C#缓存使用 C#中缓存的基本使用方法
王继峰 人气:0前言
缓存主要是为了提高数据的读取速度。因为服务器和应用客户端之间存在着流量的瓶颈,所以读取大容量数据时,使用缓存来直接为客户端服务,可以减少客户端与服务器端的数据交互,从而大大提高程序的性能。
缓存这个东西可大可小,小到一个静态的字段,大到将整个数据库Cache起来。项目开发过程中缓存的应用到处可见,本文主要介绍一下使用的方法,下面话不多说了,来一起看看详细的介绍吧
1.在ASP.NET中页面缓存的使用方法简单,只需要在aspx页的顶部加上一句声明即可:
<%@ OutputCache Duration="100" VaryByParam="none" %>
Duration:缓存时间(秒为单位),必填属性
2.使用微软自带的类库System.Web.Caching
新手接触的话不建议直接使用微软提供的类库,因为这样对理解不够深刻。所以在这里我带大家自己写一套缓存操作方法,这样理解得更加清晰。
话不多说,代码开敲。
一、首先,先模拟数据来源。新建一个类,写一个数据操作方法(该方法耗时、耗资源)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Cache
{
public class DataSource
{
/// <summary>
/// 模拟从数据库读取数据
/// 耗时、耗CPU
/// </summary>
/// <param name="count"></param>
public static int GetDataByDB(int count)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------GetDataByDB-------");
int result = 0;
for (int i = count; i < 99999999; i++)
{
result += i;
}
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return result;
}
}
}
二、编写一个缓存操作类
2.1 构造一个字典型容器,用于存放缓存数据,权限设为private ,防止随意访问造成数据不安全性
//缓存容器 private static Dictionary<string, object> CacheDictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>();
2.2 构造三个方法(添加数据至缓存容器、从缓存容器获取数据、判断缓存是否存在)
/// <summary>
/// 添加缓存
/// </summary>
public static void Add(string key, object value)
{
CacheDictionary.Add(key, value);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取缓存
/// </summary>
public static T Get<T>(string key)
{
return (T)CacheDictionary[key];
}
/// <summary>
/// 判断缓存是否存在
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool Exsits(string key)
{
return CacheDictionary.ContainsKey(key);
}
三、程序入口编写测试方法
3.1 先看一下普通情况不适用缓存,它的执行效率有多慢
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Cache
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"------第{i}次请求------");
int result = DataSource.GetDataByDB(666);
Console.WriteLine($"第{i}次请求获得的数据为:{result}");
}
}
}
}

3.2 接下来,我们编写缓存试用方法。概念无非就是根据key前往字典容器里查找是否有相对应缓存数据,有则直接调用,没有则生成并存入字典容器里。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Cache
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"------第{i}次请求------");
//int result = DataSource.GetDataByDB(666);
int result = 0;
//key的名字一定要确保请求的准确性 DataSource GetDataByDB 666缺一不可
string key = "DataSource_GetDataByDB_666";
if (CacheHelper.Exsits(key))
{
//缓存存在,直接获取原数据
result = CacheHelper.Get<int>(key);
}
else
{
//缓存不存在,去生成缓存,并加入容器
result = DataSource.GetDataByDB(666);
CacheHelper.Add(key, result);
}
Console.WriteLine($"第{i}次请求获得的数据为:{result}");
}
}
}
}
3.3 我们看看加入缓存之后的效率如何
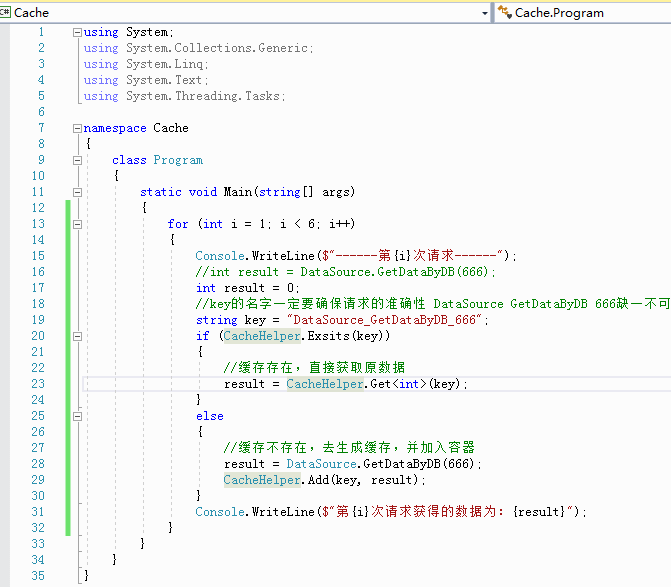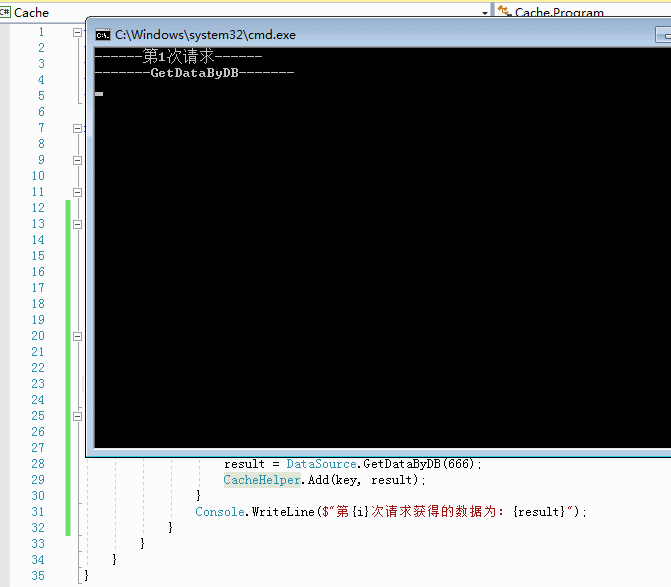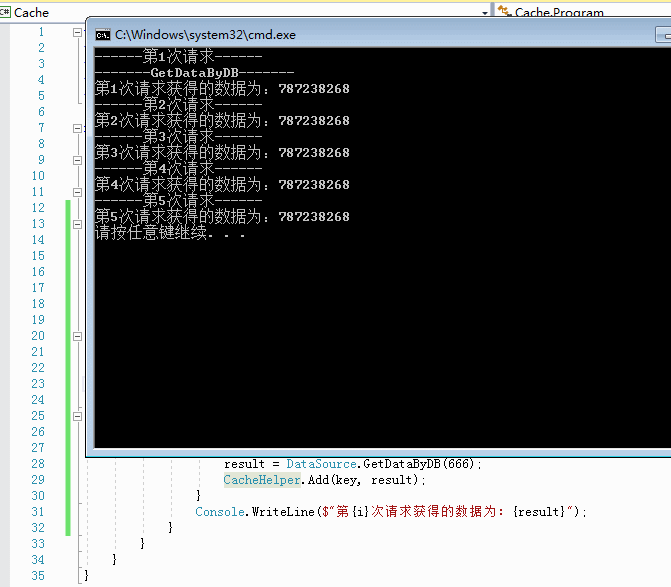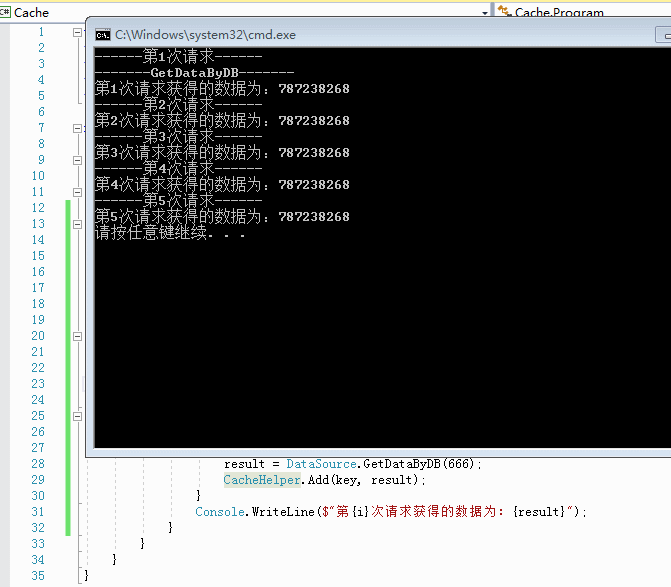
四、可以看到,瞬间完成。事已至此,缓存的使用基本是完成了。但是回过头来我们想想看。一个系统成百上千个地方使用缓存的话,那岂不是要写成百上千个if else判断缓存是否存在,然后获取?
答案显而易见,肯定不合理的。所以我们要对代码进行优化。
4.1 缓存操作类(CacheHelper)编写一个通用的获取方法
/// <summary>
/// 缓存获取方法
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="key">缓存字典容器对应key</param>
/// <param name="func">委托方法 传入操作对象</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static T GetCache<T>(string key, Func<T> func)
{
T t = default(T);
if (CacheHelper.Exsits(key))
{
//缓存存在,直接获取原数据
t = CacheHelper.Get<T>(key);
}
else
{
//缓存不存在,去生成缓存,并加入容器
t = func.Invoke();
CacheHelper.Add(key, t);
}
return t;
}
4.2 程序入口进行调用,传入的委托参数为lamad表达式优化后的代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Cache
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"------第{i}次请求------");
int result = 0;
//key的名字一定要确保请求的准确性 DataSource GetDataByDB 666缺一不可
string key = "DataSource_GetDataByDB_666";
//将需要执行的获取数据操作编写成委托传入方法(重点)
//Func<int> func = new Func<int>(() => { return DataSource.GetDataByDB(666); });
result = CacheHelper.GetCache(key, () => DataSource.GetDataByDB(666));
Console.WriteLine($"第{i}次请求获得的数据为:{result}");
}
}
}
}
到这里,缓存的使用基本结束了。最好值得一提的是,缓存尽量在数据量小、重复查询量大的情况下使用。因为缓存也是要耗内存的,服务器内存是有限的!
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对的支持。
加载全部内容