C语言 数组指针
清风自在 流水潺潺 人气:0一、数组类型
- C语言中的数组有自己特定的类型
- 数组的类型由元素类型和数组大小共同决定
例:int array[5] 的类型为 int[5]
二、定义数据类型
C语言中通过 typedef 为数组类型重命名:typedef type(name)[size];
数组类型:
typedef int(AINT5)[5];
typedef float(AFLOAT10)[10];
数组定义:
AINT5 iArray;
AFLOAT10 fArray;
三、数组指针
- 数组指针用于指向一个数组
- 数组名是数组首元素的起始地址,但并不是数组的起始地址
- 通过将取地址符 & 作用于数组名可以得到数组的起始地址
- 可通过数组类型定义数组指针:ArrayType* pointer;
- 也可以直接定义:type(*pointer)[n];
pointer 为数组指针变量名,type 为指向的数组的元素类型,n 为指向的数组的大小
下面看一个数组指针的示例:
#include <stdio.h>
typedef int(AINT5)[5];
typedef float(AFLOAT10)[10];
typedef char(ACHAR9)[9];
int main()
{
AINT5 a1;
float fArray[10];
AFLOAT10* pf = &fArray;
ACHAR9 cArray;
char(*pc)[9] = &cArray;
char(*pcw)[4] = cArray;
int i = 0;
printf("%d, %d\n", sizeof(AINT5), sizeof(a1));
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
(*pf)[i] = i; // ==> fArray[i] = i;
}
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%f\n", fArray[i]);
}
printf("%p, %p, %p\n", &cArray, pc + 1, pcw + 1);
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
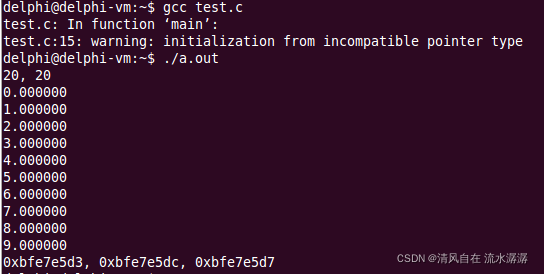
注意char(*pcw)[4] = cArray; 是不对的,cArray 数组名代表的地址是首元素的地址,类型为 char* ,而 pcw 指针类型为 char[4],所以这样就不合法。
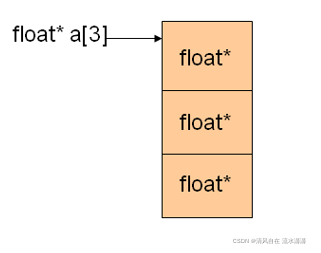
四、指针数组
- 指针数组是一个普通的数组
- 指针数组中每个元素为一个指针
- 数组的定义:
type* pArray[n];
type*为数组中每个元素的类型,pArray为数组名,n 为数组大小
例如:
下面看一个指针数组的应用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DIM(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(*a))
int lookup_keyword(const char* key, const char* table[], const int size) // const char* table[] <==> const char** table
{
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if(strcmp(key, table[i]) == 0)
{
ret = i;
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
const char* keyword[] = {
"do",
"for",
"if",
"register",
"return",
"switch",
"while",
"case",
"static"
};
printf("%d\n", lookup_keyword("return", keyword, DIM(keyword)));
printf("%d\n", lookup_keyword("main", keyword, DIM(keyword)));
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
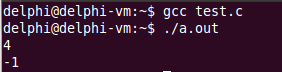
注意const char* table[ ] <==> const char** table ,两种写法都可以,只是 const char* table[ ] 更直观
五、小结
- 数组的类型由元素类型和数组大小共同决定
- 数组指针是一个指针,指向对应类型的数组
- 指针数组是一个数组,其中每个元素都为指针
- 数组指针遵循指针运算法则
- 指针数组拥有C语言数组的各种特性
加载全部内容