python 批量重命名文件 Python基于mediainfo批量重命名图片文件
武散人 人气:0案例故事:
大部分带彩色屏幕的终端设备,不管是手机,车机,电视等等,都需要涉及图片的显示,
作为一名专业的多媒体测试人员,我们需要一堆的规范化标准的图片测试文件,
但是现有的图片资源名字命名的很随意比如:IMG_20200325_161111.jpg,
以上命名不能看出图片文件的具体图片编码格式,分辨率等信息,
测试经理要求我进行批量重命名工作,模板如下,
图片编码格式_分辨率_位深度_容器.容器, 例如:
JPEG_1920x1080_32bit_jpg.jpg
图片编解码基本知识
图片编码:将某各风景画面取景转成图片数据文件的过程,取景肯定涉及取景的范围,
图片解码:将图片数据文件显示到屏幕上的过程。
主要涉及以下技术参数:
| 图片技术参数 | 参数释义 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 图片编码格式 (压缩技术) |
即像素点压缩的一类技术, 不同的编码格式, 其压缩率与压缩效果不一样。 |
JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, Webp, RAW, Heic |
| 图片分辨率 (单位:Pixel) |
图片长像素点的数量*图片宽像素点的数量 | 4096×2160(4K), 1920x1080, 1280x720,720×480, 640x480, 320x480等 甚至10亿像素的图片都存在的。 |
| 位深度 (单位:bit) |
每个像素点所包含的数据量的大小 | 8bit, 16bit, 32bit |
| 图片容器 | 文件后缀,将图片像素点封装的一种文件格式 | .jpg; .png; .gif; .bmp; .heic; .webp等 |
我们碰到的任何图片文件,都是数据的集合,
一般数据越大,其图片越清晰。
准备阶段
- 确保mediainfo.exe 命令行工具已经加入环境变量
- 以下是某个图片文件的mediainfo信息, 都是文本,Python处理起来肯定很简单的。
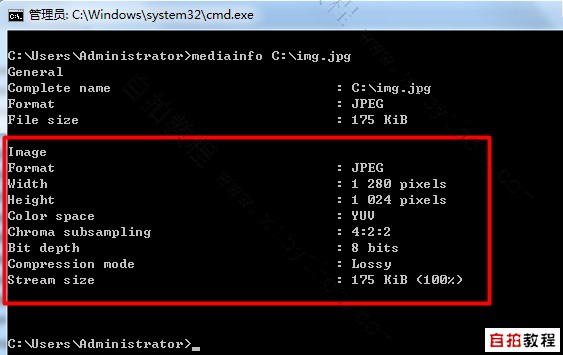
- 如果要进行批量重命名图片,我们还是用输入输出文件架构,如下:
+---Input_Image #批量放入待命名的图片文件
| 1.jpg
| 2.png
|
+---Output_Image #批量输出已命名的图片文件
| JPEG_1920x1080_32bit_jpg.jpg
| PNG_1280x720_32bit_png.png
|
\image_info.py # 获取图片文件info信息的模块,
\rename_image.py #调用image_info.py并实现重名,可双击运行
定义image_info.py模块
由于涉及较复杂的代码,建议直接用面向对象类的编程方式实现:
# coding=utf-8
import os
import re
import subprocess
class ImageInfoGetter():
'''获取图片文件的Formate, 分辨率,位深度'''
def __init__(self, image_file):
'''判断文件是否存在,如果存在获取其mediainfo信息'''
if os.path.exists(image_file):
self.image_file = image_file
p_obj = subprocess.Popen('mediainfo "%s"' % self.image_file, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
self.info = p_obj.stdout.read().decode("utf-8") # 解决非英文字符的编码问题
else:
raise FileNotFoundError("Not this File!") # 如果多媒体文件路径不存在,必须中断
def get_image_format(self):
'''获取图片的格式,比如JPEG, PNG, BMP等'''
try:
image_codec = re.findall(r"Format\s+:\s(.*)", self.info)[-1] # 取第最后一个Format字段
image_codec = image_codec.strip() # 去除前后的空格
if image_codec == "RGB":
image_codec = "BMP"
except:
image_codec = "undef" # 防止程序因为异常而中断
return image_codec
def get_image_resolution(self):
'''获取图片的分辨率'''
try:
image_widget = re.findall(r'Width\s+:\s(.*)pixels', self.info)[-1]
image_widget = image_widget.replace(" ", "")
image_height = re.findall(r'Height\s+:\s(.*)pixels', self.info)[-1]
image_height = image_height.replace(" ", "")
image_resolution = image_widget + "x" + image_height
except:
image_resolution = "undef" # 防止程序因为异常而中断
return image_resolution
def get_image_bit_depth(self):
'''获取图片的位深度'''
try:
image_bit_depth = re.findall(r"Bit depth\s+:\s(.*bit)s", self.info)[-1].strip()
image_bit_depth = image_bit_depth.replace(" ", "") # 去空格
except:
image_bit_depth = "undef" # 防止程序因为异常而中断
return image_bit_depth
def get_image_container(self):
'''获取图片容器,即文件后缀名'''
_, image_container = os.path.splitext(self.image_file)
if not image_container:
raise NameError("This file no extension")
image_container = image_container.replace(".", "")
image_container = image_container.lower() # 全部转成小写
return image_container
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 以下代码块,只是用来测试本模块的,一般不建议直接在这里大面积调用本模块'''
i_obj = ImageInfoGetter("C:\\img.jpg")
image_format = i_obj.get_image_format()
print(image_format)
image_resolution = i_obj.get_image_resolution()
print(image_resolution)
image_bit_depth = i_obj.get_image_bit_depth()
print(image_bit_depth)
image_container = i_obj.get_image_container()
print(image_container)
调用image_info.py模块并实现批量重命名
# coding=utf-8
import os
import image_info
from shutil import copyfile
curdir = os.getcwd()
# 输入文件夹,放入待重命名的图片
input_image_path = os.path.join(curdir, "Input_Image")
filelist = os.listdir(input_image_path) # 获取文件列表
# 输出文件夹,已命名的图片存放在这里
output_image_path = os.path.join(curdir, "Output_Image")
# 如果没有Output_Image这个文件夹,则创建这个文件夹
if not os.path.exists(output_image_path):
os.mkdir(output_image_path)
if filelist: # 如果文件列表不为空
for i in filelist: # 遍历文件列表
# 以下代码块,只是用来测试本模块的,一般不建议直接在这里大面积调用本模块'''
image_file = os.path.join(input_image_path, i)
i_obj = image_info.ImageInfoGetter(image_file)
image_format = i_obj.get_image_format()
image_resolution = i_obj.get_image_resolution()
image_bit_depth = i_obj.get_image_bit_depth()
image_container = i_obj.get_image_container()
new_image_name = image_format + "_" + image_resolution + "_" + image_bit_depth + "_" \
+ image_container + "." + image_container
print(new_image_name)
new_image_file = os.path.join(output_image_path, new_image_name)
copyfile(image_file, new_image_file) # 复制文件
else:
print("It's a Empty folder, please input the image files which need to be renamed firstly!!!")
os.system("pause")
本案例练手素材下载
包含:mediainfo.exe(更建议丢到某个环境变量里去),
各种编码格式的图片文件,image_info.py模块,rename_image.py批处理脚本
点我下载
运行效果如下:
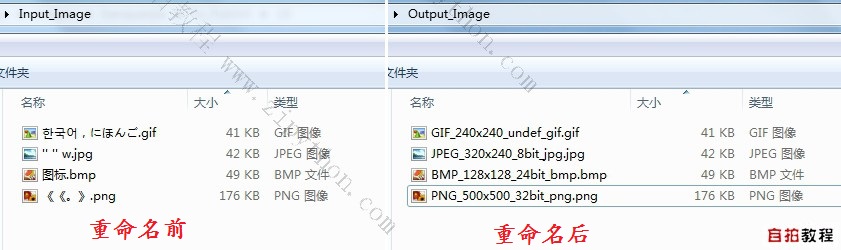
以上可以看出,输入输出文件架构的好处, 我只需要将不同名字不同字符的,
待重命名的图片丢到Input_Image文件夹下,运行程序脚本后查看Output_Image输出文件,
就可以测试脚本的运行是否正常,健壮性(容错)是否符合要求,从而对这个程序脚本实现了“灰盒测试”。
小提示:
比如Android手机,Google推出了CDD(Compatibiltiy Definition Document兼容性定义文档),
其第5部分,涉及了很多图片编解码格式的规定:
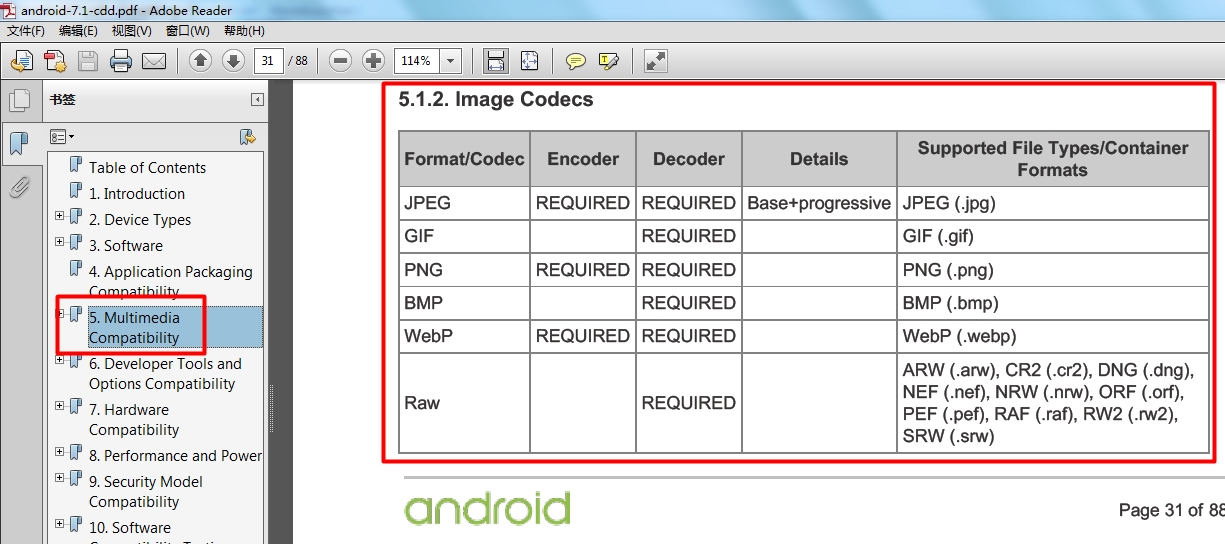
这就是Android最主要的图片多媒体编解码测试需求。
加载全部内容