐渐增加群集的流量以衡量性能。
- Load Shedding - 为每种类型的请求分配容量并删除超过限制的请求
- 静态响应处理 - 直接在边缘构建一些响应,而不是将它们转发到内部集群
添加网关
- 新建api-gateway子模块,作为服务网关、服务发现客户端、获取配置客户端,因此需要引入以下依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-client</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-zuul</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependencies>- 在启动类上增加
EnableDiscoveryClient和@EnableZuulProxy注解。
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableZuulProxy
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApiGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiGatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}- 启动服务,看看是否能正常获取配置,并注册到Eureka Server。
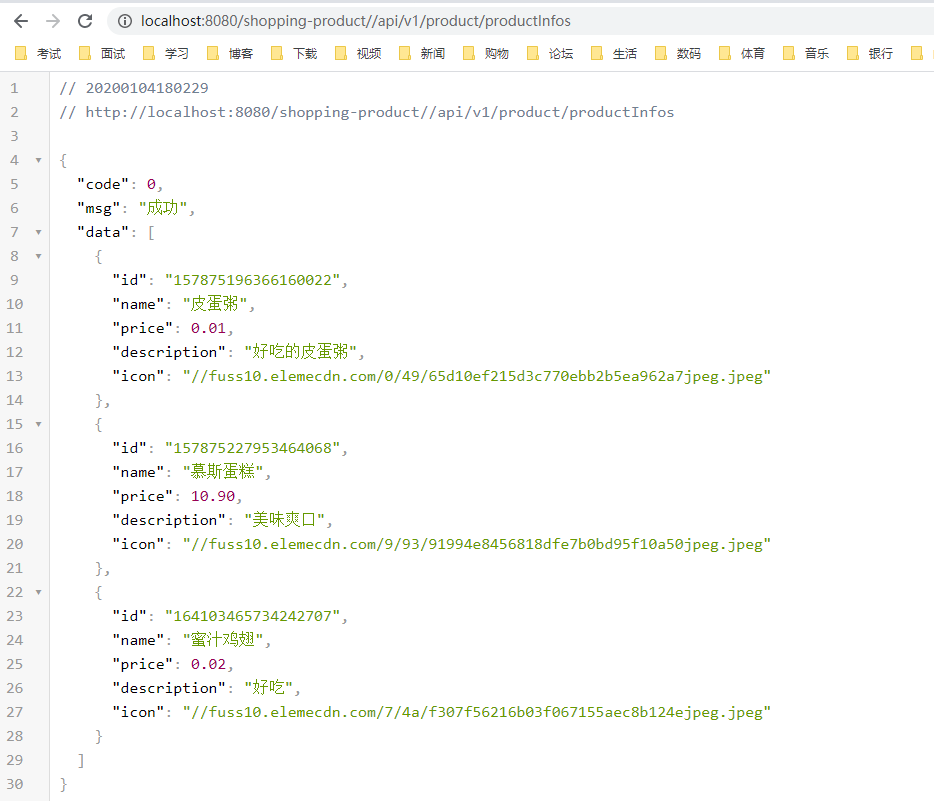
- Zuul网关目前暴露的端口是8080,之前我们访问商品服务的api,是通过调用 http://localhost:11100/api/v1/product/productInfos来访问的,现在我们就可以通过Zuul,根据商品的服务名称shopping-produc来访问 http://localhost:8080/shopping-product//api/v1/product/productInfos,非常轻松的实现了路由的功能。
自定义路由
默认的路由规则是按照服务的名称来路由服务,当然我们也可以自定义。在zuul中,路由匹配的路径表达式采用ant风格定义
| 通配符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ? | 匹配任意单个字符 |
| * | 匹配任意数量的字符 |
| ** | 匹配任意数量的字符,支持多级目录 |
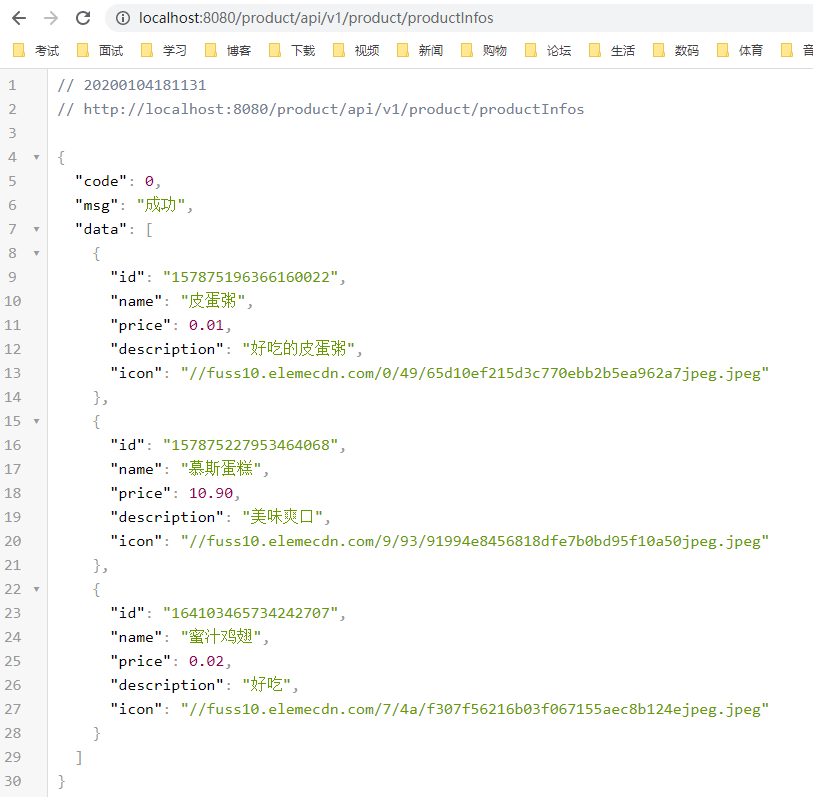
zuul:
routes:
# 简洁写法
shopping-product: /product/**- 将命名为product的所有路径都映射到shopping-product服务中去,然后通过product名称来访问,依旧能访问成功。
- 如果我们需要查看目前所有的路径映射呢,首先得引入actuator
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 其次,需要放开actuator维护端口的权限
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
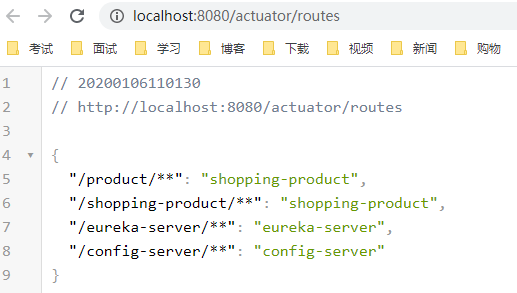
include: "*"- 访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/routes ,可以看到目前网关的所有路由映射
- 如果需要定义哪些方法不能通过网关调用,还可以设置排除哪些路由的规则
zuul:
routes:
# 简洁写法
shopping-product: /product/**
# 排除某些路由
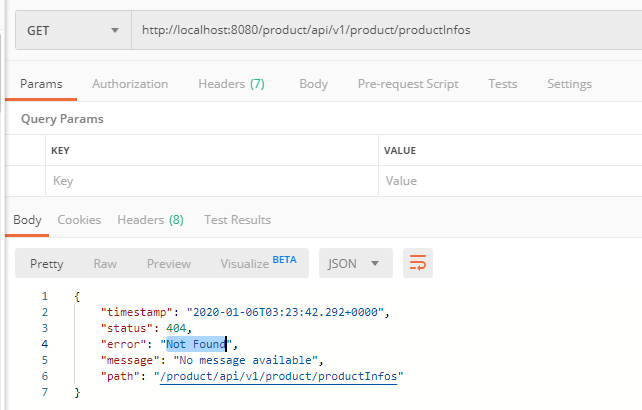
ignored-patterns:
- /**/productInfos这样我们再访问这个接口时,就提示 Not Found 错误了
Cookie与头信息
默认情况下,spring cloud zuul在请求路由时,会过滤掉http请求头信息中一些敏感信息,防止它们被传递到下游的外部服务器。默认的敏感头信息通过zuul.sensitiveHeaders参数定义,默认包括cookie,set-Cookie,authorization三个属性。所以,我们在开发web项目时常用的cookie在spring cloud zuul网关中默认时不传递的,这就会引发一个常见的问题,如果我们要将使用了spring security,shiro等安全框架构建的web应用通过spring cloud zuul构建的网关来进行路由时,由于cookie信息无法传递,我们的web应用将无法实现登录和鉴权。有时候,针对某些路由,我们需要传递这个cookie。
zuul:
routes:
# 完全写法
product-route:
path: /product/**
serviceId: shopping-product
# 将指定路由的敏感头设置为空
sensitiveHeaders:动态路由
之前路由的配置都是写在配置文件中,如果路由规则变化以后,需要重启网关服务。但是实际生产环境,一般都需要动态的加载路由的配置,不能轻易重启网关服务。
- 将配置信息集中到统一配置中心服务进行管理,具体实施参考前面章节-统一配置中心。
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://eureka1:8761/eureka/,http://eureka2:8762/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway #应用名称
cloud:
config:
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: config-server- 将zuul配置属性定义成支持动态刷新,增加
@RefreshScope注解
@Component
public class ZuulConfiguration {
@ConfigurationProperties("zuul")
@RefreshScope
public ZuulProperties zuulProperties(){
return new ZuulProperties();
}
}
自定义Filter
设想以下场景:我们需要判断用户请求的参数是否包含认证信息,如果包含token信息,则可以访问,否则禁止访问。可以用Zuul Filter很方便的实现在网关端,统一进行认证。
- 新建自定义的Filter,并继承ZuulFilter,默认需要实现4个接口
- filterType():返回 filter 的类型,设置为
PRE_TYPE - filterOrder():返回 filter 的顺序,设置为
PRE_DECORATION_FILTER_ORDER-1 - shouldFilter():是否启用 filter,设置为
true - run():执行具体的过滤器逻辑
- filterType():返回 filter 的类型,设置为
/**
* 验证token 过滤器
*/
@Component
public class TokenFilter extends ZuulFilter {
@Override
public String filterType() {
return PRE_TYPE;
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Object run() throws ZuulException {
RequestContext currentContext = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
HttpServletRequest request = currentContext.getRequest();
//测试在url参数中获取token
String token = request.getParameter("token");
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(token)){
currentContext.setSendZuulResponse(false);
currentContext.setResponseStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value());
}
return null;
}
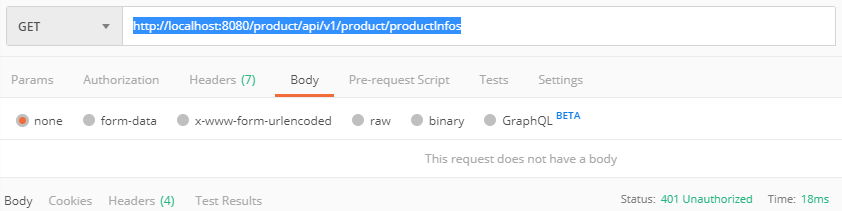
}- 验证结果,如果url中添加了 token 参数,TokenFilter 验证通过,正确返回结果;如果没有 token 参数,则返回 401(UNAUTHORIZED)错误
- 还可以在调用接口返回中,设置响应头
@Component
public class AddResHeaderFilter extends ZuulFilter{
@Override
public String filterType() {
return POST_TYPE;
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return SEND_RESPONSE_FILTER_ORDER - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Object run() {
RequestContext requestContext = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
HttpServletResponse response = requestContext.getResponse();
response.setHeader("X-Foo", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
return null;
}
}限流
这里介绍一种限流的设计方案:
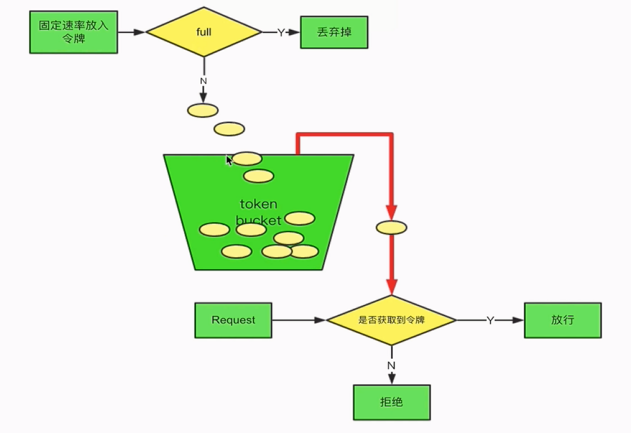
对于很多应用场景来说,除了要求能够限制数据的平均传输速率外,还要求允许某种程度的突发传输。这时候漏桶算法可能就不合适了,令牌桶算法更为适合。如图所示,令牌桶算法的原理是系统会以一个恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌,而如果请求需要被处理,则需要先从桶里获取一个令牌,当桶里没有令牌可取时,则拒绝服务。
Google公司已经实现了上述的令牌桶的算法,直接使用 RateLimiter 就可以通过Zuul实现限流的功能:
@Component
public class RateLimitFilter extends ZuulFilter {
private static final RateLimiter RATE_LIMITER = RateLimiter.create(100);
@Override
public String filterType() {
return PRE_TYPE;
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return SERVLET_DETECTION_FILTER_ORDER - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Object run() {
if (!RATE_LIMITER.tryAcquire()) {
throw new RuntimeException("未能获取到令牌.");
}
return null;
}
}小结
整体项目结构如下:
spring-cloud-app
--api-gateway(服务网关)
--config-server(统一配置中心)
--eureka-server(服务注册中心)
--shopping-common(购物公共模块)
--shopping-product(商品服务模块)
--shopping-order(订单服务模块)
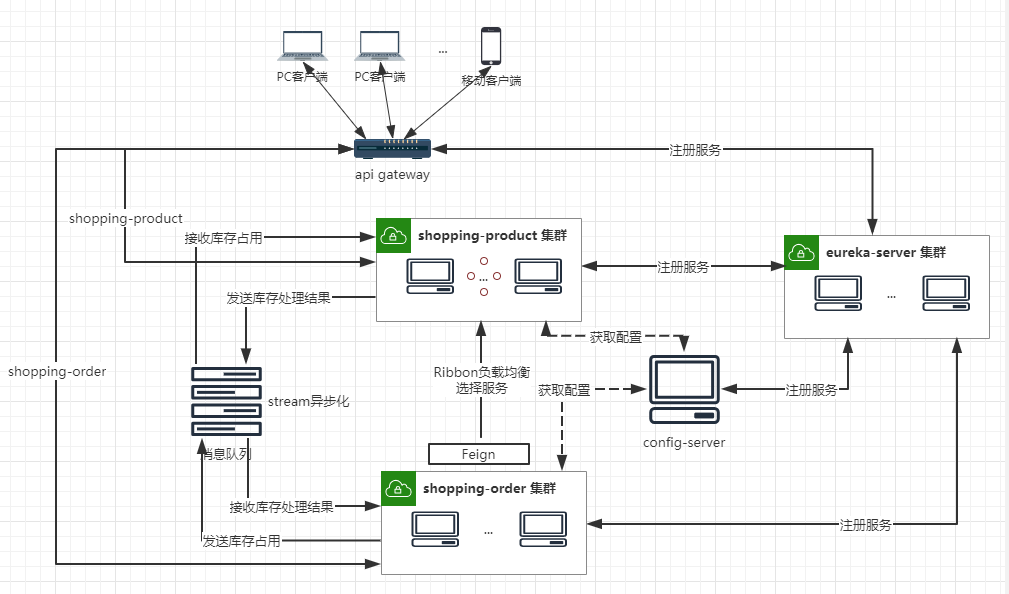
目前所有的客户端请求,首先被发送到统一网关服务处理,然后由网关进行限流、熔断、权限验证、记录日志等等,然后根据自定义的路由规则,再分发到不同的应用服务中去,应用服务器返回处理结果后,由网关统一返回给客户端。
服务容错(Hystrix)
在分布式环境中,许多服务依赖项中的一些必然会失败。Hystrix是一个库,通过添加延迟容忍和容错逻辑,帮助你控制这些分布式服务之间的交互。Hystrix通过隔离服务之间的访问点、停止级联失败和提供回退选项来实现这一点,所有这些都可以提高系统的整体弹性。
设计原则
- 防止任何单个依赖项耗尽所有容器(如Tomcat)用户线程。
- 甩掉包袱,快速失败而不是排队。
- 在任何可行的地方提供回退,以保护用户不受失败的影响。
- 使用隔离技术(如隔离板、泳道和断路器模式)来限制任何一个依赖项的影响。
- 通过近实时的度量、监视和警报来优化发现时间。
- 通过配置的低延迟传播来优化恢复时间。
- 支持对Hystrix的大多数方面的动态属性更改,允许使用低延迟反馈循环进行实时操作修改。
- 避免在整个依赖客户端执行中出现故障,而不仅仅是在网络流量中。
如何实现
- 用一个HystrixCommand 或者 HystrixObservableCommand (这是命令模式的一个例子)包装所有的对外部系统(或者依赖)的调用,典型地它们在一个单独的线程中执行
- 调用超时时间比你自己定义的阈值要长。有一个默认值,对于大多数的依赖项你是可以自定义超时时间的。
- 为每个依赖项维护一个小的线程池(或信号量);如果线程池满了,那么该依赖性将会立即拒绝请求,而不是排队。
- 调用的结果有这么几种:成功、失败(客户端抛出异常)、超时、拒绝。
- 在一段时间内,如果服务的错误百分比超过了一个阈值,就会触发一个断路器来停止对特定服务的所有请求,无论是手动的还是自动的。
- 当请求失败、被拒绝、超时或短路时,执行回退逻辑。
- 近实时监控指标和配置变化。
触发降级
在实际工作中,尤其是分布式、微服务越来越普遍的今天,一个服务经常需要调用其他的服务,即RPC调用,而调用最多的方式还是通过http请求进行调用,这里面就有一个问题了,如果调用过程中,因为网络等原因,造成某个服务调用超时,如果没有熔断机制,此处的调用链路将会一直阻塞在这里,在高并发的环境下,如果许多个请求都卡在这里的话,服务器不得不为此分配更多的线程来处理源源不断涌入的请求。
更恐怖的是,如果这是一个多级调用,即此处的服务的调用结果还被其他服务调用了,这就形成了所谓的雪崩效应,后果将不堪设想。因此,需要某种机制,在一定的异常接口调用出现的时候,能够自动发现这种异常,并快速进行服务降级。
- 首先,shopping-order项目模拟一个远程调用shopping-product服务http请求
/**
* Hystrix 测试
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/hystrix")
public class HystrixController {
@GetMapping("/getProductEnv")
public String getProductEnv() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:11100/api/env", null, String.class);
}
}- 如果此时将shopping-product服务关闭,则shopping-order调用远程服务不可用,进入等待,超时时返回 Error Page的错误页面。其实我们希望服务不可用的时候直接处理,返回通知服务的不可用状态。可以引入Hystrix。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 在启动类上增加
@EnableCircuitBreaker注解,或者将@SpringBootApplication、@EnableDiscoveryClient、@EnableCircuitBreaker三个合并成一个@SpringCloudApplication注解。
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "tech.lancelot.shoppingorder.client")
//@SpringBootApplication
//@EnableDiscoveryClient
//@EnableCircuitBreaker
@SpringCloudApplication
public class ShoppingOrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ShoppingOrderApplication.class, args);
}
}- 修改 HystrixController,增加
@HystrixCommand注解,并指定调用方法失败时的错误处理回调。也可以为整个类增加@DefaultProperties注解,定义一个默认的返回方法
/**
* Hystrix 测试
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/hystrix")
public class HystrixController {
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "defaultFallback")
@GetMapping("/getProductEnv")
public String getProductEnv() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:11100/api/env", null, String.class);
}
// 默认服务不可达的返回信息
private String defaultFallback() {
return "太拥挤了, 请稍后再试~~";
}
}- 重启启动后,再次访问接口,就会发现接口直接返回错误信息,不会阻塞在这里。
超时设置
如果我们没有配置默认的超时时间,Hystrix 将取 default_executionTimeoutInMilliseconds(1秒)作为默认超时时间,也可以自定义超时时间。
- 代码中修改默认超时配置(改为3秒):
@HystrixCommand(commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value = "3000")})这样的话,shopping-order调用远程服务,超过3s之后,立刻返回错误处理,不会再阻塞。
- 可以在配置文件中定义HystrixCommand属性
hystrix:
command:
default: # 方法默认属性
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 1000
getProductEnv: # 该名称方法属性
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 3000熔断机制
如果某个目标服务调用慢或者有大量超时,此时,熔断该服务的调用,对于后续调用请求,不在继续调用目标服务,直接返回,快速释放资源。如果目标服务情况好转则恢复调用。
熔断器有三个状态 CLOSED、OPEN、HALF_OPEN 熔断器默认关闭状态,当触发熔断(至少有 circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold 个请求,错误率达到 circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage)后状态变更为 OPEN,在等待到指定的时间(circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds),Hystrix会放请求检测服务是否开启,这期间熔断器会变为HALF_OPEN 半开启状态,熔断探测服务可用则继续变更为 CLOSED关闭熔断器。
- 在方法上增加熔断属性的相关设置
@HystrixCommand(commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.enabled", value = "true"), //设置熔断
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "10"),//请求数达到后才计算
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds", value = "10000"), //休眠时间窗
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "60"), //错误率
})可视化组件
Spring Coud 还给 Hytrix 提供了一个可视化的组件:
- 首先引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 启动类上增加
@EnableHystrixDashboard注解
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "tech.lancelot.shoppingorder.client")
//@SpringBootApplication
//@EnableDiscoveryClient
//@EnableCircuitBreaker
@SpringCloudApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class ShoppingOrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ShoppingOrderApplication.class, args);
}
}- 重启 shopping-order 服务,访问 http://localhost:11110/hystrix ,进入可视化管理界面

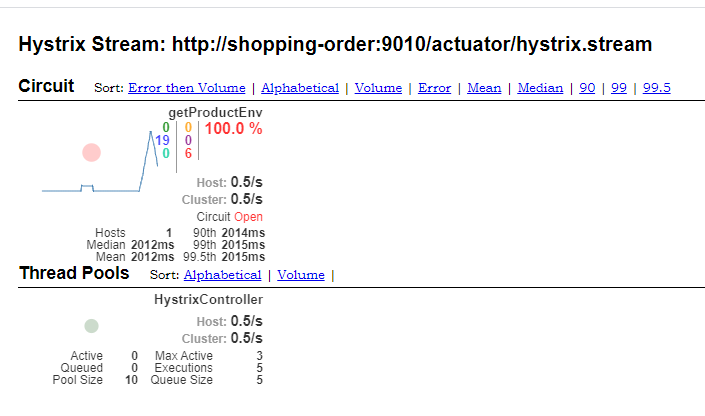
- 填上我们监听的地址:http://shopping-order:11110/actuator/hystrix.stream ,点击Monitor Stream。进入监控的界面,我们再多刷新调用接口api,看看熔断执行的效果。
小结
通过以上容错方法的实现,就可以构建更加稳定、可靠的分布式系统:
服务追踪(Sleuth)
微服务架构是一个分布式架构,它按业务划分服务单元,一个分布式系统往往有很多个服务单元。由于服务单元数量众多,业务的复杂性,如果出现了错误和异常,很难去定位。主要体现在,一个请求可能需要调用很多个服务,而内部服务的调用复杂性,决定了问题难以定位。所以微服务架构中,必须实现分布式链路追踪,去跟进一个请求到底有哪些服务参与,参与的顺序又是怎样的,从而达到每个请求的步骤清晰可见,出了问题,很快定位。
OpenTracing
OpenTracing 是一个轻量级的标准化层,它位于应用程序/类库和追踪或日志分析程序之间。
+-------------+ +---------+ +----------+ +------------+
| Application | | Library | | OSS | | RPC/IPC |
| Code | | Code | | Services | | Frameworks |
+-------------+ +---------+ +----------+ +------------+
| | | |
| | | |
v v v v
+------------------------------------------------------+
| OpenTracing |
+------------------------------------------------------+
| | | |
| | | |
v v v v
+-----------+ +-------------+ +-------------+ +-----------+
| Tracing | | Logging | | Metrics | | Tracing |
| System A | | Framework B | | Framework C | | System D |
+-----------+ +-------------+ +-------------+ +-----------+OpenTracing 的优势
- OpenTracing 已进入 CNCF,正在为全球的分布式追踪,提供统一的概念和数据标准。
- OpenTracing 通过提供平台无关、厂商无关的 API,使得开发人员能够方便的添加(或更换)追踪系统的实现。
OpenTracing 数据模型
OpenTracing 中的 Trace(调用链)通过归属于此调用链的 Span 来隐性的定义。
特别说明,一条 Trace(调用链)可以被认为是一个由多个 Span 组成的有向无环图(DAG图),Span 与 Span 的关系被命名为 References。
例如:下面的示例 Trace 就是由8个 Span 组成:
单个 Trace 中,span 间的因果关系
[Span A] ←←←(the root span)
|
+------+------+
| |
[Span B] [Span C] ←←←(Span C 是 Span A 的孩子节点, ChildOf)
| |
[Span D] +---+-------+
| |
[Span E] [Span F] >>> [Span G] >>> [Span H]
↑
↑
↑
(Span G 在 Span F 后被调用, FollowsFrom)有些时候,使用下面这种,基于时间轴的时序图可以更好的展现 Trace(调用链):
单个 Trace 中,span 间的时间关系
––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–––––––|–> time
[Span A···················································]
[Span B··············································]
[Span D··········································]
[Span C········································]
[Span E·······] [Span F··] [Span G··] [Span H··]每个 Span 包含以下的状态:(译者注:由于这些状态会反映在 OpenTracing API 中,所以会保留部分英文说明)
- An operation name,操作名称
- A start timestamp,起始时间
- A finish timestamp,结束时间
- Span Tag,一组键值对构成的 Span 标签集合。键值对中,键必须为 string,值可以是字符串,布尔,或者数字类型。
- Span Log,一组 span 的日志集合。
每次 log 操作包含一个键值对,以及一个时间戳。
键值对中,键必须为 string,值可以是任意类型。
但是需要注意,不是所有的支持 OpenTracing 的 Tracer,都需要支持所有的值类型。
- SpanContext,Span 上下文对象 (下面会详细说明)
- References(Span间关系),相关的零个或者多个 Span(Span 间通过 SpanContext 建立这种关系)
每一个 SpanContext 包含以下状态:
- 任何一个 OpenTracing 的实现,都需要将当前调用链的状态(例如:trace 和 span 的 id),依赖一个独特的 Span 去跨进程边界传输
- Baggage Items,Trace 的随行数据,是一个键值对集合,它存在于 trace 中,也需要跨进程边界传输
更多关于 OpenTracing 数据模型的知识,请参考 OpenTracing语义标准。
OpenTracing 实现
这篇文档列出了所有 OpenTracing 实现。在这些实现中,比较流行的为 Jaeger 和 Zipkin。
事件类型
cs ( Client Send ) :客户端发起请求的时间
cr ( Client Received ) :客户端收到处理完请求的时间。
ss ( Server Send ) :服务端处理完逻辑的时间。
sr ( Server Received ) :服务端收到调用端请求的时间。
客户端调用时间=cr-cs
服务端处理时间=sr-ss
链路追踪
- 打开 shopping-order 项目,增加引入相应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
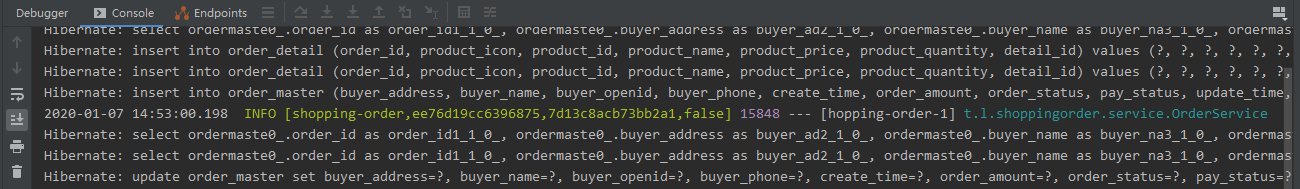
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 重启服务,用postman调用创建订单的接口,观察控制台的日志信息,发现多了sleuth记录的链路日志信息
- 第一个参数shopping-order:应用名称,对应我们application.yml中定义的application-name。
- 第二个参数ee76d19cc6396875:Trace ID, 标识一条请求链路,一条请求链路包含一个Trace ID,多个Span ID。一条链路上的Trace ID是相同的,注意上面的日志信息第二个参数即Trace ID是一样的。
- 第三个参数7d13c8acb73bb2a1:Span ID,一个基本的工作单元,如一个http请求。
- 第四个参数true:表示是否要将该信息输出到Zipkin等服务中来收集和展示。
- 同样,shopping-product项目,也增加引入相应的依赖,看看sleuth记录的日志信息有啥不同。可以看到他们的 Trace ID 是相同的,而 Span ID 是不同的
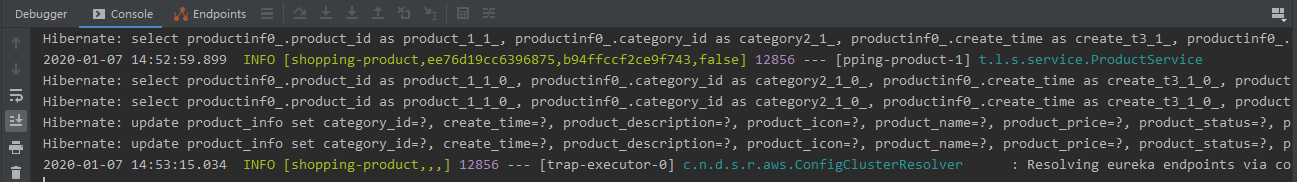
Zipkin
目前,链路追踪组件有Google的Dapper,Twitter 的 Zipkin,以及阿里的Eagleeye (鹰眼)等,它们都是非常优秀的链路追踪开源组件。本文主要讲述如何在Spring Cloud Sleuth中集成Zipkin。
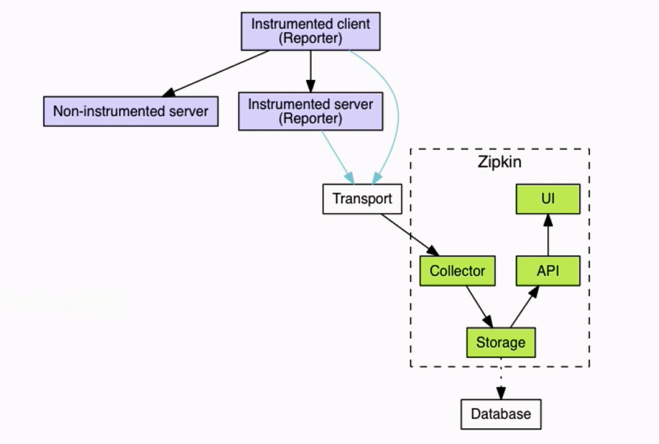
Zipkin Server主要包括四个模块:
Collector 接收或收集各应用传输的数据
Storage 存储接受或收集过来的数据,当前支持Memory,MySQL,Cassandra,ElasticSearch等,默认存储在内存中。
API(Query) 负责查询Storage中存储的数据,提供简单的JSON API获取数据,主要提供给web UI使用
Web 提供简单的web界面
首先,安装 zipkin,为了方便直接用 docker 进行安装,具体详见容器化部署章节,这里不再详述。
引入sleuth-zipkin相关依赖,因为 starter-zipkin 已经包含 starter-sleuth 的依赖,所以可以把原先的 sleuth依赖去掉。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
<https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dependency>- 配置 Zipkin Server服务的地址
spring:
zipkin:
base-url: http://zipkin:9411/- Sleuth 有个抽样比例的属性,默认是0.1,就是默认会将10%的链路信息上传,为了方便测试观察,我们把这个属性值调成100%
spring:
sleuth:
sampler:
rate: 100
zipkin:
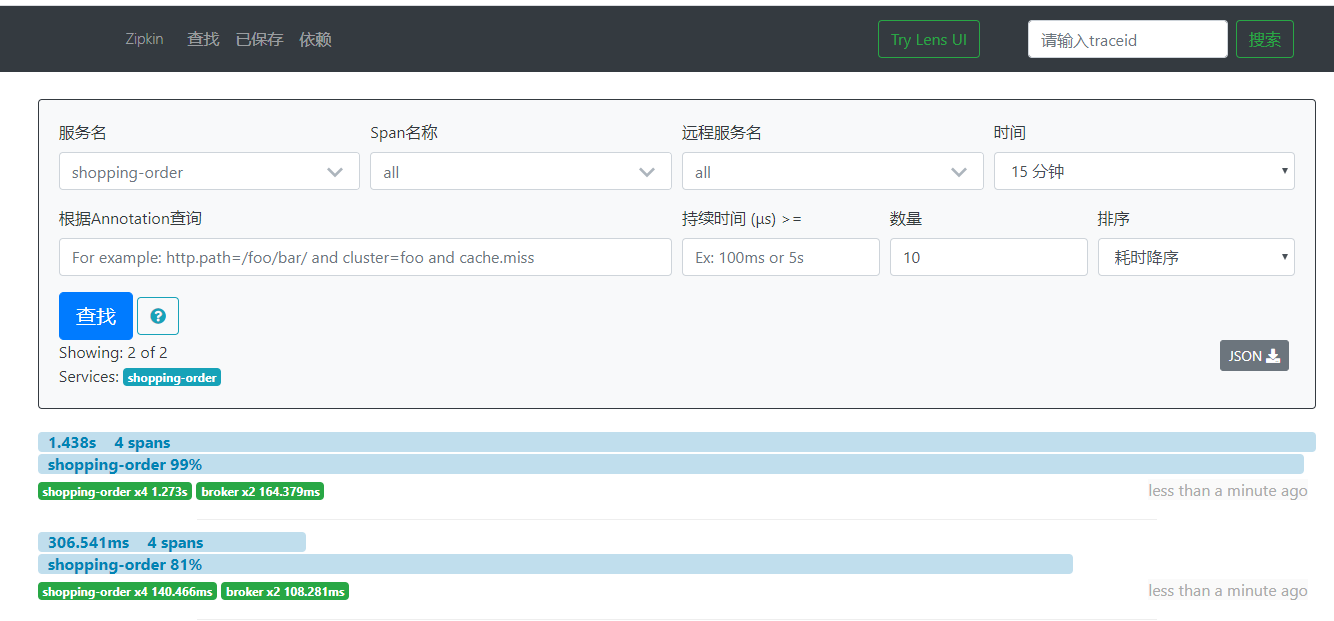
base-url: http://zipkin:9411/- 重启服务,调用2次api接口。再次访问 Zipkin Server 管理界面,可以看到对应的链路信息。
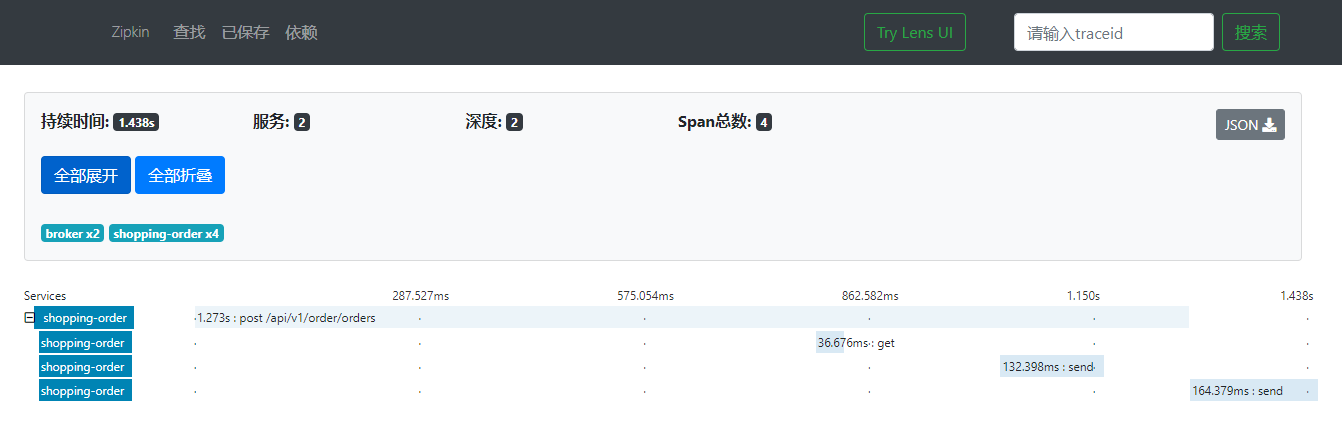
- 可以点击查看详情,很方便的看到一次链路调用,每个节点的访问时间,利于我们排查性能问题
小结
在服务调用的过程中,通过Sleuth将链路信息(经过抽样后的信息)统一上报给Zipkin,通过Zipkin就可以集中查看和管理微服务架构中的调用链路信息,便于开发人员与运维人员跟踪和调试问题。
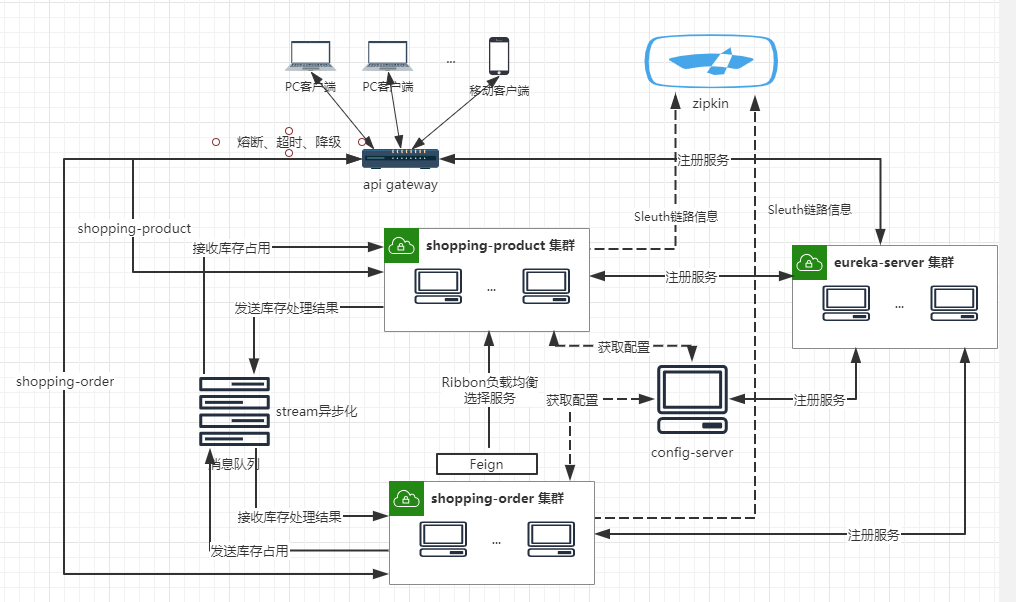
容器化部署
安装Docker
[root@localhost ~]# yum install docker
[root@localhost ~]# systemctrl enable docker #设置docker开机启动
[root@localhost ~]# systemctrl start docker #启动docker- 配置vi /etchttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/dockerhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/deamon.json,添加国内加速镜像
{
"registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com"],
"registry-mirrors": ["https://njrds9qc.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}- 重启生效
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart docker- 验证是否成功安装
[root@localhost ~]# docker -v
Docker version 1.13.1, build 7f2769b/1.13.1安装Docker-Compose
- 检查是否安装python-pip
[root@localhost ~]# pip -V- 已安装pip则跳过该步骤,否则安装pip
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install epel-release
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install python-pip
[root@localhost ~]# pip install --upgrade pip- 安装docker-compose
[root@localhost ~]# pip install docker-compose- 安装过程中如果出现Command errored python setup.py egg_info 可尝试升级setuptools
[root@localhost ~]# pip install more-itertools==5.0.0- 验证是否成功安装
[root@localhost ~]# docker-compose -v
docker-compose version 1.25.0, build b42d419Eureka部署
- 首先我们创建2个节点的配置文件
application.yml:
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server #应用名称
profiles:
active: peer1application-peer1.yml:
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://peer2:8762/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址
server:
port: 8761 #应用服务端口application-peer2.yml:
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://peer1:8761/eureka/ #指定服务注册地址
server:
port: 8762 #应用服务端口- 在eureka-server项目下新建Dockerfile文件
FROM hub.c.163.com/library/java:8-alpine
ADD target/*.jar app.jar
EXPOSE 8761
EXPOSE 8762
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]- 构建镜像:
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true -U
docker build -t spring-cloud-app/eureka-server:v1 .MySQL部署
- 拉取MySQL的镜像文件
[root@localhost ~]# docker pull mysql:5.7- 在docker-compose.yml文件中相关配置
mysql:
image: docker.io/mysql:5.7
hostname: mysql
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: "123456"
volumes:
- "./mysql/conf:/etc/mysql"
- "./mysql/logs:/var/log/mysql"
- "./mysqlhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/data:/var/lib/mysql"RabbitMQ
-management 表示有管理界面的,可以浏览器访问。5672是访问端口,15672是管理端口。
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -d --hostname rabbitmq -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3.8.2-management访问端口管理界面,输入默认用户名/密码 :guest/guest

OpenZipkin
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -d -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin
编排镜像
docker-compose.yml:
version: "2"
services:
eureka1:
image: spring-cloud-app/eureka-server:v1
hostname: eureka1
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "8761:8761"
environment:
- spring.profiles.active=peer1
eureka2:
image: spring-cloud-app/eureka-server:v1
hostname: eureka2
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "8762:8762"
environment:
- spring.profiles.active=peer2
config-server:
image: spring-cloud-app/config-server:v1
hostname: config-server
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "8888:8888"
mysql:
image: docker.io/mysql:5.7
hostname: mysql
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: "123456"
volumes:
- "./mysql/conf:/etc/mysql"
- "./mysql/logs:/var/log/mysql"
- "./mysqlhttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/data:/var/lib/mysql"
rabbitmq:
image: docker.io/rabbitmq:3.8.2-management
hostname: rabbitmq
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "5672:5672"
- "15672:15672"
zipkin:
image: docker.io/openzipkin/zipkin:2.19.2
hostname: zipkin
networks:
- eureka-net
ports:
- "9411:9411"
networks:
eureka-net:
driver: bridge加载全部内容