SpringBoot Application深入学习
空夜 人气:0本节主要介绍SpringBoot Application类相关源码的深入学习。
主要包括:
- SpringBoot应用自定义启动配置
- SpringBoot应用生命周期,以及在生命周期各个阶段自定义配置。
本节采用SpringBoot 2.1.10.RELASE,对应示例源码在:https://github.com/laolunsi/spring-boot-examples
SpringBoot应用启动过程:
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(DemoApplication.class);
application.run(args);一、Application类自定义启动配置
创建SpringApplication对象后,在调用run方法之前,我们可以使用SpringApplication对象来添加一些配置,比如禁用banner、设置应用类型、设置配置文件(profile)
举例:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(DemoApplication.class);
// 设置banner禁用
application.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
// 将application-test文件启用为profile
application.setAdditionalProfiles("test");
// 设置应用类型为NONE,即启动完成后自动关闭
application.setWebApplicationType(WebApplicationType.NONE);
application.run(args);
}
} 也可以使用SpringApplicationBuilder类来创建SpringApplication对象,builder类提供了链式调用的API,更方便调用,增强了可读性。
new SpringApplicationBuilder(YqManageCenterApplication.class)
.bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF)
.profiles("test")
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.run(args);二、application生命周期
SpringApplication的生命周期主要包括:
- 准备阶段:主要包括加载配置、设置主bean源、推断应用类型(三种)、创建和设置SpringBootInitializer、创建和设置Application监听器、推断主入口类
- 运行阶段:开启时间监听、加载运行监听器、创建Environment、打印banner、创建和装载context、广播应用已启动、广播应用运行中
我们先来看一下源码的分析:
SpringBootApplication构造器:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 设置默认配置
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.addConversionService = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 设置主bean源
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 推断和设置应用类型(三种)
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 创建和设置SpringBootInitializer
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 创建和设置SpringBoot监听器
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 推断和设置主入口类
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}SpringApplication.run方法源码:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 开启时间监听
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// 加载Spring应用运行监听器(SpringApplicationRunListenter)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
// 创建environment(包括PropertySources和Profiles)
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印banner
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// 创建context(不同的应用类型对应不同的上下文)
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
// 装载context(其中还初始化了IOC容器)
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 调用applicationContext.refresh
this.refreshContext(context);
// 空方法
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop(); // 关闭时间监听;这样可以计算出完整的启动时间
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 广播SpringBoot应用已启动,会调用所有SpringBootApplicationRunListener里的started方法
listeners.started(context);
// 遍历所有ApplicationRunner和CommadnLineRunner的实现类,执行其run方法
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
// 广播SpringBoot应用运行中,会调用所有SpringBootApplicationRunListener里的running方法
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
// run出现异常时,处理异常;会调用报错的listener里的failed方法,广播应用启动失败,将异常扩散出去
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}三、application生命周期自定义配置
在SpringApplication的生命周期中,我们还可以添加一些自定义的配置。
下面的配置,主要是通过实现Spring提供的接口,然后在resources下新建META-INF/spring.factories文件,在里面添加这个类而实现引入的。
在准备阶段,可以添加如下自定义配置:
3.1 自定义ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类
@Order(100)
public class MyInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext) {
System.out.println("自定义的应用上下文初始化器:" + configurableApplicationContext.toString());
}
}再定义一个My2Initializer,设置@Order(101)
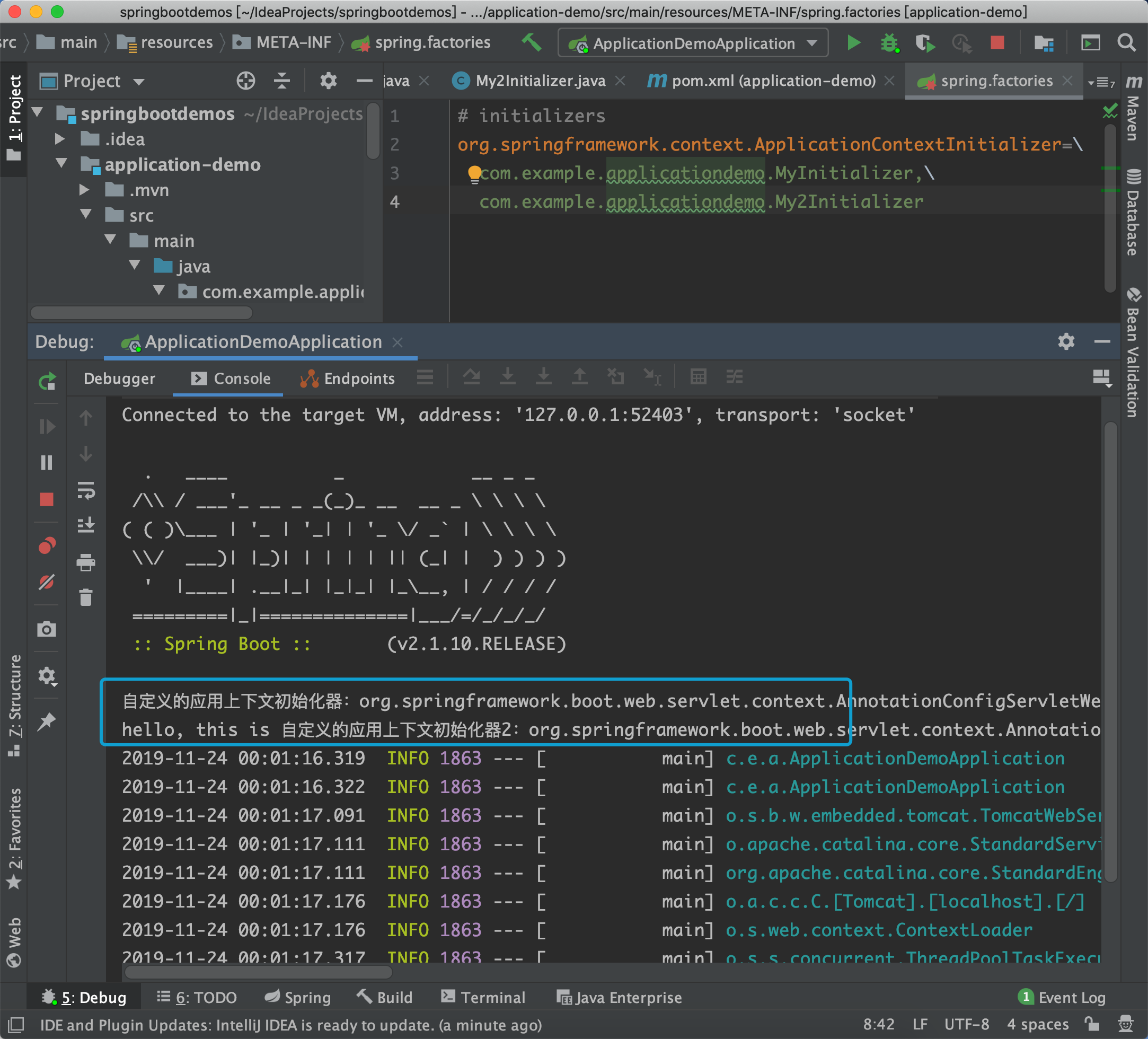
然后在spring.factories文件里如下配置:
# initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
com.example.applicationdemo.MyInitializer,\
com.example.applicationdemo.My2Initializer启动项目:
3.2 自定义ApplicationListener的实现类
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E var1);
}即监听ApplicationEvents类的ApplicationListener接口的实现类。
首先查看有多少种ApplicationEvents:
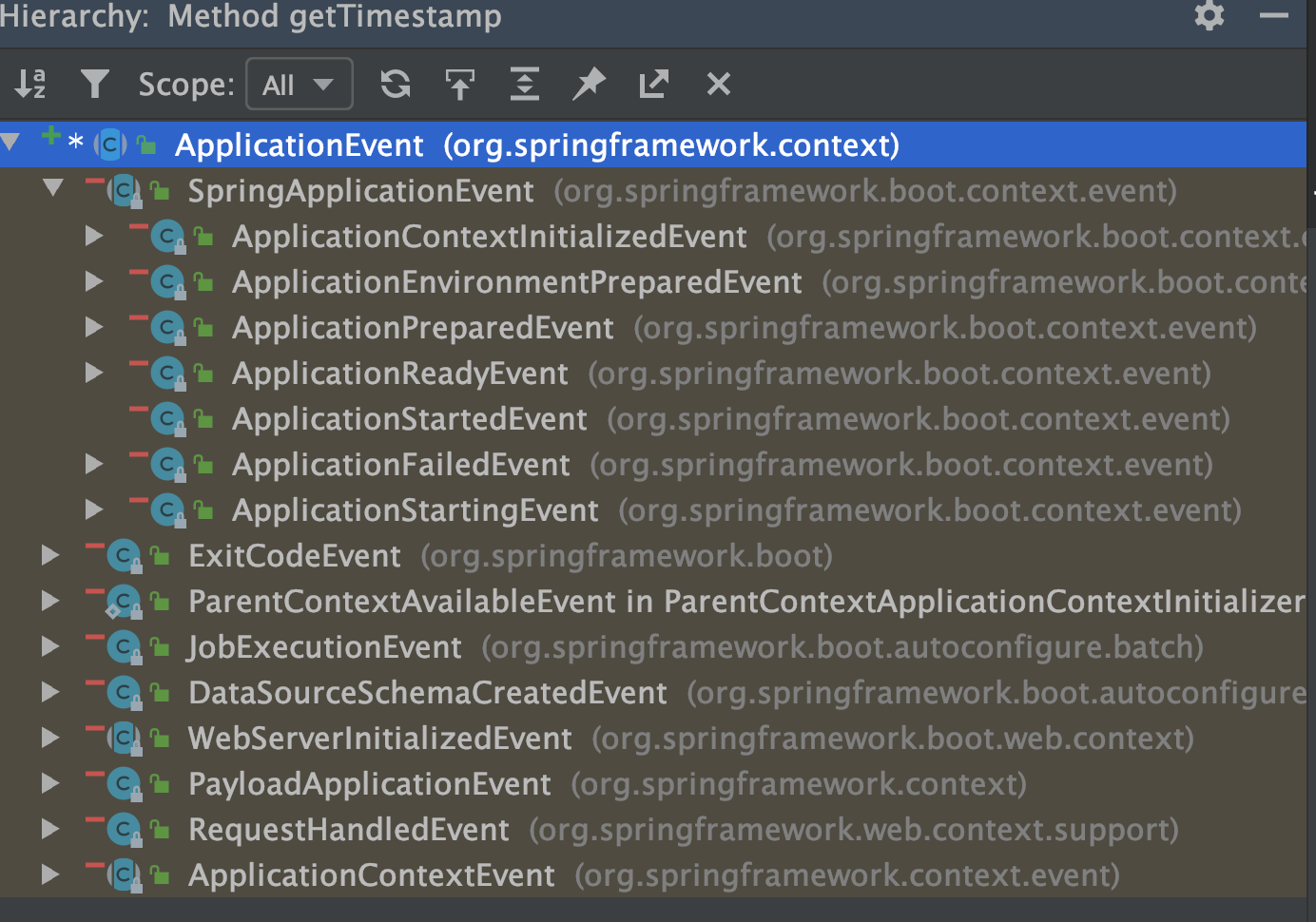
里面还可以进行拆分。
我们这里设置两个ApplicationListener,都用于监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
@Order(200)
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent applicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
System.out.println("MyApplicationListener: 应用环境准备完毕" + applicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.toString());
}
}在spring.factories中加入applicationListener的配置:
# application-listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
com.example.applicationdemo.MyApplicationListener,\
com.example.applicationdemo.MyApplicationListener2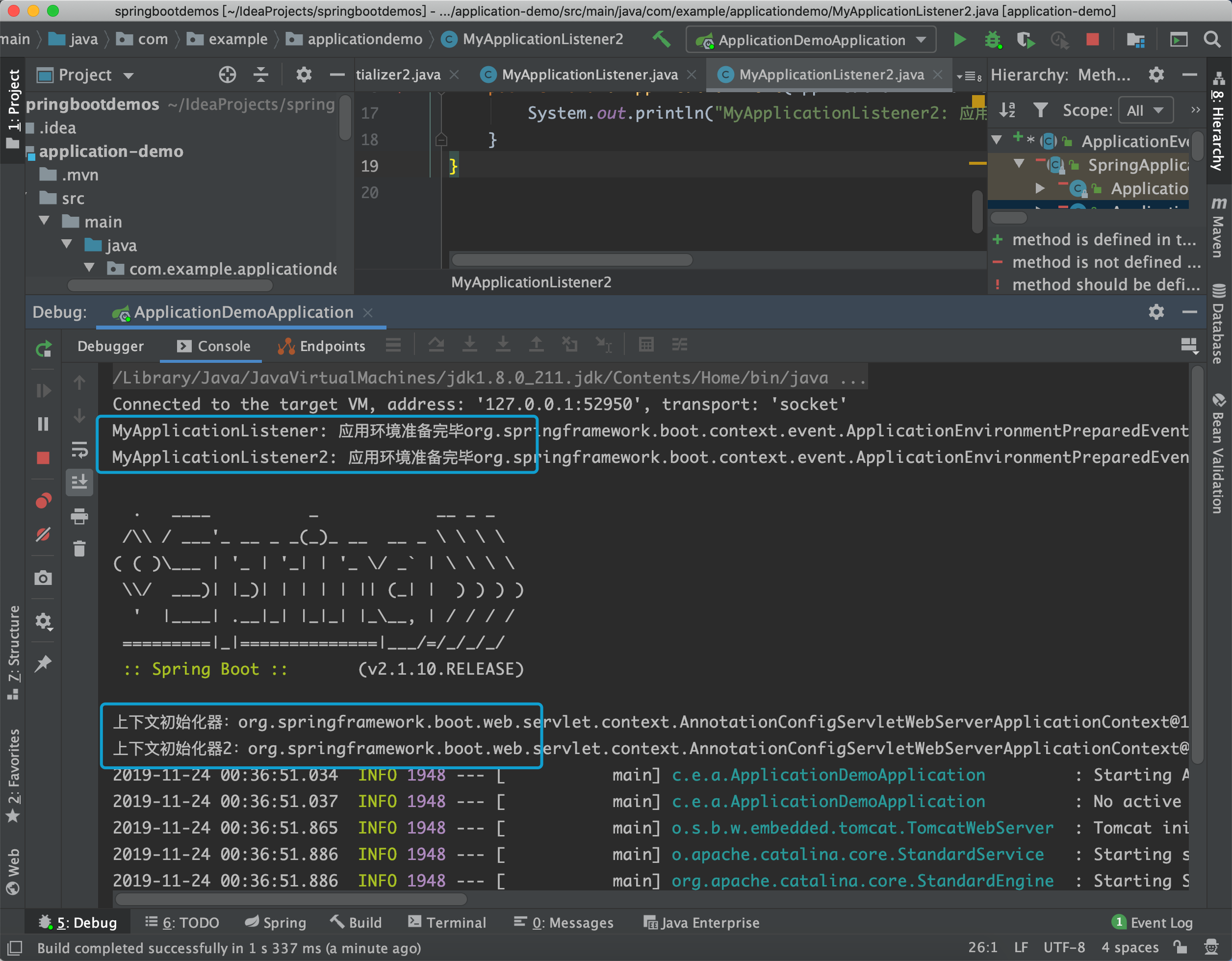
在启动阶段,可以添加如下自定义配置:
3.3 自定义SpringBootRunListener的实现类
监听整个SpringBoot应用生命周期
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
// 应用启动
void starting();
// 应用ConfigurableEnvironment准备完毕,此刻可以将其调整
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
// 上下文准备完毕
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 上下文装载完毕
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 启动完成(Beans已经加载到容器中)
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 应用运行中
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 应用运行失败
void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception);
}我们可以自定义SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类,通过重写以上方法来定义自己的listener。
比如:
public class MyRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
// 注意要加上这个构造器,两个参数都不能少,否则启动会报错,报错的详情可以看这个类的最下面
public MyRunListener(SpringApplication springApplication, String[] args) {
}
@Override
public void starting() {
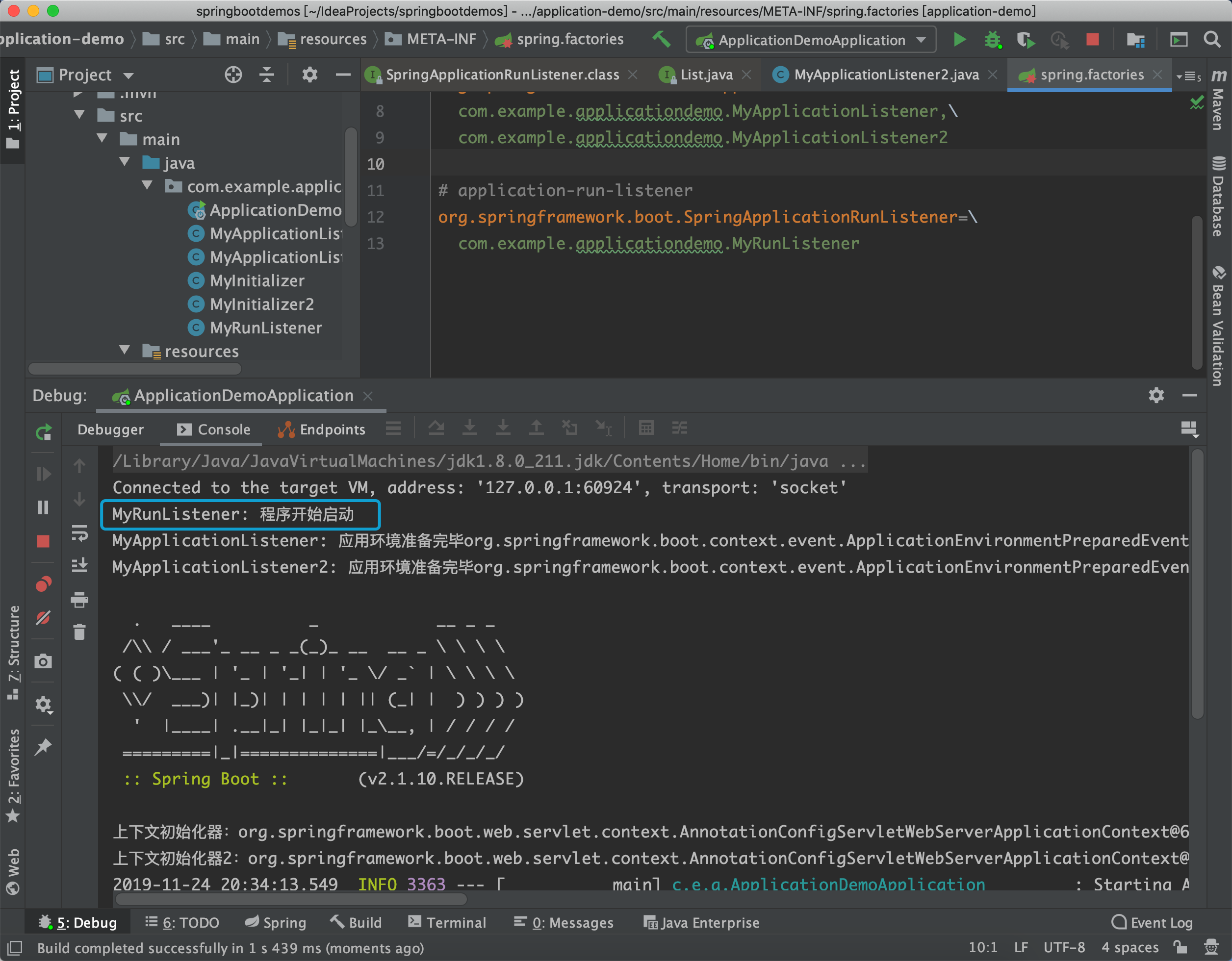
System.out.println("MyRunListener: 程序开始启动");
}
// 其他方法省略,不做修改
}然后在spring.factories文件中添加这个类:
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
com.example.applicationdemo.MyRunListener启动:
3.4 自定义ApplicationRunner或CommandLineRunner
application的run方法中,有这样一行:
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);仔细分析源码,发现这一句的作用是:SpringBoot应用启动过程中,会遍历所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner,执行其run方法。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
Iterator var4 = (new LinkedHashSet(runners)).iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Object runner = var4.next();
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
this.callRunner((ApplicationRunner)runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
this.callRunner((CommandLineRunner)runner, args);
}
}
}@FunctionalInterface
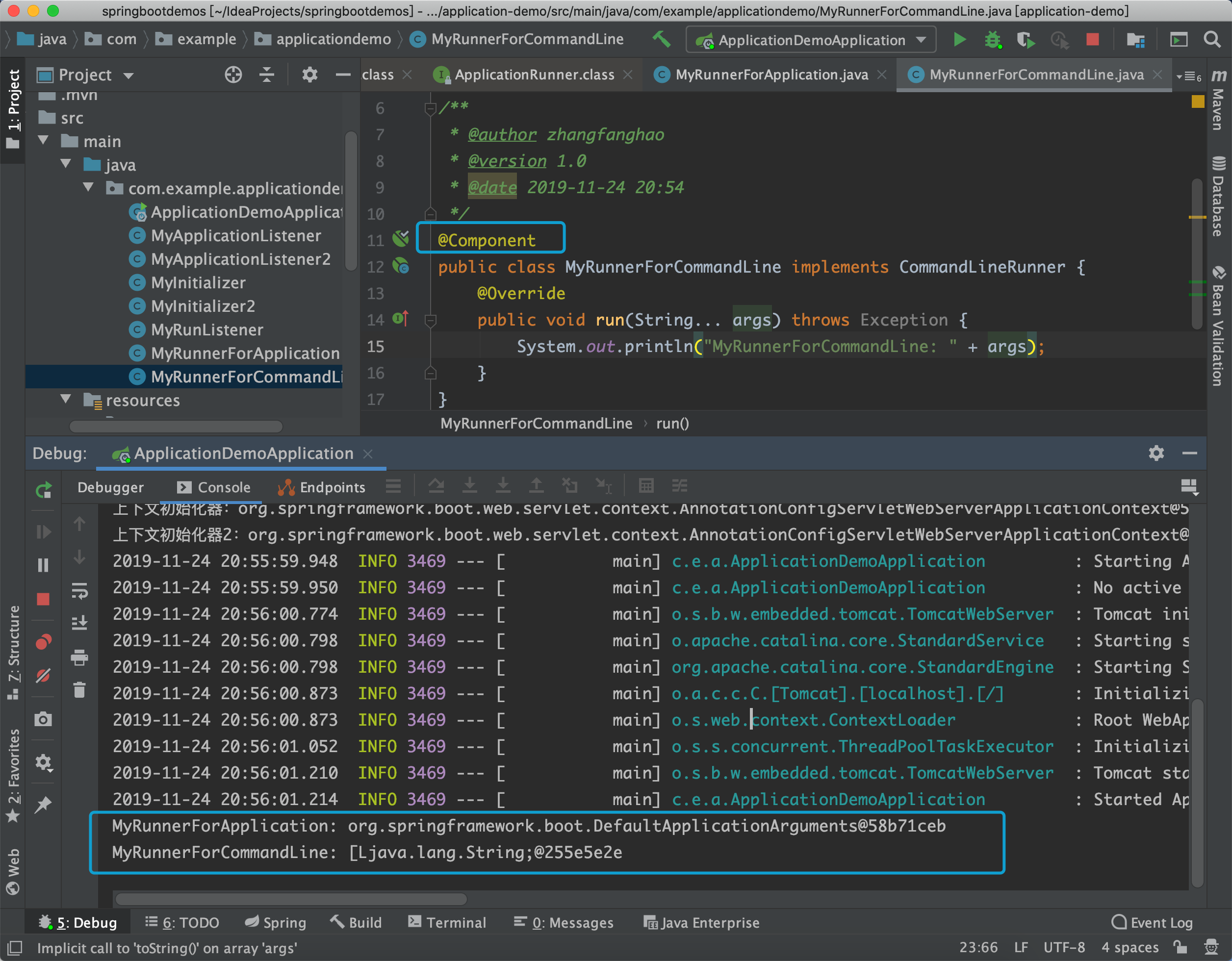
public interface CommandLineRunner {
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}分别定义一个实现类,添加@Component,这两个实现类不需要在spring.factories中配置。
好了,关于这些自定义配置的具体使用,后续会继续进行介绍,请持续关注!感谢!
具体示例代码请去https://github.com/laolunsi/spring-boot-examples查看。
加载全部内容