SpringBoot Redis缓存 SpringBoot 开启Redis缓存及使用方法
Dean_xiu 人气:0之前不是说过Redis可以当作缓存用嘛
现在我们就配置一下SpringBoot使用Redis的缓存
Redis缓存
为什么用Redis作缓存
用redis做缓存,是因为redis有着很优秀的读写能力,在集群下可以保证数据的高可用
主要步骤
1、pom.xml文件添加依赖
2、yml文件配置redis集群
3、编写RedisConfig配置序列化及缓存配置,添加缓存注解
4、编写业务Controller,添加缓存注解
5、编写启动类
具体实践
整体目录结构
pom.xml添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBoot_Redis</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--整合redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--spring boot test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>

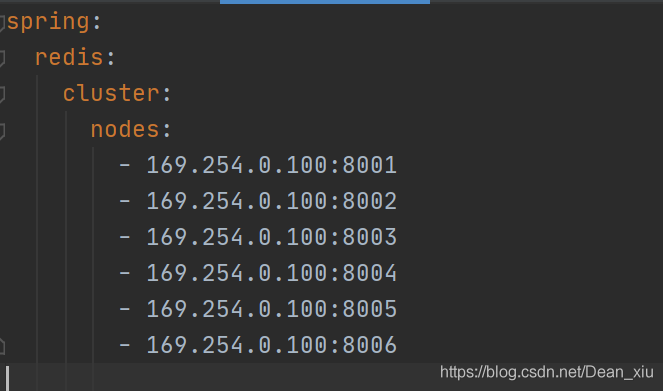
yml文件里配置Redis集群
结构是ip+port
spring:
redis:
cluster:
nodes:
- 169.254.0.100:8001
- 169.254.0.100:8002
- 169.254.0.100:8003
- 169.254.0.100:8004
- 169.254.0.100:8005
- 169.254.0.100:8006
编写RedisConfig配置序列化及缓存配置,添加缓存注解
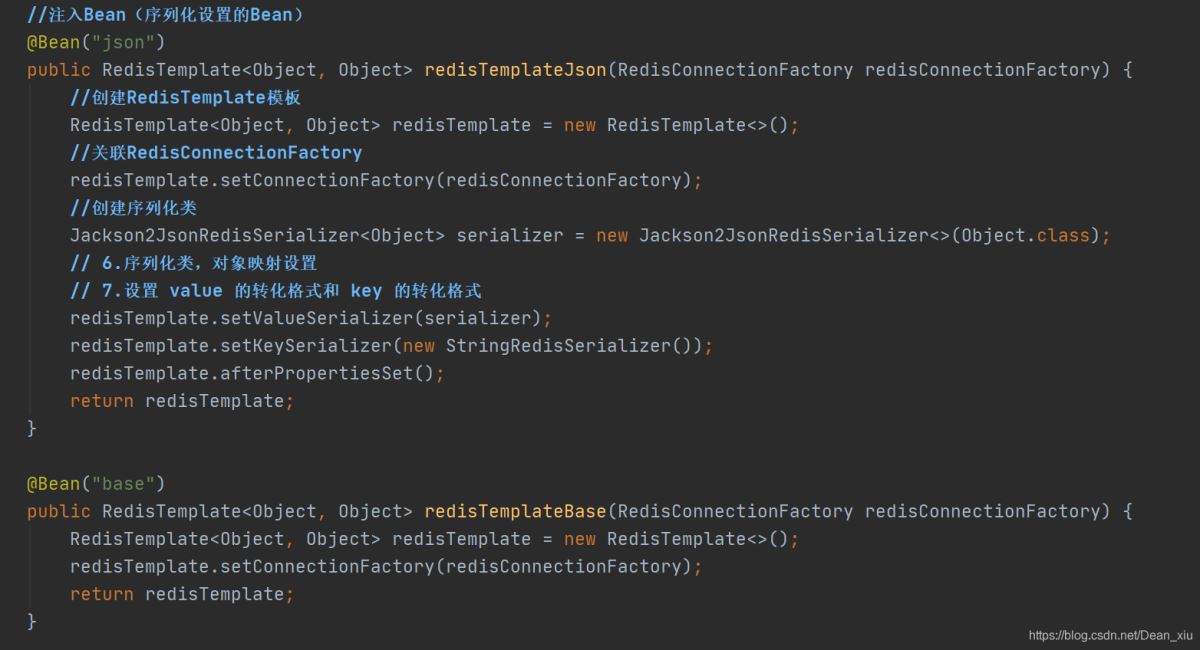
设置序列化的Bean
设置缓存的Bean
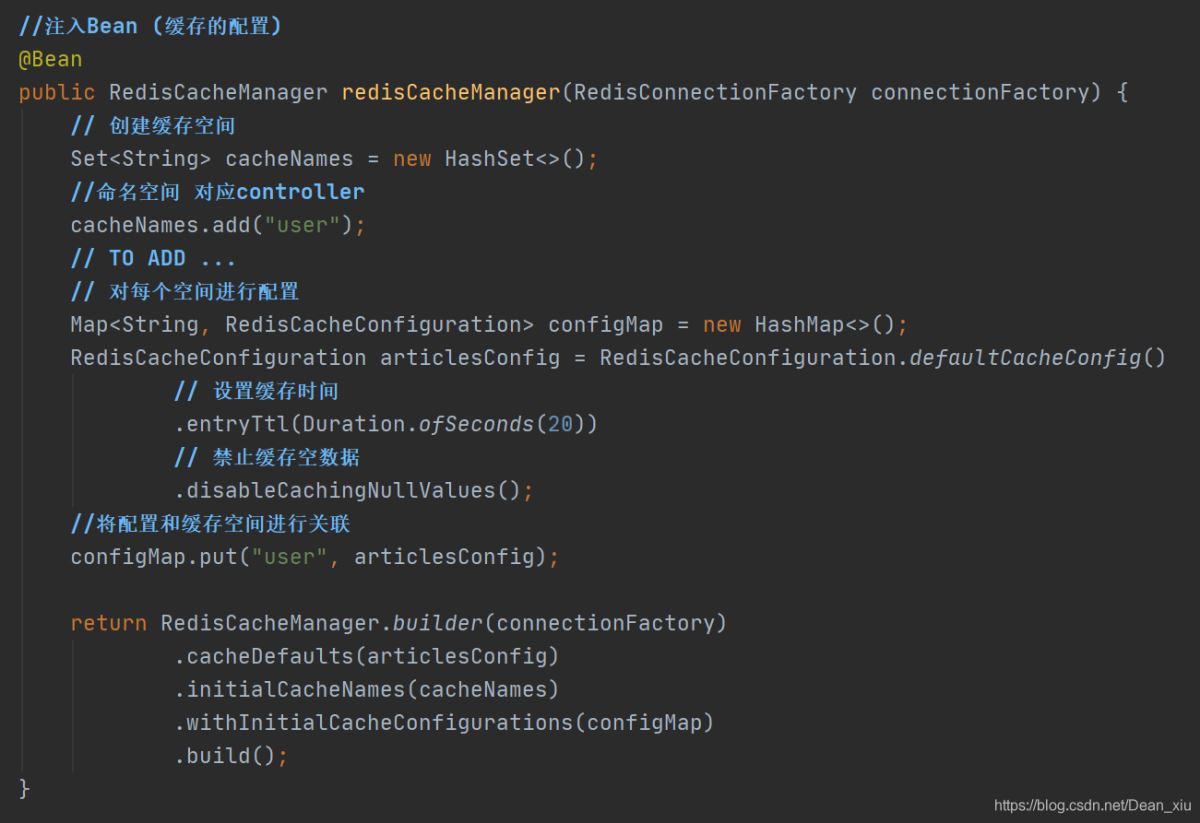
这里有必要解释一下
- cacheNames.add() 这里我理解的是和controller进行绑定,毕竟很多controller的时候,这里可以确定到底那个controller开启缓存,以及每个controller对缓存的要求可能也不一样
- configMap这里就是将我们对缓存的一些配置和命名空间进行关联
- 设置缓存时间和禁止缓存空数据应该还好理解
编写业务Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class RedisCacheController {
@Cacheable(value = "user",key = "#root.methodName+#root.args[0]")
@GetMapping("findWord/{id}")
public String findWord(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("Cacheing");
HashMap<String, String> words = new HashMap<>();
words.put("1", "java");
words.put("2", "redis");
words.put("3", "cache");
return words.get(id);
}
}
@Cacheable一定要加在方法之上
value就是之前在RedisConfig中定义的命名空间,也是缓存保存的空间
key就是缓存保存的key,这里以方法名为key,但是为避免方法名重复导致的key重复,所以加入id,来避免重复
关于缓存的其他注解
- @CachePut
在支持Spring Cache的环境中,对于使用@Cacheale标注的方法,Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同的key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是从缓存中获取结果直接进行返回,若不存在才会执行方法并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中
@Cacheput也可以生命一个方法支持缓存功能,与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行并不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入缓存中。
- @CacheEvict
CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。
当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作
@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。
其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些缓存(命名空间)上的
key表示要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会谁用默认策略生成的key,condition表示清除操作发生的条件
allEntries属性
allEntries是boolean类型的,表示是否要清除缓存中的所有元素,默认为false,当指定为true时,会忽略指定的key
beforeInvocation属性
清除操作默认时在对应方法成功执行后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回也不会触发清除操作
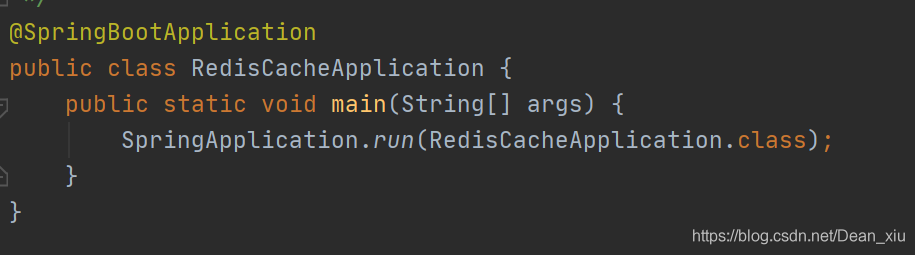
使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素 编写启动类
就是传统的启动类
检验结果
使用postman发送请求进行检测
第一次的时候可以看到控制台打印
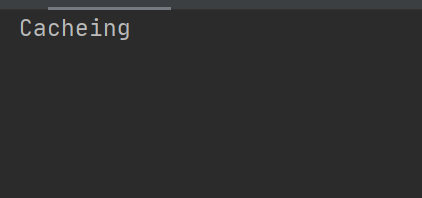
这说明方法执行了
但是第二次发送相同请求的时候,可以看到拿到了数据,但是方法没有执行,说明缓存有用了
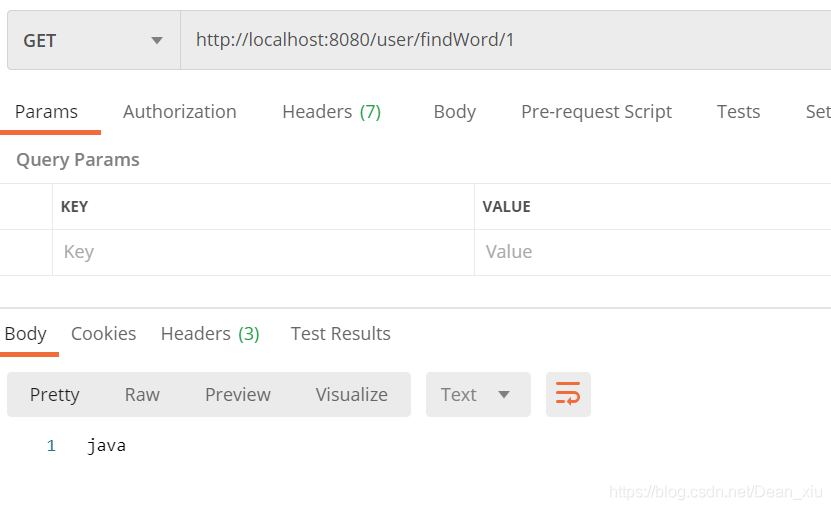
好了,到此结束。
加载全部内容