Python生成迷宫并自动寻路 Python实现随机生成迷宫并自动寻路
WA的一声哭出来 pnq 人气:0想了解Python实现随机生成迷宫并自动寻路的相关内容吗,WA的一声哭出来 pnq在本文为您仔细讲解Python生成迷宫并自动寻路的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:Python随机生成迷宫,Python,迷宫自动寻路,下面大家一起来学习吧。
Python深搜版:
核心在于带随机的深搜(见代码第23到27行,其实也可以用22行代替这几行代码,你可以试着把第24行的数字4改大或者改小,即调整随机程度)
import os import random from queue import Queue import numpy import colorama from colorama import Fore, Back, Style import sys from bmpEditor import bmp colorama.init() # numpy.random.seed(1) _xy = [0,2,0,-2,0] size = 31 sys.setrecursionlimit(100000000) road = set() def dfs(curr_pos): road.add(curr_pos) # for i in numpy.random.permutation(4): p = [0,1,2,3] for i in range(4): l = random.randint(0,3) r = random.randint(0,3) p[l], p[r] = p[r], p[l] for i in p: next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i], curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]) if (0<=next_pos[0]<size and 0<=next_pos[1]<size and next_pos not in road ): road.add(((curr_pos[0] + next_pos[0])/2, (curr_pos[1] + next_pos[1])/2)) dfs(next_pos) dfs((0,0)) q = Queue() q.put((0,0)) ans_road = set() def dfs_getans(curr_pos): # print(curr_pos) ans_road.add(curr_pos) if (size-1, size-1) in ans_road: return for i in range(4): next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i]//2, curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]//2) if (0<=next_pos[0]<size and 0<=next_pos[1]<size and next_pos in road and next_pos not in ans_road and (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road): dfs_getans(next_pos) if (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road: ans_road.remove(curr_pos) dfs_getans((0,0)) for i in range(size): for j in range(size): print((Back.WHITE + ' ') if (i,j) in road else (Back.BLACK + ' '), end=' ') print() wall_width = 2 cell_size = 6 image = bmp((size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, (size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, 0x000000) for i in range(size+3): for j in range(size+3): if (i-1, j-1) in road: image.paint_rect(i*cell_size, j*cell_size, cell_size*2-wall_width, cell_size*2-wall_width, 0xffffff) file_name = "%dmaze.bmp"%size image.save_image(file_name) os.system(file_name) for p in ans_road: # image.paint_rect(p[0]+1, p[1]+1) image.paint_rect(( p[0]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2, (p[1]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2, cell_size, cell_size, 0xff0000 ) file_name = "%dans.bmp"%size image.save_image(file_name) os.system(file_name)
效果
3131:

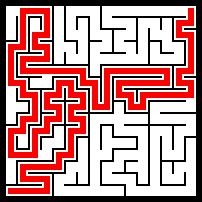
8181:
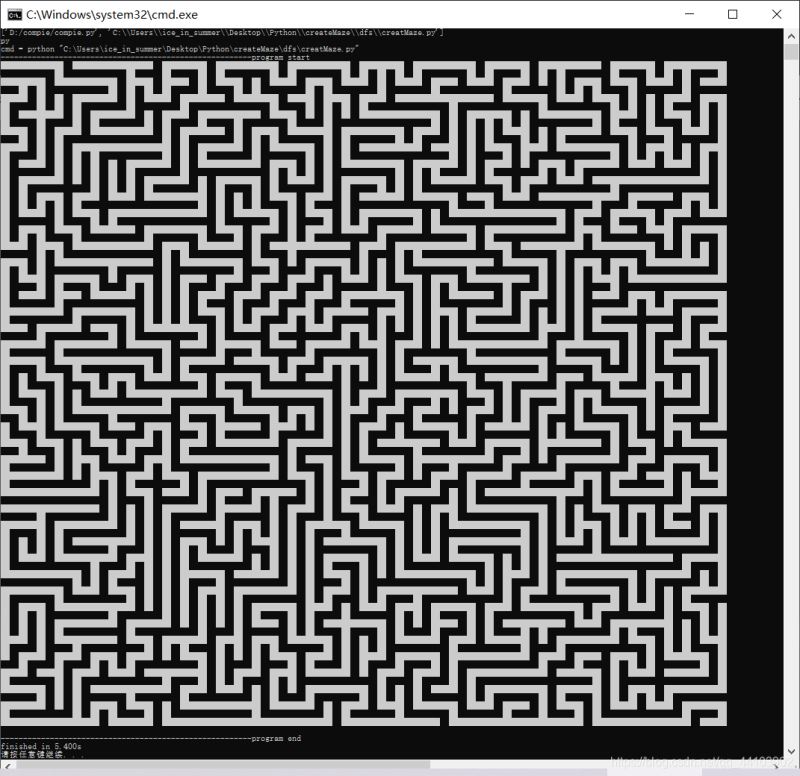
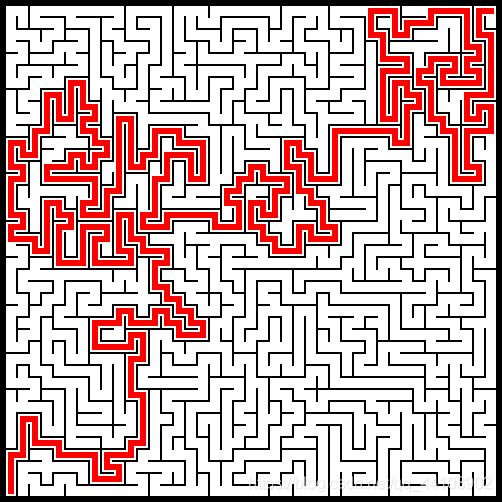
坐标系有翻转,控制台中的左上角对应图片中的左下角
其中bmpEditor不是官方库,代码地址(文件名为bmpEditor.py,和这以上代码放同一个路径下即可)
Python 广搜版
在队列的基础上把队列中的元素顺序打乱(第24行)
import os import random from queue import Queue import numpy import colorama from colorama import Fore, Back, Style import sys import random from bmpEditor import bmp colorama.init() numpy.random.seed(1) _xy = [0,2,0,-2,0] size = 59 sys.setrecursionlimit(size*size//4+size) q = [] q.append((0,0)) road = set() road.add((0,0)) while len(q) != 0: random.shuffle(q) curr_pos = q.pop() # print(curr_pos) for i in range(4): next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i], curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]) if ( 0<=next_pos[0]<size and 0<=next_pos[1]<size and next_pos not in road ): road.add( ((curr_pos[0] + next_pos[0])//2, (curr_pos[1] + next_pos[1])//2) ) q.append(next_pos) road.add(next_pos) ans_road = set() def dfs_getans(curr_pos): ans_road.add(curr_pos) if (size-1, size-1) in ans_road: return for i in range(4): next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i]//2, curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]//2) if ( 0<=next_pos[0]<size and 0<=next_pos[1]<size and next_pos in road and next_pos not in ans_road and (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road): dfs_getans(next_pos) if (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road: ans_road.remove(curr_pos) dfs_getans((0,0)) print(len(ans_road)) for i in range(0, size): for j in range(0, size): print((Back.WHITE + ' ') if (i,j) in road else (Back.BLACK + ' '), end=' ') print() wall_width = 1 cell_size = 5 image = bmp((size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, (size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, 0x000000) for i in range(size+3): for j in range(size+3): if (i-1, j-1) in road: image.paint_rect(i*cell_size, j*cell_size, cell_size*2-wall_width, cell_size*2-wall_width, 0xffffff) file_name = "%dmaze.bmp"%size image.save_image(file_name) os.system(file_name) for p in ans_road: # image.paint_rect(p[0]+1, p[1]+1) image.paint_rect(( p[0]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2, (p[1]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2, cell_size, cell_size, 0xff0000 ) file_name = "%dans.bmp"%size image.save_image(file_name) os.system(file_name)
效果:

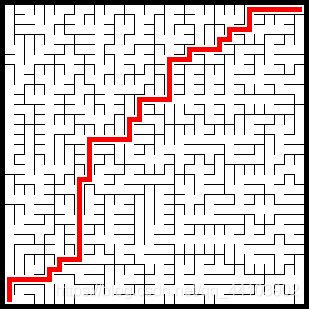
相比深度优先的,这种迷宫会更加“直”一些
lua版:
大体上是深搜,加了一定的随机性使得搜索过程中有一定概率暂时放弃当前路径。见表stop_points,(第7行、第74行及其后面的repeat循环)
local _xy = {0,2,0,-2,0}
local size = 41
local base = size+1
local road = {}
stop_points = {}
function dfs(curr_x, curr_y)
road[curr_x*base+curr_y] = true
if math.random(1,10) <= 3 then
stop_points[curr_x*base+curr_y] = true
return
end
-- os.execute("cls")
-- print_map()
local permutation = {1,2,3,4}
for i=1, 4 do
local l = math.random(1,4)
local r = math.random(1,4)
permutation[l], permutation[r] = permutation[r], permutation[l]
end
for i=1, 4 do
local next_x = curr_x+_xy[permutation[i]]
local next_y = curr_y+_xy[permutation[i]+1]
if next_x>=1 and next_x<=size and
next_y>=1 and next_y<=size and
road[next_x*base+next_y] == nil then
local mid_x = math.floor((curr_x+next_x)/2)
local mid_y = math.floor((curr_y+next_y)/2)
road[mid_x*base+mid_y] = true
dfs(next_x, next_y)
end
end
end
local ans_geted = false
local parent = {}
function get_ans(curr_x, curr_y)
-- print(curr_x, curr_y)
for i=1, 4 do
next_x = (curr_x + math.floor(_xy[i])/2 )
next_y = (curr_y + math.floor(_xy[i+1])/2 )
-- print(next_x, next_y)
if next_x >= 1 and next_x <= size and
next_y >= 1 and next_y <= size and
road[next_x*base+next_y] and
parent[next_x*base+next_y]==nil
then
parent[next_x*base+next_y] = curr_x*base+curr_y
get_ans(next_x, next_y)
end
end
end
local ans_road = {}
function print_map()
for i=0, size+1 do
local line = ""
for j=0, size+1 do
if ans_road [i*base+j] then
line = line..".."
elseif road[i*base+j]==true then
line = line.." "
else
line = line.."HH"
end
end
print(line)
end
end
stop_points[1*base+1] = true
-- create maze
repeat
local has_point = false
for v,_ in pairs(stop_points) do
has_point = true
stop_points[v] = nil
dfs(math.floor(v/base), v%base)
break
end
-- print(has_point)
until not has_point
get_ans(1,1)
parent[1*base+1] = nil
print("")
-- for k,v in pairs(parent) do
-- print(string.format("[%d,%d]->[%d,%d]", math.floor(k/base), k%base, math.floor(v/base), v%base))
-- end
print("")
local x = size
local y = size
repeat
-- print(x,y)
ans_road[x*base+y] = true
local v = parent[x*base+y]
x = math.floor(v/base)
y = v%base
until --[[(x==1 and y== 1)]] not parent[x*base+y]
ans_road[1*base+1] = true
print_map()
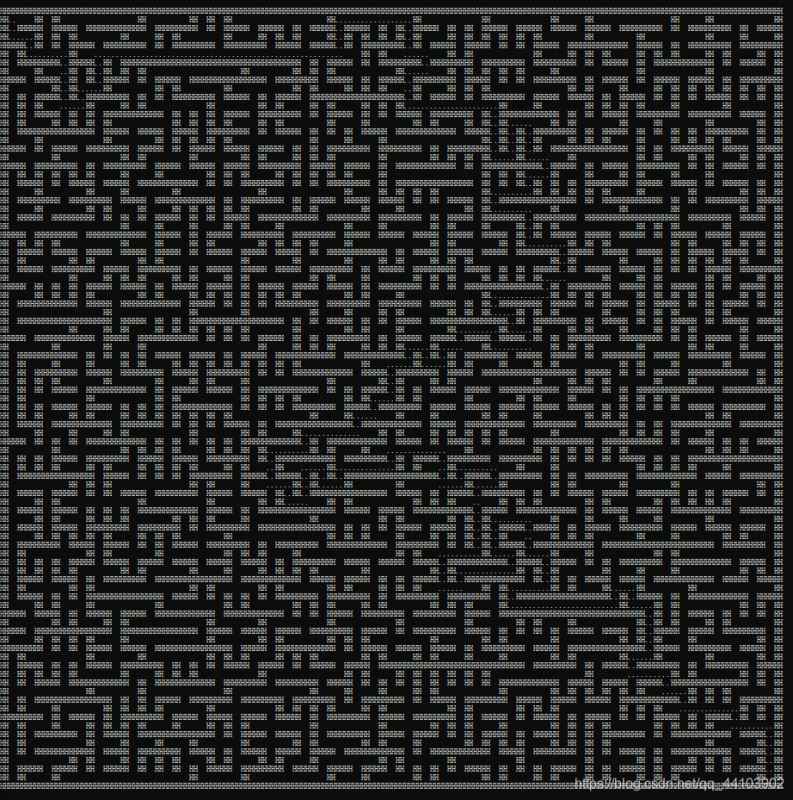
效果:
4141:
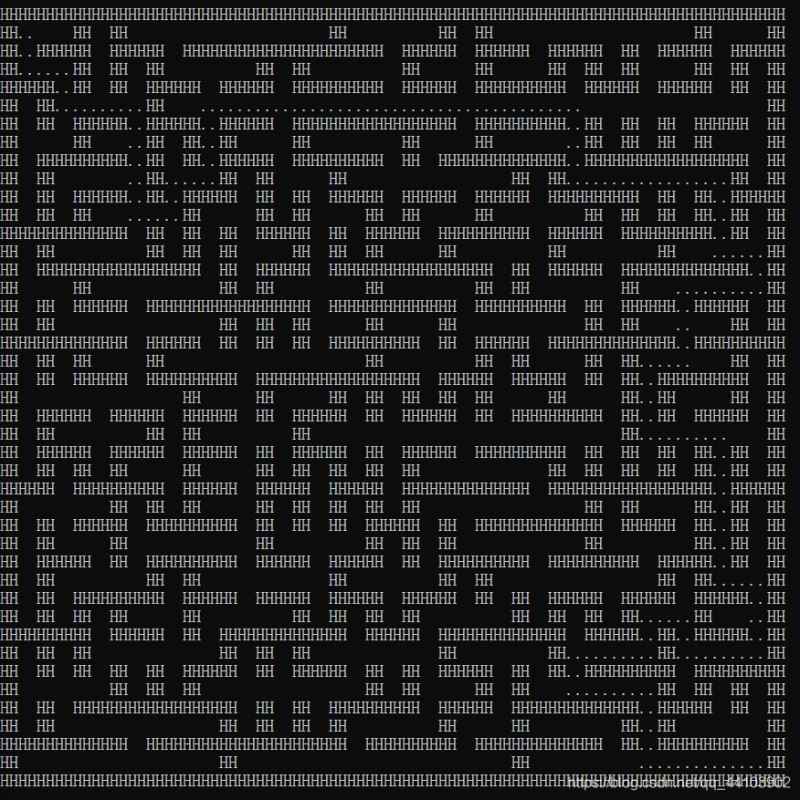
8989
加载全部内容