matplotlib绘制多子图共享鼠标光标的方法示例
mighty13 人气:0这篇文章主要介绍了matplotlib绘制多子图共享鼠标光标的方法示例,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
matplotlib官方除了提供了鼠标十字光标的示例,还提供了同一图像内多子图共享光标的示例,其功能主要由widgets模块中的MultiCursor类提供支持。
MultiCursor类与Cursor类参数类似,差异主要在:
Cursor类参数只有一个ax,即需要显示光标的子图;MultiCursor类参数为canvas和axes,其中axes为需要共享光标的子图列表。Cursor类中,光标默认是十字线;MultiCursor类中,光标默认为竖线。
官方示例
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.widgets import MultiCursor t = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01) s1 = np.sin(2*np.pi*t) s2 = np.sin(4*np.pi*t) fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, sharex=True) ax1.plot(t, s1) ax2.plot(t, s2) multi = MultiCursor(fig.canvas, (ax1, ax2), color='r', lw=1) plt.show()
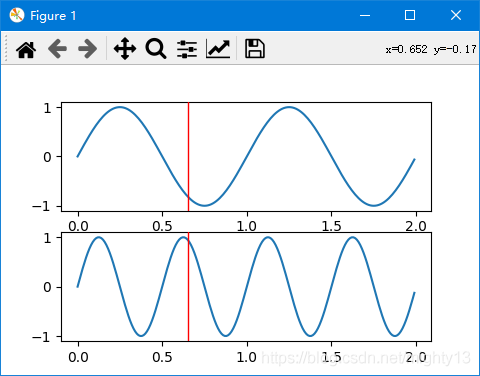
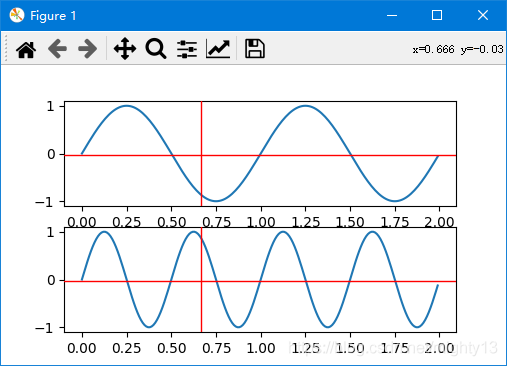
简易修改版
multi = MultiCursor(fig.canvas, (ax1, ax2), color='r', lw=1, horizOn=True, vertOn=True)
MultiCursor类源码
class MultiCursor(Widget):
"""
Provide a vertical (default) and/or horizontal line cursor shared between
multiple axes.
For the cursor to remain responsive you must keep a reference to it.
Example usage::
from matplotlib.widgets import MultiCursor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, sharex=True)
t = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
ax1.plot(t, np.sin(2*np.pi*t))
ax2.plot(t, np.sin(4*np.pi*t))
multi = MultiCursor(fig.canvas, (ax1, ax2), color='r', lw=1,
horizOn=False, vertOn=True)
plt.show()
"""
def __init__(self, canvas, axes, useblit=True, horizOn=False, vertOn=True,
**lineprops):
self.canvas = canvas
self.axes = axes
self.horizOn = horizOn
self.vertOn = vertOn
xmin, xmax = axes[-1].get_xlim()
ymin, ymax = axes[-1].get_ylim()
xmid = 0.5 * (xmin + xmax)
ymid = 0.5 * (ymin + ymax)
self.visible = True
self.useblit = useblit and self.canvas.supports_blit
self.background = None
self.needclear = False
if self.useblit:
lineprops['animated'] = True
if vertOn:
self.vlines = [ax.axvline(xmid, visible=False, **lineprops)
for ax in axes]
else:
self.vlines = []
if horizOn:
self.hlines = [ax.axhline(ymid, visible=False, **lineprops)
for ax in axes]
else:
self.hlines = []
self.connect()
def connect(self):
"""Connect events."""
self._cidmotion = self.canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event',
self.onmove)
self._ciddraw = self.canvas.mpl_connect('draw_event', self.clear)
def disconnect(self):
"""Disconnect events."""
self.canvas.mpl_disconnect(self._cidmotion)
self.canvas.mpl_disconnect(self._ciddraw)
def clear(self, event):
"""Clear the cursor."""
if self.ignore(event):
return
if self.useblit:
self.background = (
self.canvas.copy_from_bbox(self.canvas.figure.bbox))
for line in self.vlines + self.hlines:
line.set_visible(False)
def onmove(self, event):
if self.ignore(event):
return
if event.inaxes is None:
return
if not self.canvas.widgetlock.available(self):
return
self.needclear = True
if not self.visible:
return
if self.vertOn:
for line in self.vlines:
line.set_xdata((event.xdata, event.xdata))
line.set_visible(self.visible)
if self.horizOn:
for line in self.hlines:
line.set_ydata((event.ydata, event.ydata))
line.set_visible(self.visible)
self._update()
def _update(self):
if self.useblit:
if self.background is not None:
self.canvas.restore_region(self.background)
if self.vertOn:
for ax, line in zip(self.axes, self.vlines):
ax.draw_artist(line)
if self.horizOn:
for ax, line in zip(self.axes, self.hlines):
ax.draw_artist(line)
self.canvas.blit()
else:
self.canvas.draw_idle()
加载全部内容