Vue watch原理
Young soul2 人气:0由于我在从源码看vue(v2.7.10)的computed的实现原理中详细的讲解过computed的实现,本篇跟computed的原理类似。我就带大家简单分析一下。
添加依赖
代码如下:
<template>
<div>
{{a}}
<button @click="addModule">新增</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TestWebpackTest",
mounted() {
console.log(this);
},
data() {
return {
num: 1,
a:2
};
},
watch:{
a: function (val, oldVal) {
console.log(val, oldVal)
},
},
methods: {
addModule() {
this.a++;
}
}
};
</script>
<style lang="scss">
div {
.test {
width: 10px;
height: 15px;
background-color: blue;
}
}
</style>初始化watch方法发生在initState(vm)方法中,该方法执行initWatch方法:
function initState(vm) {
var opts = vm.$options;
...
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}
...
function initWatch(vm, watch) {
for (var key in watch) {
var handler = watch[key];
if (isArray(handler)) {
for (var i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i]);
}
}
else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler);
}
}
}
...
function createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, handler, options) {
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler;
handler = handler.handler;
}
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
handler = vm[handler];
}
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options);
}initWatch函数会判断当前的watch方法a是不是个数组,不是数组执行else的 createWatcher(vm, key, handler)方法。主要执行vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)方法:
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (expOrFn, cb, options) {
var vm = this;
...
options = options || {};
options.user = true;
var watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options);
...
return function unwatchFn() {
watcher.teardown();
};
};$watch方法主要是实例化了一个观察者Watcher:
function Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options, isRenderWatcher) {
...
this.dirty = this.lazy; // for lazy watchers
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = [];
...
// expOrFn = 'a'
if (isFunction(expOrFn)) {
this.getter = expOrFn;
}
else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
...
}
this.value = this.lazy ? undefined : this.get();
}由于expOrFn是字符串’a’,所以会执行 parsePath(expOrFn)方法:
function parsePath(path) {
...
// ['a']
var segments = path.split('.');
return function (obj) {
for (var i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) {
if (!obj)
return;
obj = obj[segments[i]];
}
return obj;
};
}
该方法返回一个函数,并赋值给watcher实例的getter方法。此时执行完this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)方法,继续执行this.get()方法:
Watcher.prototype.get = function () {
pushTarget(this);
var value;
var vm = this.vm;
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
}
catch (e) {
...
}
finally {
...
popTarget();
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value;
};
该方法执行pushTarget将Dep.target设置为当前观察者(watcher),然后执行 this.getter.call(vm, vm)方法,由于getter方法是parsePath(expOrFn)方法的返回函数:
// obj = 'vm' segments = ['a']
function (obj) {
for (var i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) {
if (!obj)
return;
obj = obj[segments[i]];
}
return obj;
}这里可以看出遍历watch方法的key值,这里是’a’,然后去当前的vm实例中获取该变量,触发该变量的getter方法从而建立该观察者和该变量之间的关系。
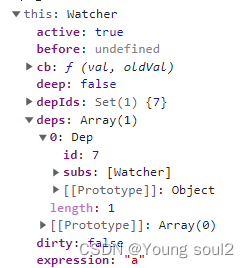
当前的watch方法a有一个deps放的就是发布者,该发布者的更新要触发订阅者,所以subs里面放的是watch方法a的watcher。
触发依赖
触发依赖的过程很简单,当数据改变时会触发变量的setter方法。会获取该变量的订阅者,并执行订阅者中的update方法:
Dep.prototype.notify = function (info) {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
var subs = this.subs.slice();
...
for (var i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
if (info) {
var sub = subs[i];
sub.onTrigger &&
sub.onTrigger(__assign({ effect: subs[i] }, info));
}
subs[i].update();
}
};
Watcher.prototype.update = function () {
// this.lazy = false
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true;
}
...
else {
queueWatcher(this);
}
};最后会执行queueWatcher(this)方法,接下来一系列的过程就是异步执行watcher.run()方法:
Watcher.prototype.run = function () {
if (this.active) {
var value = this.get();
if (value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep) {
// set new value
var oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
if (this.user) {
var info = "callback for watcher \"".concat(this.expression, "\"");
// this.cb是watch方法a的函数
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info);
}
else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
}
}
}
};
该方法获取将新值和旧值放入invokeWithErrorHandling函数中:
function invokeWithErrorHandling(handler, context, args, vm, info) {
var res;
try {
res = args ? handler.apply(context, args) : handler.call(context);
if (res && !res._isVue && isPromise(res) && !res._handled) {
res.catch(function (e) { return handleError(e, vm, info + " (Promise/async)"); });
res._handled = true;
}
}
catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, info);
}
return res;
}该方法执行回调,至此watch方法a执行完毕。
总结
- 初始化执行initWatch(vm, opts.watch)方法创建watcher并定义了watcher的getter方法,随后触发getter方法去触发变量的getter方法建立变量和watcher相互之间的联系。
- 变量发生变化会触发变量的订阅者的update方法并执行run方法去获取最新的值,并通过执行订阅者的cb方法传入新旧值。
加载全部内容