SpringBoot Trick 详解SpringBoot中关于%2e的Trick
Ruilin 人气:0分享一个SpringBoot中关于%2e的小Trick。先说结论,当SpringBoot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下, alwaysUseFullPath 为默认值false,这会使得其获取ServletPath,所以在路由匹配时会对 %2e 进行解码,这可能导致身份验证绕过。而反过来由于高版本将 alwaysUseFullPath 自动配置成了true从而开启全路径,又可能导致一些安全问题。
这里我们来通过一个例子看一下这个Trick,并分析它的原因。
首先我们先来设置SprinBoot版本
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
编写一个Controller
@RestController
public class httpbinController {
@RequestMapping(value = "no-auth", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String noAuth() {
return "no-auth";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "auth", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String auth() {
return "auth";
}
}
接下来配置对应的Interceptor来实现对除no-auth以外的路由的拦截
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(handlerInterceptor())
//配置拦截规则
.addPathPatterns("/**");
}
@Bean
public HandlerInterceptor handlerInterceptor() {
return new PermissionInterceptor();
}
}
@Component
public class PermissionInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
uri = uri.replaceAll("//", "/");
System.out.println("RequestURI: "+uri);
if (uri.contains("..") || uri.contains("./") ) {
return false;
}
if (uri.startsWith("/no-auth")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
由上面代码可以知道它使用了getRequestURI来进行路由判断。通常你可以看到如 startsWith , contains 这样的判断方式,显然这是不安全的,我们绕过方式由很多比如 .. 或 ..; 等,但其实在用 startsWith 来判断白名单时构造都离不开跨目录的符号 ..
那么像上述代码这种情况又如何来绕过呢?答案就是 %2e
发起请求如下
$ curl -v "http://127.0.0.1:8080/no-auth/%2e%2e/auth" * Trying 127.0.0.1... * TCP_NODELAY set * Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 8080 (#0) > GET /no-auth/%2e%2e/auth HTTP/1.1 > Host: 127.0.0.1:8080 > User-Agent: curl/7.64.1 > Accept: */* > < HTTP/1.1 200 < Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8 < Content-Length: 4 < Date: Wed, 14 Apr 2021 13:22:03 GMT < * Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intact auth * Closing connection 0
RequestURI输出为
RequestURI: /no-auth/%2e%2e/auth
可以看到我们通过 %2e%2e 绕过了PermissionInterceptor的判断,同时匹配路由成功,很显然应用在进行路由匹配时对 %2e 进行了解码。
我们再来切换SpringBoot版本再来看下
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
发起请求,当然也是过了拦截,但没有匹配路由成功,返回404
$ curl -v "http://127.0.0.1:8080/no-auth/%2e%2e/auth" * Trying 127.0.0.1... * TCP_NODELAY set * Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 8080 (#0) > GET /no-auth/%2e%2e/auth HTTP/1.1 > Host: 127.0.0.1:8080 > User-Agent: curl/7.64.1 > Accept: */* > < HTTP/1.1 404 < Vary: Origin < Vary: Access-Control-Request-Method < Vary: Access-Control-Request-Headers < Content-Length: 0 < Date: Wed, 14 Apr 2021 13:17:26 GMT < * Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intact * Closing connection 0
RequestURI输出为
RequestURI: /no-auth/%2e%2e/auth
可以得出结论当SpringBoot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下,其在路由匹配时会对 %2e 进行解码,这可能导致身份验证绕过。
那么又为什么会这样?
在SpringMVC进行路由匹配时会从DispatcherServlet开始,然后到HandlerMapping中去获取Handler,在这个时候就会进行对应path的匹配。
我们来跟进代码看这个关键的地方 org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper#getLookupPathForRequest(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest)
这里就出现有趣的现象,在2.3.0.RELEASE中 alwaysUseFullPath 为默认值false

而在2.3.1.RELEASE中 alwaysUseFullPath 被设置成了true

这也就导致了不同的结果,一个走向了 getPathWithinApplication 而另一个走向了 getPathWithinServletMapping
在 getPathWithinServletMapping 中会获取ServletPath,ServletPath会对其解码,这个很多讲Tomcat url差异的文章都提过了,就不多说了。所以解释了最终出现绕过的情况。
那么Trick的具体描述就成了当SpringBoot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下, alwaysUseFullPath 为默认值false,这会使得其获取ServletPath,所以在路由匹配时会对 %2e 进行解码,这可能导致身份验证绕过。
而这和Shiro的CVE-2020-17523中的一个姿势形成了呼应,只要高版本SpringBoot就可以了不用非要手动设置 alwaysUseFullPath
$ curl -v http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/%2e * Trying 127.0.0.1... * TCP_NODELAY set * Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 8080 (#0) > GET /admin/%2e HTTP/1.1 > Host: 127.0.0.1:8080 > User-Agent: curl/7.64.1 > Accept: */* > < HTTP/1.1 200 < Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8 < Content-Length: 10 < Date: Wed, 14 Apr 2021 13:48:33 GMT < * Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intact admin page* Closing connection 0
感兴趣的可以再看看说不定有额外收获
话说回来,可是为什么在高版本中 alwaysUseFullPath 会被设置成true呢?
这就要追溯到 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration.WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter#configurePathMatch
在spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.0.RELEASE中
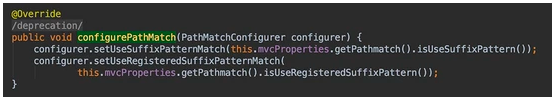
在spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.1.RELEASE中

为什么要这样设置?我们查看git log这里给出了答案。

https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/commit/a12a3054c9c5dded034ee72faac20e578b5503af
当Servlet映射为”/”时,官方认为这样配置是更有效率的,因为需要请求路径的处理较少。
配置servlet.path可以通过如下,但通常不会这样配置除非有特殊需求。
spring.mvc.servlet.path=/test/
所以最后,当SpringBoot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下, alwaysUseFullPath 为默认值false,这会使得其获取ServletPath,所以在路由匹配时会对 %2e 进行解码,这可能导致身份验证绕过。而高版本为了提高效率对 alwaysUseFullPath 自动配置成了true从而开启全路径,这又造就了Shiro的CVE-2020-17523中的一个利用姿势。
加载全部内容