vue-router 控制路由权限的实现
__此间少年 人气:0本文着重讲解了vue-router 控制路由权限的实现,文中通过代码实例讲解的非常细致,对大家的工作和学习具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
注意:vue-router是无法完全控制前端路由权限。
1、实现思路
使用vue-router实例函数addRoutes动态添加路由规则,不多废话直接上思维导图:
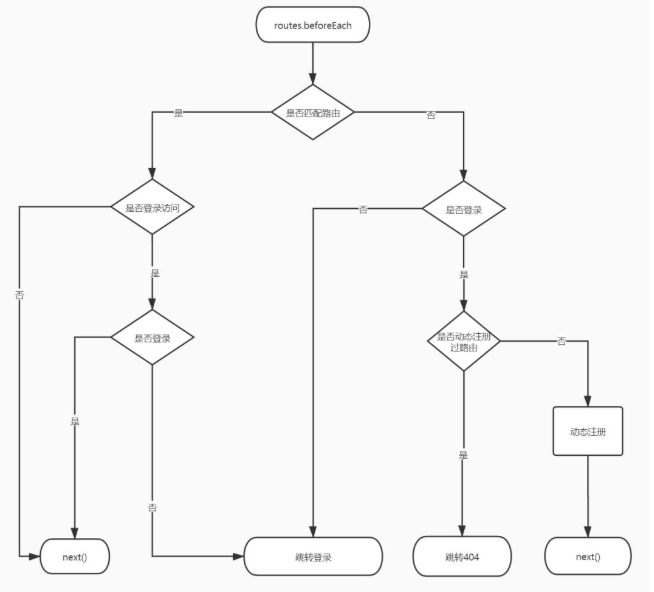
2、实现步骤
2.1、路由匹配判断
// src/router.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Store from '@/store';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import Cookie from 'js-cookie';
const routers = new Router({
base : "/test",
// 定义默认路由比如登录、404、401等
routes : [{
path : "/404",
// ...
},{
path : "/401",
// ...
}]
})
// ...省略部分代码
routes.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const { meta, matched, path } = to;
let isMatched = matched && matched.length > 0; // 是否匹配路由
if(isMatched){
}else{
}
})
通过vue-router前置守卫beforeEach中参数to来简单的实现匹配结果
2.2、登录访问控制
在实际开发中路由常常存在是否登录访问和是否需要登录访问的情况,于是可以通过token和路由配置meta信息中定义isAuth字段来区分。
// ...省略部分重复代码
const openRouters = [];
const authRouters = [{
path : "order/list",
// ...
meta : {
// 是否身份验证(至于默认定义false还是true由开发者自定义)
isAuth : true
}
}];
routes.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const { meta, matched, path } = to;
let isMatched = matched && matched.length > 0; // 是否匹配路由
let isLogin = Cookie.get("token") || null;
let { isAuth } = (meta || {});
if(isMatched){
// 匹配到路由
if(isAuth){
// 需要登录访问
if(isLogin){
// 已登录访问
next(); // 调用钩子函数
}else{
// 未登录访问
next("/login"); // 跳转登录
}
}else{
// 不需要登录访问
next(); // 调用钩子函数
}
}else{
// 未匹配到路由
if(isLogin){
// 已登录访问
}else{
// 未登录访问
next("/login"); // 跳转登录
}
}
})
2.3、动态添加路由规则
实现动态添加路由规则只需要使用vue-router实例方法router.addRoutes(routes: Array) 。
那么问题来了,我们怎么才能获取到需要动态添加的路由规则呢?
2.4、构建路由规则匹配函数
假如后台获取到的路由权限列表是这样的:
[{
resourceUrl : "/order/list",
childMenu : ...
}]
为了对比用户权限和路由是否匹配我们需要提取出权限路由数组
// 简单的通过递归获取到了所有权限url
export function getAuthRouters(authMenu) {
let authRouters = [];
(authMenu || []).forEach((item) => {
const { resourceUrl, childMenu } = item;
resourceUrl && authRouters.push(resourceUrl);
if (childMenu && childMenu.length > 0) {
// 合并子级菜单
authRouters = [...authRouters, ...getAuthRouters(childMenu)];
}
});
return authRouters;
}
通过getAuthRouters函数获取到了所有用户路由权限,接下来是要怎么和vue-router路由匹配呢?
这要和(我这里使用的是RBAC模型)系统配置权限关联上。vue-router路由规则要和权限配置保持一致。所以通过递归动态拼接vue-router路由规则和用户拥有的路由权限做对比。如果匹配就保留该路由;然后得到一份过滤后的vue-router路由规则配置。最后通过实例方法addRoutes添加路由规则。具体实现代码如下:
// src/utils/index.js
const { pathToRegexp } = require('path-to-regexp');
export function createAuthRouters(authRouters) {
const isAuthUrl = (url) => {
return (authRouters || []).some((cUrl) => {
return pathToRegexp(url).toString() === pathToRegexp(cUrl).toString();
});
};
return function createRouters(routers, upperPath) {
let nRouters = [];
(routers || []).forEach((item) => {
const { children, path, name } = item;
let isMatched = false,
nItem = { ...item },
fullPath = `${upperPath || ''}/${path}`.replace(/\/{2,}/, '/'),
nChildren = null;
children && (nChildren = createRouters(children, fullPath));
// 1.当前路由匹配
if (isAuthUrl(fullPath)) {
isMatched = true;
}
// 2.存在子路由匹配
if (nChildren && nChildren.length > 0) {
nItem.children = nChildren;
isMatched = true;
}
// 特殊处理(不需要可以删除)
if(name === "home"){
isMatched = true;
}
// nItem
isMatched && nRouters.push(nItem);
});
return nRouters;
};
}
值得注意的是createAuthRouters方法通过变量isMatched控制是否保留,之所以通过变量来决定是因为嵌套路由中父路由可能无法匹配,但是子路由能匹配所以父路由规则也需要子路参与是否保留。比如:
// 路由规则
const routers = new Router({
base : "/test",
// 定义默认路由比如登录、404、401等
routes : [{
path : "/",
...
children : [{
path : "login",
...
},{
path : "about",
...
},{
path : "order",
...
children : [{
path : "id"
}]
}]
}]
})
// 用户权限
["/order/id"]; // 在匹配的过程中 "/" 不等于 "/order/id" 、"/" 不等于 "/order" 但是子路由 "/order/id" == "/order/id" 所以不但要保留 path : "/",还得保留 path : "order" 嵌套层。
2.5、动态注册
// ...省略部分重复代码
const openRouters = [];
const authRouters = [{
path : "order/list",
// ...
meta : {
// 是否身份验证(至于默认定义false还是true由开发者自定义)
isAuth : true
}
}];
/* 动态注册路由 */
async function AddRoutes() {
// 获取用户路由权限
let res = await POST(API.AUTH_RESOURCE_LISTSIDEMENU);
try {
const { code, data } = res || {};
if (code === '000') {
let newAuthRoutes = createAuthRouters(getAuthRouters(data))(authRouters, routes.options.base);
// 注册路由
routes.addRoutes([].concat(newAuthRoutes, openRouters));
// 设置已注册
Store.commit('UPDATE_IS_ADD_ROUTERS', true);
// 保存菜单信息
Store.commit('UPDATE_MENU_INFO', data);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('>>> AddRoutes() - error:', error);
}
}
routes.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const { meta, matched, path } = to;
let isMatched = matched && matched.length > 0; // 是否匹配路由
let isLogin = Cookie.get("token") || null;
let { isAuth } = (meta || {});
if(isMatched){
// 匹配到路由
if(isAuth){
// 需要登录访问
if(isLogin){
// 已登录访问
next(); // 调用钩子函数
}else{
// 未登录访问
next("/login"); // 跳转登录
}
}else{
// 不需要登录访问
next(); // 调用钩子函数
}
}else{
// 未匹配到路由
if(isLogin){
// 已登录访问
AddRoutes();
next();
}else{
// 未登录访问
next("/login"); // 跳转登录
}
}
})
2.6、归类整理
/* 路由前置 */
let { origin } = window.location || {};
routes.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const { meta, matched, path } = to;
let isMatched = matched && matched.length > 0; // 是否匹配
let isAuth = (meta || {}).isAuth; // 是否授权访问
let { isAddRoutes } = Store.state; // 注册路由
let isLogin = Cookie.get('token') || null; // 是否登录
if ((isMatched && !isAuth) || (isMatched && isAuth && isLogin)) {
// next()
// 1.匹配路由 && 未登录访问
// 2.匹配路由 && 登录访问 && 登录
next();
} else if ((isMatched && isAuth && !isLogin) || (!isMatched && !isLogin)) {
// 登录
// 1.匹配路由 && 登录访问 && 未登录
// 2.未匹配路由 && 未登录
next(`/login?r=${origin}/e-lottery${path}`);
} else if (!isMatched && isLogin && isAddRoutes) {
// 404
// 1.未匹配路由 && 登录 && 动态注册路由
next('/404');
} else if (!isMatched && isLogin && !isAddRoutes) {
// 注册路由
// 1.未匹配路由 && 登录 && 未动态注册路由
AddRoutes();
next();
}
});
嗯! 这下看起来舒服多了。
3、完整实现代码
// src/utils/index.js
const { pathToRegexp } = require('path-to-regexp');
export function getAuthRouters(authMenu) {
let authRouters = [];
(authMenu || []).forEach((item) => {
const { resourceUrl, childMenu } = item;
resourceUrl && authRouters.push(resourceUrl);
if (childMenu && childMenu.length > 0) {
// 合并子级菜单
authRouters = [...authRouters, ...getAuthRouters(childMenu)];
}
});
return authRouters;
}
/**
*
* @param { Array } authRouters
*/
export function createAuthRouters(authRouters) {
const isAuthUrl = (url) => {
return (authRouters || []).some((cUrl) => {
return pathToRegexp(url).toString() === pathToRegexp(cUrl).toString();
});
};
return function createRouters(routers, upperPath) {
let nRouters = [];
(routers || []).forEach((item) => {
const { children, path, name } = item;
let isMatched = false,
nItem = { ...item },
fullPath = `${upperPath || ''}/${path}`.replace(/\/{2,}/, '/'),
nChildren = null;
children && (nChildren = createRouters(children, fullPath));
// 1.当前路由匹配
if (isAuthUrl(fullPath)) {
isMatched = true;
}
// 2.存在子路由匹配
if (nChildren && nChildren.length > 0) {
nItem.children = nChildren;
isMatched = true;
}
// 特殊处理
if(name === "home"){
isMatched = true;
}
// nItem
isMatched && nRouters.push(nItem);
});
return nRouters;
};
}
// src/router.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Store from '@/store';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import Cookie from 'js-cookie';
const openRouters = [];
const authRouters = [{
path : "order/list",
// ...
meta : {
// 是否身份验证(至于默认定义false还是true由开发者自定义)
isAuth : true
}
}];
/* 动态注册路由 */
async function AddRoutes() {
// 获取用户路由权限
let res = await POST(API.AUTH_RESOURCE_LISTSIDEMENU);
try {
const { code, data } = res || {};
if (code === '000') {
let newAuthRoutes = createAuthRouters(getAuthRouters(data))(authRouters, routes.options.base);
// 注册路由
routes.addRoutes([].concat(newAuthRoutes, openRouters));
// 设置已注册
Store.commit('UPDATE_IS_ADD_ROUTERS', true);
// 保存菜单信息
Store.commit('UPDATE_MENU_INFO', data);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('>>> AddRoutes() - error:', error);
}
}
/* 路由前置 */
let { origin } = window.location || {};
routes.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const { meta, matched, path } = to;
let isMatched = matched && matched.length > 0; // 是否匹配
let isAuth = (meta || {}).isAuth; // 是否授权访问
let { isAddRoutes } = Store.state; // 注册路由
let isLogin = Cookie.get('token') || null; // 是否登录
if ((isMatched && !isAuth) || (isMatched && isAuth && isLogin)) {
// next()
// 1.匹配路由 && 未登录访问
// 2.匹配路由 && 登录访问 && 登录
next();
} else if ((isMatched && isAuth && !isLogin) || (!isMatched && !isLogin)) {
// 登录
// 1.匹配路由 && 登录访问 && 未登录
// 2.未匹配路由 && 未登录
next(`/login?r=${origin}/e-lottery${path}`);
} else if (!isMatched && isLogin && isAddRoutes) {
// 404
// 1.未匹配路由 && 登录 && 动态注册路由
next('/404');
} else if (!isMatched && isLogin && !isAddRoutes) {
// 注册路由
// 1.未匹配路由 && 登录 && 未动态注册路由
AddRoutes();
next();
}
});
虽然前端能够通过vue-router实现对路由权限的控制,但是实际是伪权限控制,无法达到完全控制;强烈建议对于需要控制路由权限的系统采用后端控制。
到此这篇关于vue-router 控制路由权限的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关vue-router 控制路由权限内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!
加载全部内容