Spring MVC异步请求Servlet异步 Spring-MVC异步请求之Servlet异步处理
li563868273 人气:0在Servlet3.0的规范中新增了对异步请求的支持,SpringMVC又在此基础上对异步请求提供了方便。
异步请求是在处理比较耗时的业务时先将request返回,然后另起线程处理耗时的业务,处理完后在返回给用户。
异步请求可以给我们带来很多方便,最直接的用法就是处理耗时的业务,比如,需要查询数据库,需要调用别的服务器来处理等情况下可以先将请求返回给客户端,然后启用新线程处理耗时业务。
如果我们合适的扩展可以实现订阅者模式的消息订阅功能,比如,当有异常情况发生时可以主动将相关信息发送给运维人员,还有现在的很多邮箱自动回复都是使用这种技术。
Http协议是单向的,只能客户端自己拉不能服务器主动推,Servlet对异步请求的支持并没有修改Http,而是对Http的巧妙利用。异步请求的核心原理主要分为两大类,一类是轮询,另一类是长连接。
轮询就是定时自动发起请求检查有没有需要返回的数据,这种对资源浪费比较大。长连接的原理是客户端发起请求,服务端处理并返回后并不结束连接,这样就可以在后面再次返回给客户端数据。
Servlet对异步请求的支持其实采用的是长连接的方式,也就是说,异步请求中在原始的请求返回的时候并没有关闭连接,关闭的只是处理请求的那个县城,只有在异步请求全部处理完之后才会关闭连接。
Servlet3.0对异步请求的支持
在Servlet3.0规范中使用异步处理请求非常简单,只需要在请求处理过程中调用request的startAsync返回AsyncContext。
什么是AsyncContext在异步请求中充当着非常重要的角色,可以称为异步请求上下文也可以称为异步请求容器。类似于ServletContext.我们多次调用startAsync都是返回的同一个AsyncContext。代码如下:
public interface AsyncContext {
String ASYNC_REQUEST_URI = "javax.servlet.async.request_uri";
String ASYNC_CONTEXT_PATH = "javax.servlet.async.context_path";
String ASYNC_PATH_INFO = "javax.servlet.async.path_info";
String ASYNC_SERVLET_PATH = "javax.servlet.async.servlet_path";
String ASYNC_QUERY_STRING = "javax.servlet.async.query_string";
ServletRequest getRequest();
ServletResponse getResponse();
boolean hasOriginalRequestAndResponse();
void dispatch();
void dispatch(String var1);
void dispatch(ServletContext var1, String var2);
void complete();
void start(Runnable var1);
void addListener(AsyncListener var1);
void addListener(AsyncListener var1, ServletRequest var2, ServletResponse var3);
<T extends AsyncListener> T createListener(Class<T> var1) throws ServletException;
void setTimeout(long var1);
long getTimeout();
}
getResponse() 用于获取response。dispatch用于分发新地址。complete用于通知容器已经处理完了,start方法用于启动实际处理线程,addListener用于添加监听器;setTimeout方法用于修改超时时间。
Servlet3.0处理异步请求实例
@WebServlet(
name = “WorkServlet”,
urlPatterns = “/work”,
asyncSupported = true
)
public class WorkServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID =1L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//设置ContentType,关闭缓存
resp.setContentType("text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
resp.setHeader("Cache-Control","private");
resp.setHeader("Pragma","no-cache");
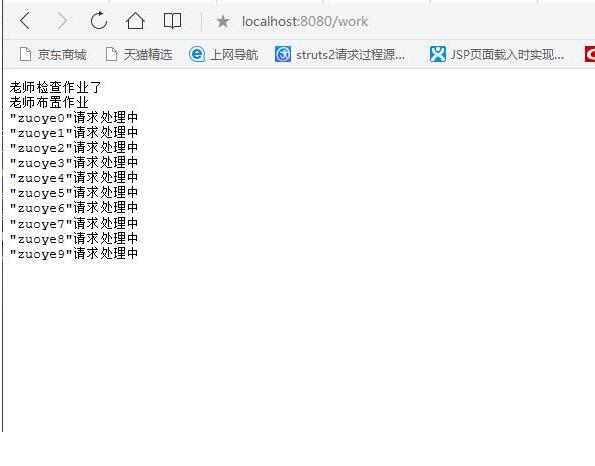
final PrintWriter writer= resp.getWriter();
writer.println("老师检查作业了");
writer.flush();
List<String> zuoyes=new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
zuoyes.add("zuoye"+i);;
}
final AsyncContext ac=req.startAsync();//开启异步请求
doZuoye(ac,zuoyes);
writer.println("老师布置作业");
writer.flush();
}
private void doZuoye(final AsyncContext ac, final List<String> zuoyes) {
ac.setTimeout(1*60*60*1000L);
ac.start(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//通过response获得字符输出流
try {
PrintWriter writer=ac.getResponse().getWriter();
for (String zuoye:zuoyes) {
writer.println("\""+zuoye+"\"请求处理中");
Thread.sleep(1*1000L);
writer.flush();
}
ac.complete();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
异步请求监听器
在上面的程序是我们最基本的异步请求,不过不够完善。老师是需要思考宏观问题,所以在写完作业之后需要给老师汇报哪些题难,哪些题目有问题或者自己的这次经验总结,不过这些事不应该由做作业的学生来做,应该由专门的学习汇报员来统计分析。所以就有了监听器。
public class TeacherListener implements AsyncListener {
final SimpleDateFormat formatter=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
@Override
public void onComplete(AsyncEvent event) throws IOException {
System.out.println("在"+formatter.format(new Date())+"工作处理完成");
}
@Override
public void onTimeout(AsyncEvent event) throws IOException {
System.out.println("在"+formatter.format(new Date())+"工作超时");
}
@Override
public void onError(AsyncEvent event) throws IOException {
System.out.println("在"+formatter.format(new Date())+"工作处理错误");
}
@Override
public void onStartAsync(AsyncEvent event) throws IOException {
System.out.println("在"+formatter.format(new Date())+"工作处理开始");
}
}
所有代码具体参照github地址
https://github.com/lzggsimida123/ServletAsync
补充:SpringMVC对Servlet3异步请求的支持
SpringMVC对Servlet3异步请求的支持有两种方式,分别是通过处理器方法返回Callable和DeferredResult。
按照Servlet3的规范,支持异步请求时需要配置对应的Servlet和Filter支持异步请求,为了使SpringMVC支持异步请求的处理,需要在定义DispatcherServlet时配置其支持异步请求,在DispatcherServlet之前定义的Filter也需要配置支持异步请求。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<!-- 启用异步支持 -->
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
返回Callable
当处理器的返回方法是Callable类型时会默认发起异步请求,并使用一个TaskExecutor来调用返回的Callable,之后的处理就跟正常的SpringMVC请求是一样的。Callable的返回结果也跟正常请求SpringMVC的一样,可以返回Model、ModelAndView、String、Object等,也可以结合@ResponseBody使用,具体可以参考CallableMethodReturnValueHandler的handleReturnValue()。
@RequestMapping("/callable")
public Callable<String> forCallable(Model model) throws Exception {
return () -> {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);//睡眠1秒,模仿某些业务操作
model.addAttribute("a", "aaaaaaa");
return "async_request_callable";
};
}
如果需要针对于单个Callable请求指定超时时间,我们可以把Callable用一个WebAsyncTask包裹起来。然后还可以指定超时回调和正常处理完成的回调。
@RequestMapping("/callable/timeout")
public WebAsyncTask<String> forCallableWithTimeout(Model model) throws Exception {
long timeout = 5 * 1000L;
WebAsyncTask<String> asyncTask = new WebAsyncTask<>(timeout, () -> {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(timeout + 10);
model.addAttribute("a", "aaaaaaa");
return "async_request_callable";
});
asyncTask.onTimeout(() -> {
System.out.println("响应超时回调");
return "async_request_callable_timeout";
});
asyncTask.onCompletion(() -> {
System.out.println("响应callable调用完成的回调");
});
return asyncTask;
}
返回DeferredResult
使用DeferredResult的返回结果的编程通常是在处理器方法中创建一个DeferredResult实例,把它保存起来后再进行返回,比如保存到一个队列中,然后在另外的一个线程中会从这个队列中拿到相应的DeferredResult对象进行相应的业务处理后会往DeferredResult中设置对应的返回值。返回了DeferredResult后SpringMVC将创建一个DeferredResultHandler用于监听DeferredResult,一旦DeferredResult中设置了返回值后,DeferredResultHandler就将对返回值进行处理。DeferredResult的处理过程见DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler的handleReturnValue()。
@RequestMapping("/deferredresult")
public DeferredResult<String> forDeferredResult() throws Exception {
DeferredResult<String> result = new DeferredResult<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
result.setResult("async_request_deferredresult");
}).start();
return result;
}
对于DeferredResult也是可以单独指定超时时间和超时后的回调的,它的超时时间可以直接通过构造函数传递,单位是毫秒。
@RequestMapping("/deferredresult/timeout")
public DeferredResult<String> forDeferredResultWithTimeout() throws Exception {
DeferredResult<String> result = new DeferredResult<>(10 * 1000);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(31);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
result.setResult("async_request_deferredresult");
}).start();
result.onTimeout(() -> {
System.out.println("响应超时回调函数");
});
result.onCompletion(() -> {
System.out.println("响应完成的回调函数");
});
return result;
}
配置
可以通过<mvc:annotation-driven/>的子元素<mvc:async-support/>来定义处理异步请求默认的超时时间和需要使用的TaskExecutor。如果不指定默认超时时间则默认会使用容器的异步请求超时时间,如果不指定需要使用的TaskExecutor,则默认会使用一个SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor。在下面的配置中我们就配置了默认的超时时间是15秒,且处理异步请求的TaskExecutor是bean容器中名为asyncTaskExecutor的TaskExecutor。
<mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:async-support default-timeout="15000" task-executor="asyncTaskExecutor"/> </mvc:annotation-driven>
拦截器
返回Callable类型的请求可以通过实现CallableProcessingInterceptor接口自定义一个拦截器来拦截,也可以通过继承CallableProcessingInterceptorAdapter抽象类来定义拦截器,这样就只需要选择自己感兴趣的方法进行实现。CallableProcessingInterceptor接口定义如下:
public interface CallableProcessingInterceptor {
static final Object RESULT_NONE = new Object();
static final Object RESPONSE_HANDLED = new Object();
/**
* Invoked <em>before</em> the start of concurrent handling in the original
* thread in which the {@code Callable} is submitted for concurrent handling.
*
* <p>
* This is useful for capturing the state of the current thread just prior to
* invoking the {@link Callable}. Once the state is captured, it can then be
* transferred to the new {@link Thread} in
* {@link #preProcess(NativeWebRequest, Callable)}. Capturing the state of
* Spring Security's SecurityContextHolder and migrating it to the new Thread
* is a concrete example of where this is useful.
* </p>
*
* @param request the current request
* @param task the task for the current async request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void beforeConcurrentHandling(NativeWebRequest request, Callable<T> task) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked <em>after</em> the start of concurrent handling in the async
* thread in which the {@code Callable} is executed and <em>before</em> the
* actual invocation of the {@code Callable}.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param task the task for the current async request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void preProcess(NativeWebRequest request, Callable<T> task) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked <em>after</em> the {@code Callable} has produced a result in the
* async thread in which the {@code Callable} is executed. This method may
* be invoked later than {@code afterTimeout} or {@code afterCompletion}
* depending on when the {@code Callable} finishes processing.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param task the task for the current async request
* @param concurrentResult the result of concurrent processing, which could
* be a {@link Throwable} if the {@code Callable} raised an exception
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void postProcess(NativeWebRequest request, Callable<T> task, Object concurrentResult) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked from a container thread when the async request times out before
* the {@code Callable} task completes. Implementations may return a value,
* including an {@link Exception}, to use instead of the value the
* {@link Callable} did not return in time.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param task the task for the current async request
* @return a concurrent result value; if the value is anything other than
* {@link #RESULT_NONE} or {@link #RESPONSE_HANDLED}, concurrent processing
* is resumed and subsequent interceptors are not invoked
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> Object handleTimeout(NativeWebRequest request, Callable<T> task) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked from a container thread when async processing completes for any
* reason including timeout or network error.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param task the task for the current async request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void afterCompletion(NativeWebRequest request, Callable<T> task) throws Exception;
}
它的配置是通过<mvc:callable-interceptors/>配置的。
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:async-support default-timeout="15000" task-executor="asyncTaskExecutor">
<mvc:callable-interceptors>
<bean class="YourCallableProcessingInterceptor"/>
</mvc:callable-interceptors>
</mvc:async-support>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
返回DeferredResult的也可以进行拦截,这需要我们实现DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor接口或者继承自DeferredResultProcessingInterceptorAdapter。DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor接口定义如下:
public interface DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor {
/**
* Invoked immediately before the start of concurrent handling, in the same
* thread that started it. This method may be used to capture state just prior
* to the start of concurrent processing with the given {@code DeferredResult}.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult for the current request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void beforeConcurrentHandling(NativeWebRequest request, DeferredResult<T> deferredResult) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked immediately after the start of concurrent handling, in the same
* thread that started it. This method may be used to detect the start of
* concurrent processing with the given {@code DeferredResult}.
*
* <p>The {@code DeferredResult} may have already been set, for example at
* the time of its creation or by another thread.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult for the current request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void preProcess(NativeWebRequest request, DeferredResult<T> deferredResult) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked after a {@code DeferredResult} has been set, via
* {@link DeferredResult#setResult(Object)} or
* {@link DeferredResult#setErrorResult(Object)}, and is also ready to
* handle the concurrent result.
*
* <p>This method may also be invoked after a timeout when the
* {@code DeferredResult} was created with a constructor accepting a default
* timeout result.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult for the current request
* @param concurrentResult the result to which the {@code DeferredResult}
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void postProcess(NativeWebRequest request, DeferredResult<T> deferredResult, Object concurrentResult) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked from a container thread when an async request times out before
* the {@code DeferredResult} has been set. Implementations may invoke
* {@link DeferredResult#setResult(Object) setResult} or
* {@link DeferredResult#setErrorResult(Object) setErrorResult} to resume processing.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult for the current request; if the
* {@code DeferredResult} is set, then concurrent processing is resumed and
* subsequent interceptors are not invoked
* @return {@code true} if processing should continue, or {@code false} if
* other interceptors should not be invoked
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> boolean handleTimeout(NativeWebRequest request, DeferredResult<T> deferredResult) throws Exception;
/**
* Invoked from a container thread when an async request completed for any
* reason including timeout and network error. This method is useful for
* detecting that a {@code DeferredResult} instance is no longer usable.
*
* @param request the current request
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult for the current request
* @throws Exception in case of errors
*/
<T> void afterCompletion(NativeWebRequest request, DeferredResult<T> deferredResult) throws Exception;
}
自定义的DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor是通过<mvc:deferred-result-interceptors>配置的。
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:async-support default-timeout="15000" task-executor="asyncTaskExecutor">
<mvc:deferred-result-interceptors>
<bean class="YourDeferredResultProcessingInterceptor"/>
</mvc:deferred-result-interceptors>
</mvc:async-support>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
当发起异步请求时,SpringMVC传统的HandlerInterceptor的postHandle()和afterCompletion()不会执行,但是等异步请求结束后它们还是会执行的。如果需要在异步处理完成之后做一些事情,也可以选择实现AsyncHandlerInterceptor接口的afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(),AsyncHandlerInterceptor接口继承了HandlerInterceptor。
(注:本文是基于Spring4.1.0所写)
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
加载全部内容