Vuex actions
IT利刃出鞘 人气:0简介
说明
本文用示例介绍Vuex的五大核心之一:actions。
官网
actions概述
说明
Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数。
特点
1.异步操作,通过mutations来改变state。
2.不能直接改变state里的数据。
3.包含多个事件回调函数的对象。
4.执行方式:通过执行 commit()来触发 mutation 的调用, 间接更新 state
5.触发方式: 组件中: $store.dispatch(‘action 名称’, data1)
6.可以包含异步代码(例如:定时器, 请求后端接口)。
用法
直接使用
this.$store.dispatch('actions方法名', 具体值) // 不分模块
this.$store.dispatch('模块名/actions方法名', 具体值) // 分模块
mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
// 不分模块
...mapActions(['actions方法名'])
// 分模块,不改方法名
...mapActions('模块名', ['actions方法名'])
// 分模块,不改方法名
...mapActions('模块名',{'新actions方法名': '旧actions方法名'})
}
}
示例
CounterStore.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const counterStore = new Vuex.Store(
{
state: {
count: 10
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2;
}
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--;
},
// 带参数
addNumber(state, param1) {
state.count += param1;
},
},
actions: {
asyncIncrement(context) {
console.log('CounterStore=> action: asyncIncrement');
setTimeout(() => {context.commit('increment')}, 1000)
},
asyncAddNumber(context, n) {
console.log('CounterStore=> action: asyncAddNumber');
setTimeout(() => {context.commit('addNumber', n)}, 1000)
}
}
}
);
export default counterStore;
Parent.vue(入口组件)
<template>
<div class="outer">
<h3>父组件</h3>
<component-a></component-a>
<component-b></component-b>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ComponentA from "./ComponentA";
import ComponentB from "./ComponentB";
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {ComponentA, ComponentB},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.outer {
margin: 20px;
border: 2px solid red;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
ComponentA.vue(异步修改vuex的数据)
<template>
<div class="container">
<h3>ComponentA</h3>
<button @click="thisAsyncIncrement">异步加1</button>
<button @click="thisAsyncAddNumber">异步增加指定的数</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
cnt: 5
}
},
methods:{
thisAsyncIncrement() {
this.$store.dispatch('asyncIncrement')
},
thisAsyncAddNumber() {
this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddNumber', this.cnt)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
margin: 20px;
border: 2px solid blue;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
ComponentB.vue(读取vuex的数据)
<template>
<div class="container">
<h3>ComponentB</h3>
<div>计数器的值:{{thisCount}}</div>
<div>计数器的2倍:{{thisDoubleCount}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed:{
thisCount() {
return this.$store.state.count;
},
thisDoubleCount() {
return this.$store.getters.doubleCount;
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
margin: 20px;
border: 2px solid blue;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
路由(router/index.js)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Parent from "../components/Parent";
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/parent',
name: 'Parent',
component: Parent,
}
],
})
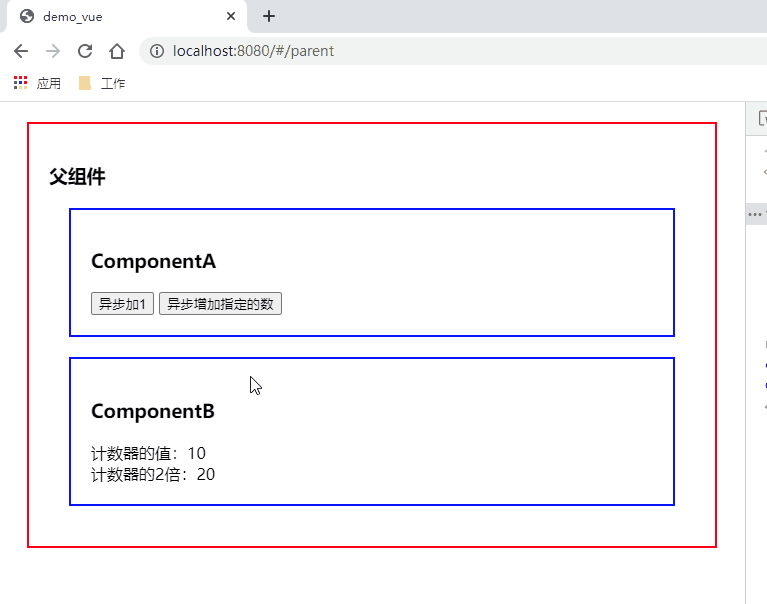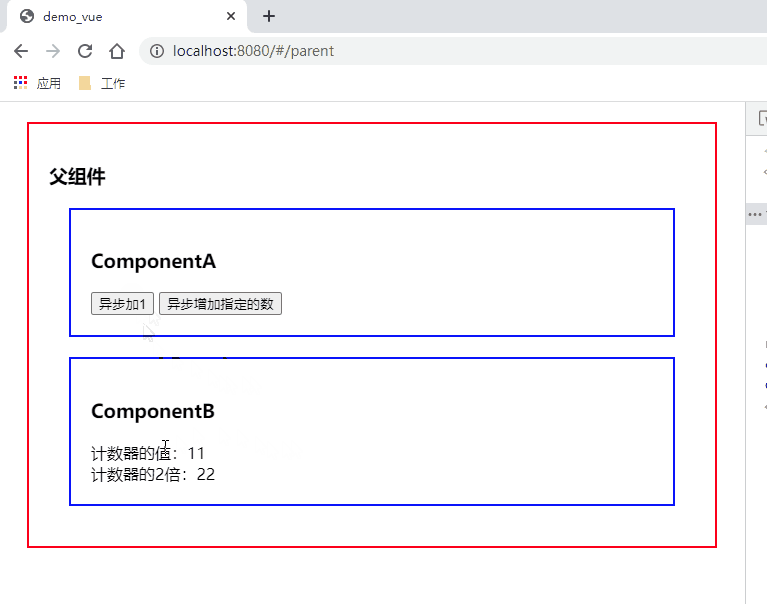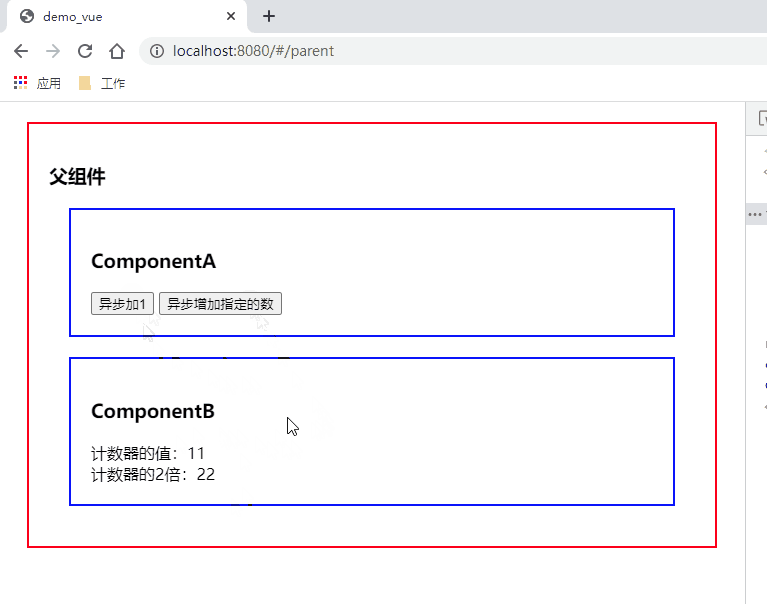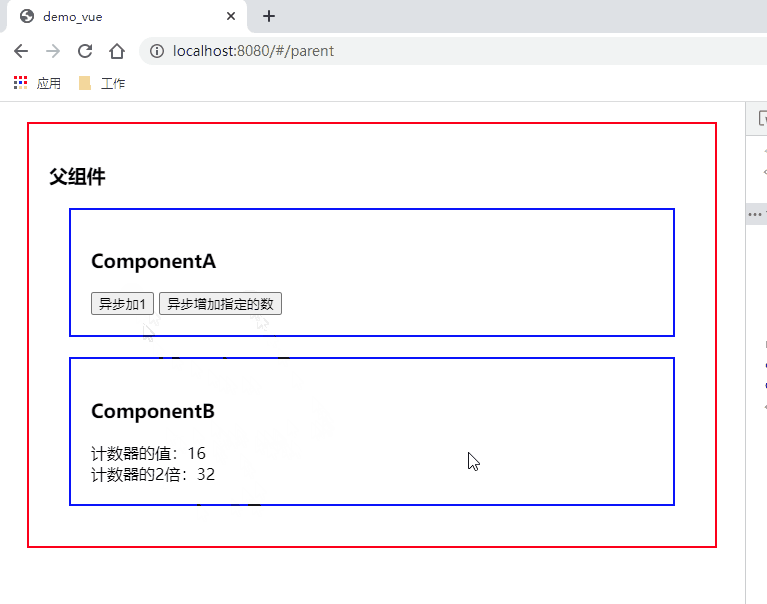
测试
访问: http://localhost:8080/#/parent
加载全部内容