Kickstart Round H 2019 Problem B. Diagonal Puzzle
basasuya 人气:5有史以来打得最差的一次kickstart竟然发生在winter camp出结果前的最后一次ks = = 感觉自己的winter camp要凉了
究其原因,无非自己太眼高手低,好好做B, C的小数据,也不至于最后才AC了第一题吧
B题,我花了两个小时也没AC = =,我的做法和题解大数据的第一种类似。
- 我们可以发现,每个点只由两个diagonal决定,然后每个diagonal至多做一次,做两次相当于白做嘛。
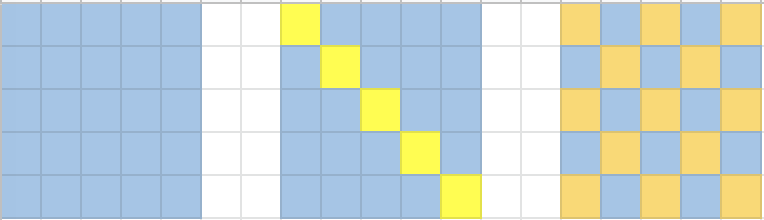
然后我们发现如果先讨论最长正对角线是否取,也就是从(0,0)到 (n-1,n-1),可以直接讨论出其中一半的diagonal和一半点的取舍问题,以5*5为例,如图所示。对于最长的正对角线上的每个元素,如果是'.', 那么必要动用他们所对应的反对角线才能翻过来,反之比不会动用这些反对角线。之后,如果这些被讨论到的反对角线上如果存在'.',那么我们就需要动用他们所对用的正对角线进行翻转。之后我们再判断是否所有点都被翻转了(图中最右边一张图重的所有黄色点)
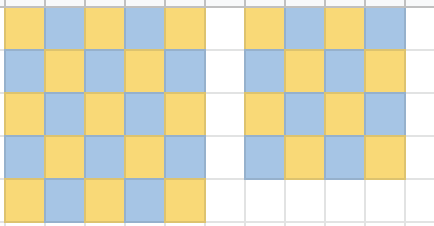
上步我们发现我们只讨论一半的点和对角线的操作。对于 另一半,偶数长度边和奇数长度边的讨论是有些许不同的(如下图所示,奇数长度边的反最长对角线不在这一半中)。但是大方向一样,寻找剩下点中反对角线最长的一条,然后做和第二步类似的操作。要注意2,3两步都要先讨论对角线翻不翻转
细节还是看下代码 = = 写的有点长
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <complex>
#include <cassert>
#include <random>
#include <cstring>
#include <numeric>
#define mp make_pair
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define null NULL
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
#define sz(a) (int)a.size()
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
#define bitCount(a) __builtin_popcount(a)
template<class T> int gmax(T &a, T b) { if (b > a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> int gmin(T &a, T b) { if (b < a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
using namespace std;
string to_string(string s) { return '"' + s + '"'; }
string to_string(const char* s) { return to_string((string) s); }
string to_string(bool b) { return (b ? "true" : "false"); }
template <typename A, typename B>
string to_string(pair<A, B> p) { return "(" + to_string(p.first) + ", " + to_string(p.second) + ")"; }
template <typename A>
string to_string(A v) { bool first = true; string res = "{"; for (const auto &x : v) { if (!first) { res += ", "; } first = false; res += to_string(x); } res += "}"; return res; }
void debug_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T) { cerr << " " << to_string(H); debug_out(T...); }
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
char seq[105][105];
int n;
int id1[105][105];
int id2[105][105];
int tmp[105][105];
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > s1;
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > s2;
void init() {
s1.clear(); s2.clear();
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; --i) {
int x = i; int y = 0;
vector<pair<int, int> > tmp;
while(1) {
id1[x][y] = cnt;
tmp.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
x ++; y ++;
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n) break;
}
s1.push_back(tmp);
cnt ++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n-1; ++i) {
int x = 0; int y = i;
vector<pair<int, int> > tmp;
while(1) {
id1[x][y] = cnt;
tmp.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
x ++; y ++;
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n) break;
}
s1.push_back(tmp);
cnt ++;
}
cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n-1; ++i) {
int x = i; int y = 0;
vector<pair<int, int> > tmp;
while(1) {
id2[x][y] = cnt;
tmp.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
x --; y ++;
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n) break;
}
s2.push_back(tmp);
cnt ++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n-1; ++i) {
int x = n-1; int y = i;
vector<pair<int, int> > tmp;
while(1) {
id2[x][y] = cnt;
tmp.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
x --; y ++;
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n) break;
}
s2.push_back(tmp);
cnt ++;
}
// debug(s1, s2);
}
int solve1(int ty) {
// debug(ty);
int cnt = ty == 1; bool suc = true;
map<int, int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
tmp[i][j] = seq[i][j] == '#';
}
}
vector<int> diagnol;
int target = s1.size() / 2;
for(int i = 0, len = s1[target].size(); i < len; ++i) {
int x = s1[target][i].first; int y = s1[target][i].second;
// debug(tmp[x][y], (ty == 1));
if(tmp[x][y] == (ty == 1) ) {
cnt ++;
diagnol.push_back(id2[x][y]);
// debug("yingying");
}
if(ty == 1) tmp[x][y] = !tmp[x][y];
}
// debug(diagnol);
for(int i = 0, len = diagnol.size(); i < len; ++i) {
for(int j = 0, len2 = s2[diagnol[i]].size(); j < len2; ++j) {
int x = s2[diagnol[i]][j].first; int y = s2[diagnol[i]][j].second;
// debug(x, y);
tmp[x][y] = !tmp[x][y];
}
}
for(int i = target % 2; i < s1.size();i += 2) {
for(auto Point : s1[i]) {
int x = Point.first; int y = Point.second;
if(tmp[x][y] == 0) {
// debug(x, y);
mp[id1[x][y]] ++;
}
}
}
for(auto it : mp) {
// debug(it.first, it.second);
cnt ++;
if(s1[it.first].size() != it.second) {
suc = false; break;
}
}
if(suc == true) {
// debug(cnt);
return cnt;
}
else return INF;
}
int solve2(int ty) {
int cnt = ty == 1; bool suc = true;
map<int, int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
tmp[i][j] = seq[i][j] == '#';
}
}
vector<int> diagnol;
int target = s2.size() / 2;
if(n % 2) target --;
for(int i = 0, len = s2[target].size(); i < len; ++i) {
int x = s2[target][i].first; int y = s2[target][i].second;
if(tmp[x][y] == (ty == 1) ) {
cnt ++;
diagnol.push_back(id1[x][y]);
}
if(ty == 1) tmp[x][y] = !tmp[x][y];
}
// debug(diagnol);
for(int i = 0, len = diagnol.size(); i < len; ++i) {
for(int j = 0, len2 = s1[diagnol[i]].size(); j < len2; ++j) {
int x = s1[diagnol[i]][j].first; int y = s1[diagnol[i]][j].second;
tmp[x][y] = !tmp[x][y];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < s2.size();i += 2) {
for(auto Point : s2[i]) {
int x = Point.first; int y = Point.second;
if(tmp[x][y] == 0) {
// debug(i, j)
mp[id2[x][y]] ++;
}
}
}
for(auto it : mp) {
cnt ++;
if(s2[it.first].size() != it.second) {
suc = false; break;
}
}
if(suc == true) return cnt;
else return INF;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int cas = 1; cas <= T; ++cas) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%s", seq[i]);
}
init();
printf("Case #%d: ", cas);
if(n == 1) {
printf("%d\n", seq[0][0] == '.');
continue;
}
printf("%d\n", min(solve1(1), solve1(0)) + min(solve2(1), solve2(0)) );
}
return 0;
}加载全部内容