从头学pytorch(十四):lenet
core! 人气:2卷积神经网络
在之前的文章里,对28 X 28的图像,我们是通过把它展开为长度为784的一维向量,然后送进全连接层,训练出一个分类模型.这样做主要有两个问题
- 图像在同一列邻近的像素在这个向量中可能相距较远。它们构成的模式可能难以被模型识别。
- 对于大尺寸的输入图像,使用全连接层容易造成模型过大。假设输入是高和宽均为1000像素的彩色照片(含3个通道)。即使全连接层输出个数仍是256,该层权重参数的形状是\(3,000,000\times 256\),按照参数为float,占用4字节计算,它占用了大约3000000 X 256 X4bytes=3000000kb=3000M=3G的内存或显存。
很显然,通过使用卷积操作可以有效的改善这两个问题.关于卷积操作,池化操作等,参见置顶文章https://www.cnblogs.com/sdu20112013/p/10149529.html.
LENET
lenet是比较早期提出来的一个神经网络,其结构如下图所示.
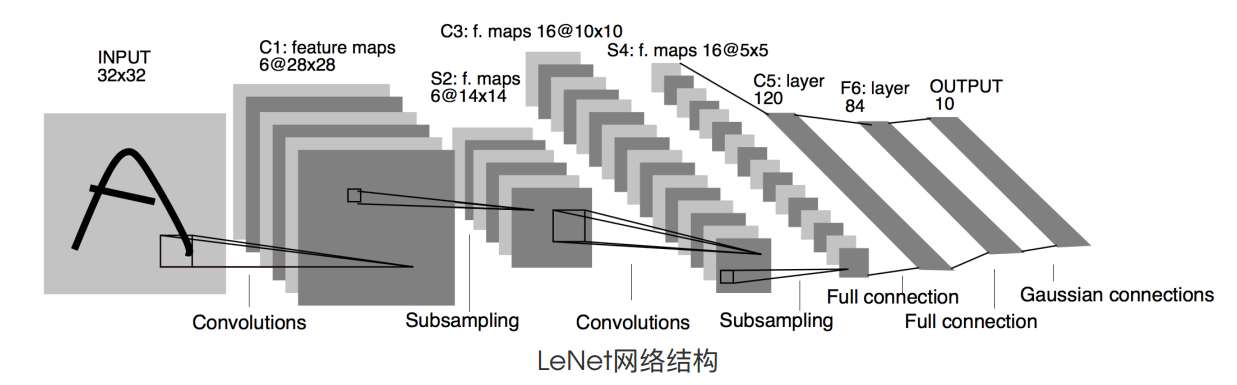
LeNet的结构比较简单,就是2次重复的卷积激活池化后面接三个全连接层.卷积层的卷积核用的5 X 5,池化用的窗口大小为2 X 2,步幅为2.
对我们的输入(28 x 28)来说,卷积层得到的输出shape为[batch,16,4,4],在送入全连接层前,要reshape成[batch,16x4x4].可以理解为通过卷积,对没一个样本,我们
都提取出来了16x4x4=256个特征.这些特征用来识别图像里的空间模式,比如线条和物体局部.
全连接层块含3个全连接层。它们的输出个数分别是120、84和10,其中10为输出的类别个数。
net0 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5), # in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # kernel_size, stride
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
batch_size=64
X = torch.randn((batch_size,1,28,28))
out=net0(X)
print(out.shape)输出
torch.Size([64, 16, 4, 4])这就是上面我们说的"对我们的输入(28 x 28)来说,卷积层得到的输出shape为[batch,16,4,4]"的由来.
模型定义
至此,我们可以给出LeNet的定义:
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5), # in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # kernel_size, stride
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16*4*4, 120),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10)
)
def forward(self, img):
feature = self.conv(img)
output = self.fc(feature.view(img.shape[0], -1))
return output在forward()中,在输入全连接层之前,要先feature.view(img.shape[0], -1)做一次reshape.
我们用gpu来做训练,所以要把net的参数都存储在显存上:
net = LeNet().cuda()数据加载
import torch
from torch import nn
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
import learntorch_utils
batch_size,num_workers=64,4
train_iter,test_iter = learntorch_utils.load_data(batch_size,num_workers)load_data定义于learntorch_utils.py,如下:
def load_data(batch_size,num_workers):
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/home/schttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/disk/keepgoing/learn_pytorch/Datasets/FashionMNIST',
train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/home/schttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/disk/keepgoing/learn_pytorch/Datasets/FashionMNIST',
train=False, download=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers)
return train_iter,test_iter定义损失函数
l = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
定义优化器
opt = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr=0.01)
定义评估函数
def test():
acc_sum = 0
batch = 0
for X,y in test_iter:
X,y = X.cuda(),y.cuda()
y_hat = net(X)
acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
batch += 1
print('acc:%f' % (acc_sum/(batch*batch_size)))训练
- 前向传播
- 计算loss
- 梯度清空,反向传播
- 更新参数
num_epochs=5
def train():
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum,batch=0,0
for X,y in train_iter:
X,y = X.cuda(),y.cuda() #把tensor放到显存
y_hat = net(X) #前向传播
loss = l(y_hat,y) #计算loss,nn.CrossEntropyLoss中会有softmax的操作
opt.zero_grad()#梯度清空
loss.backward()#反向传播,求出梯度
opt.step()#根据梯度,更新参数
train_l_sum += loss.item()
batch += 1
print('epoch %d,train_loss %f' % (epoch + 1,train_l_sum/(batch*batch_size)))
test()输出如下:
epoch 1,train_loss 0.011750
acc:0.799064
epoch 2,train_loss 0.006442
acc:0.855195
epoch 3,train_loss 0.005401
acc:0.857584
epoch 4,train_loss 0.004946
acc:0.874602
epoch 5,train_loss 0.004631
acc:0.874403加载全部内容